读书笔记摘要-标准绑定介绍
1.基于各种传输协议:HTTP、TCP、UDP、P2P、IPC和MSMQ等,编码器:二进制编码、MTOM等编码方式加上安全策略和会话设置等组合,有些不可以运行,运行时才会发现所以提出绑定的概念。
绑定:定制好的通道栈,包含协议通道、传输通道和编码器。一个绑定集成了通信模式、可靠性、安全性、事务传播和互操作性等。
根据需要可自定义全新的绑定,也可根据标准绑定修改达到目的。标准绑定列表见下图:
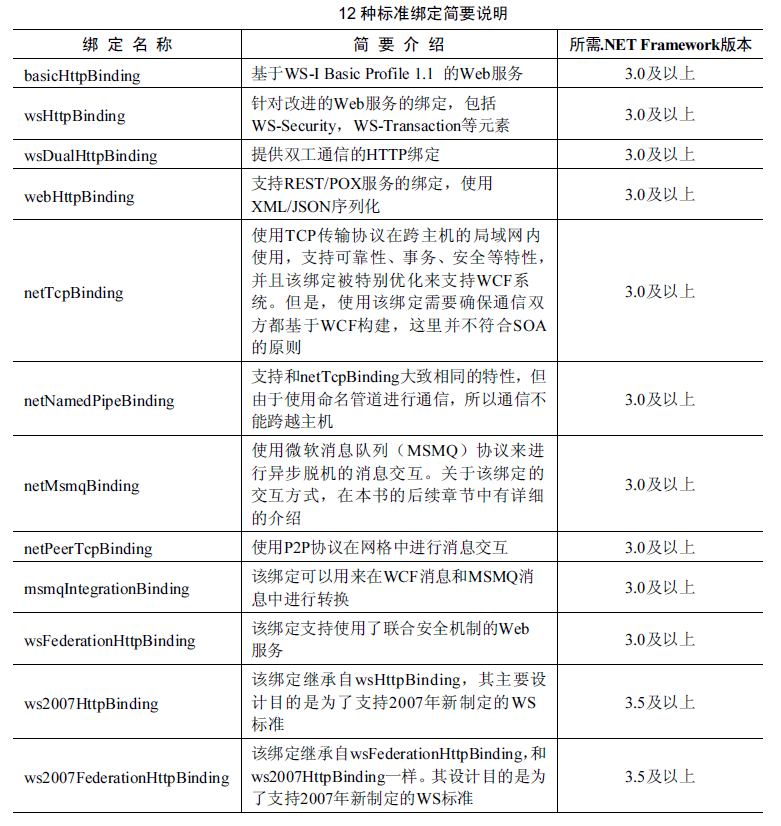
2、绑定方式:在代码中设置绑定或者带配置文件中设置绑定[推荐:适应环境容易更改,无需编译]。示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.web>
<!--允许调试-->
<compilation debug="true"></compilation>
</system.web>
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service name="HelloWorldService.Service">
<!--对地址、绑定、契约属性赋值-->
<endpoint address="HelloWorld" binding="netNamedPipeBinding" contract="HelloWorldService.IService"></endpoint>
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
代码绑定:更安全,但缺乏灵活性
public class UserClient
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//构造绑定
NetNamedPipeBinding binding = new NetNamedPipeBinding();
//构造终结点
EndpointAddress address = new EndpointAddress(new Uri("net.pipe://localhost:/HelloWorld"));
using (HelloWorldProxy proxy=new HelloWorldProxy(binding,address))
{
Console.WriteLine(proxy.HelloWorld("WCF"));//利用代理调用服务
Console.Read();
}
}
}
3、绑定的选择:根据消息的可靠性、传输模式是否跨进程、主机、网络,传输模式的支持、安全性、性能等多方面考虑,本质是其网络协议和编码器的约束。
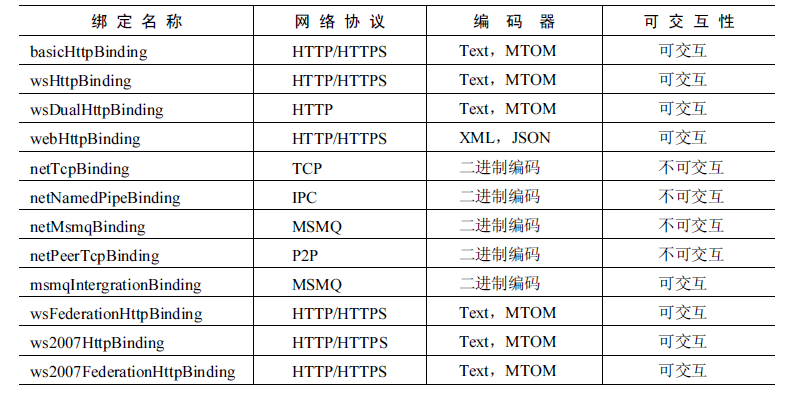
备注:可交互性是指与非WCF的服务或者客户端进行交互。
在上面图标中以net开头的绑定名称都是不可交互的,其他则是可交互的。
通常情况下使用IPC的绑定性能优于TCP的绑定,使用TCP的绑定又优于HTTP的绑定。使用WCF优化的绑定要优于非WCF系统交互的绑定。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号