5,注释、分支结构、循环结构、伪“选择结构”
注释:
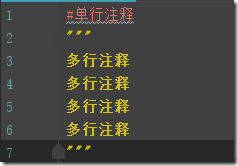
python使用#作为行注释符,使用三引号作为多行注释符
分支结构:
if-else:
a=int(input("你的成绩是:")) if a>60: print("你合格了!") else : print("你没及格!")
if-elif-else:
a = int(input("请输入一个整数")) if a<0: print("0>") elif a<10:#elif=else if print("<10") elif a<60: print("a<60") else : print("a>60")
循环结构:
for:
list1 = ["apple","banana","pine","super banana"] for i in list1: print(i,end="\t") for i in range(10): print(i,end="\t") print("\n------迭代同时显示下标------") for i, value in enumerate(['A', 'B', 'C']): print(i, value) print("\n------for-else------") for i in range(0,10,3): print(i) else:#执行完for就执行else print("你跳出了循环")
结果:
apple banana pine super banana 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ------迭代同时显示下标------ 0 A 1 B 2 C ------for--else------ 0 3 6 9 你跳出了循环
while:
n=3 while n>0: print("hello world",n) n=n-1 def while_else(count): while count>3: print("in while") count=count-1 else: print("你退出了循环") while_else(0)#不进入while while_else(5)#进入while
代码结果:
hello world 3 hello world 2 hello world 1 --------------------------- 你退出了循环 in while in while 你退出了循环
循环控制语句:
break:跳出当前循环
continue:提前结束此次循环
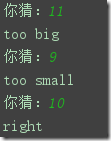
while n!=1: n=int(input("你猜:")) if n == 10: print("right") break elif n > 10 : print("too big") else : print("too small") else : print("你退出了循环")
num=10 while(num>0): if num %2==0: print(num,end='') num = num - 1 else: print(num,end='') print('-',end='') num=num-1 continue print('+',end='')
伪“选择结构”:
知乎:Python中为什么没有switch语法结构,有什么代替方案吗?
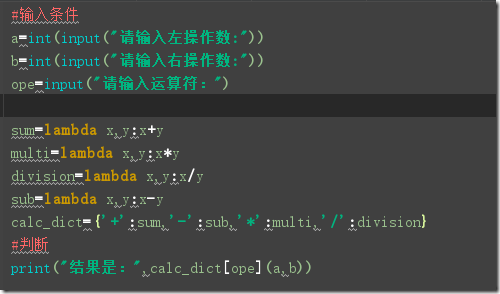
switch结构是向下逐一比对直到找到指定选择来执行,如果是比较多的选项的话,需要比较多查找时间(虽然单用户处理里面不在意这点时间),
而字典构成的伪“选择结构”,使用的是hash查找,哈希值的计算是比较快的,查找时间比switch少(多用户更有优势?)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号