https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-upside-down/description/
Given a binary tree where all the right nodes are either leaf nodes with a sibling (a left node that shares the same parent node) or empty, flip it upside down and turn it into a tree where the original right nodes turned into left leaf nodes. Return the new root.
For example:
Given a binary tree {1,2,3,4,5},
1 / \ 2 3 / \ 4 5
return the root of the binary tree [4,5,2,#,#,3,1].
4
/ \
5 2
/ \
3 1
Sol 1:
This is not a very intuitive problem for me, I have to spent quite a while drawing figures to understand it. As shown in the figure, 1 shows the original tree, you can think about it as a comb, with 1, 2, 4 form the bone, and 3, 5 as the teeth. All we need to do is flip the teeth direction as shown in figure 2. We will remove the link 1--3, 2--5, and add link 2--3, and 4--5. And node 4 will be the new root.
As the recursive solution, we will keep recurse on the left child and once we are are done, we found the newRoot, which is 4 for this case. At this point, we will need to set the new children for node 2, basically the new left node is 3, and right node is 1. Here is the recursive solution:

/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ // recursion public class Solution { public TreeNode upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null || root.left == null){ return root; } TreeNode newRoot = upsideDownBinaryTree(root.left); root.left.left = root.right; // node 2 left children root.left.right = root; //node 2 right children root.left = null; root.right = null; return newRoot; } }
Sol 2:
For the iterative solution, it follows the same thought, the only thing we need to pay attention to is to save the node information that will be overwritten.
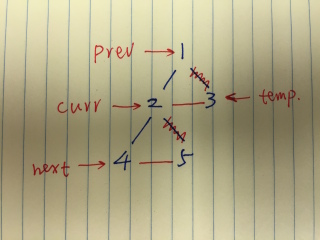
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ // For the iterative solution, it follows the same thought, the only thing we need to pay attention to is to save the node information that will be overwritten. public class Solution { public TreeNode upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { TreeNode curr = root; TreeNode next = null; TreeNode temp = null; TreeNode prev = null; while (curr != null){ next = curr.left; // swapping nodes now, need temp to keep the previous right child // create the new left connection curr.left = temp; // create the new right connection, but store the previous one temp = curr.right; curr.right = prev; // advance prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号