从零开始游戏开发——2.4 常用几何图元
实际游戏开发中,无论是游戏物理的计算,还是游戏逻辑开发,常常会用到平面、射线、球体、包围盒等几何图元,我们实现了几个常用的几何图元类。
第一个我们要介绍的是射线,射线包含了顶点和方向,与数学上的射线不同,我们用到的射线可以有距离限制,射线的参数化表示为p = o + td,p为射线上的点,o为射线的起始位置,d是射线的方向,t是表示射线长度的标量。射线类Ray代码如下:
1 template <typename T> 2 class Ray 3 { 4 public: 5 Ray(); 6 Ray(const Vector3<T> &origin, const Vector3<T> &direction); 7 8 inline const Vector3<T> &Origin() const { return _Origin; } 9 inline const Vector3<T> &Direction() const { return _Direction; } 10 inline Vector3<T> &Origin() { return _Origin; } 11 inline Vector3<T> &Direction() { return _Direction; } 12 13 template <typename T1> 14 friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Ray<T1> &ray); 15 private: 16 Vector3<T> _Origin; 17 Vector3<T> _Direction; 18 }; 19 20 template <typename T> 21 Ray<T>::Ray() 22 :_Origin(Vector3<T>(0, 0, 0)), _Direction(Vector3<T>(0, 0, -1)) 23 { 24 } 25 26 template <typename T> 27 Ray<T>::Ray(const Vector3<T> &origin, const Vector3<T> &direction) 28 :_Origin(origin), _Direction(direction) 29 { 30 } 31 32 template <typename T> 33 ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Ray<T> &ray) 34 { 35 return out << ray._Origin << ", " << ray._Direction; 36 } 37 38 typedef Ray<double> Rayd; 39 typedef Ray<float> Rayf;
这里只是简单的将位置和方向进行封装,注意在构造函数里,我们仅仅是将传入的方向直接赋值而没有进行正规化,如果传入是非单位向量,则射线是有长度的,因此可以根据实际需求传值。通常射线会与其它各种图元进行相交检测,我们将这些检测放到各自的图元类内。
下一个最为常用的图元是平面,参数化的平面方程为pn = d,其中p为平面上任意一点,n为平面的单位法向量,d是平面上任意一点到法线的投影距离,即平面到原点的距离。
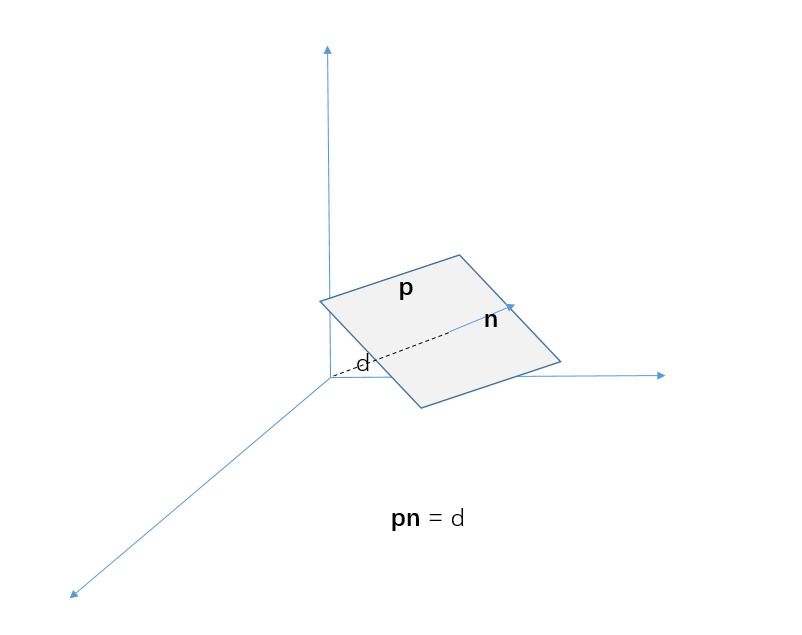
有了平面的定义,我们就可以定义平面类Plane:
1 template <typename T> 2 class Plane 3 { 4 public: 5 Plane(const Vector3<T> &normal, T distance); 6 Plane(const Vector3<T> &normal, const Vector3<T> &point); 7 8 T GetSignedDistance(const Vector3<T> &point) const; 9 10 bool Intersect(const Ray<T> &ray, float *maxDistance = nullptr, Vector3<T> *intersection = nullptr) const; 11 bool Intersect(const Sphere<T> &sphere) const; 12 13 template <typename T1> 14 friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Plane<T1> &plane); 15 16 private: 17 Vector3<T> _Normal; 18 T _Distance; 19 }; 20 21 template <typename T> 22 Plane<T>::Plane(const Vector3<T> &normal, T distance) 23 : _Normal(normal), _Distance(distance) 24 { 25 } 26 template <typename T> 27 Plane<T>::Plane(const Vector3<T> &normal, const Vector3<T> &point) 28 : _Normal(normal), _Distance(point.DotProduct(normal)) 29 { 30 } 31 32 template <typename T> 33 T Plane<T>::GetSignedDistance(const Vector3<T> &point) const 34 { 35 /** 36 * p + an = q; 37 * (p + an)*n = q * n; 38 * p * n = (an) * n = q * n; 39 * d + a = q * n; 40 * a = q * n - d 41 */ 42 return point.DotProduct(_Normal) - _Distance; 43 } 44 45 template <typename T> 46 bool Plane<T>::Intersect(const Ray<T> &ray, float *maxDistance, Vector3<T> *intersection) const 47 { 48 const Vector3<T> &rayOrigin = ray.Origin(); 49 const Vector3<T> &rayDir = ray.Direction(); 50 T toPlaneDis = GetSignedDistance(rayOrigin); 51 if (toPlaneDis < 0 /*只和正平面相交*/ || (maxDistance && *maxDistance < toPlaneDis)) 52 return false; 53 54 T angleCos = -rayDir.DotProduct(_Normal); 55 //射线方向与平面平行 56 if (FLOAT_EQUAL(angleCos, 0)) 57 return false; 58 59 if (intersection) 60 { 61 *intersection = rayOrigin + rayDir * (toPlaneDis / angleCos); 62 } 63 64 return true; 65 } 66 67 template <typename T> 68 bool Plane<T>::Intersect(const Sphere<T> &sphere) const 69 { 70 T distance = GetSignedDistance(sphere.Center()); 71 return std::abs(distance) < sphere.Radius; 72 } 73 74 template <typename T1> 75 ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Plane<T1> &plane) 76 { 77 out << plane._Normal << ", " << plane._Distance; 78 return out; 79 } 80 81 typedef Plane<double> Planed; 82 typedef Plane<float> Planef;
Plane类中GetSignedDistance计算了点到平面的有符号距离,如下图点q的位置为q = p + an,n为平面的法向量,p为q在平面上的最近点,则a为q到平面的距离,等式两边同时与n点乘,即qn = pn + ann,根据平面的定义我们知道pn = d,则a = qn - d,这就是计算点到平面距离的公式,我们也可以这样来理解这个公式,qn为点q在n方向上的投影距离减去平面到原点距离d即是点到平面的有符号距离。
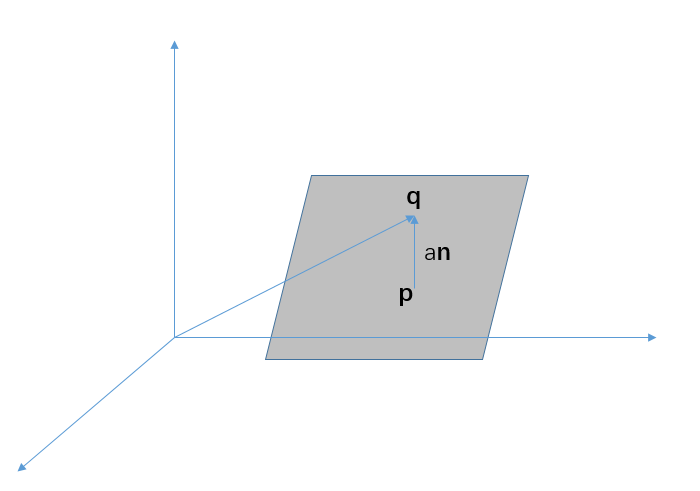
平面的Intersect函数计算了与射线、球体的相交检测,射线与平面的相交检测函数中,射线只能和平面正方向相交,首先计算了射线位置到平面的距离,如果距离为负,则射线点在平面的负半面,不能和平面正面相交。然后利用三角函数计算出射线原点到相交点距离,代入到射线方程中,即可求得射线与平面的相交点。平面和球的相交更为简单,Sphere类通过球所在的位置和半径来定义一个球体。
1 template <typename T> 2 class Sphere 3 { 4 public: 5 Sphere(const Vector3<T> ¢er, T radius); 6 7 inline const Vector3<T> &Center() const { return _Center; } 8 inline const T &Radius() const { return _Radius; } 9 inline Vector3<T> &Center() { return _Center; } 10 inline T &Radius() { return _Radius; } 11 bool Intersect(const Ray<T> &ray, T *maxDistance = nullptr, Vector3<T> *intersection = nullptr) const; 12 13 template <typename T1> 14 friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Sphere<T1> &sphere); 15 16 private: 17 Vector3<T> _Center; 18 T _Radius; 19 float a; 20 }; 21 22 template <typename T> 23 Sphere<T>::Sphere(const Vector3<T> ¢er, T radius) 24 : _Center(center), _Radius(radius) 25 { 26 } 27 28 template <typename T> 29 bool Sphere<T>::Intersect(const Ray<T> &ray, T *maxDistance, Vector3<T> *intersection) const 30 { 31 Vector3<T> rayDir = ray.Direction(); 32 rayDir.Normalize(); 33 Vector3<T> ray2Center = _Center - ray.Origin(); 34 T a = ray2Center.DotProduct(rayDir); 35 T e2 = ray2Center.SqrLength(); 36 T a2 = a * a; 37 T radius2 = _Radius * _Radius; 38 T b2 = e2 - a2; 39 40 if (b2 <= radius2) 41 { 42 if (maxDistance || intersection) 43 { 44 //射线点在球内,计算射出时的相交点 45 T t = e2 < radius2 ? a + sqrt(radius2 - b2) : a - sqrt(radius2 - b2); 46 if (maxDistance && *maxDistance < t) 47 return false; 48 49 if (intersection) 50 *intersection = ray.Origin() + ray.Direction() * t; 51 } 52 return true; 53 } 54 55 return false; 56 } 57 58 template <typename T> 59 ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Sphere<T> &sphere) 60 { 61 return out << sphere._Center << ", " << sphere._Radius; 62 } 63 64 typedef Sphere<double> Sphered; 65 typedef Sphere<float> Spheref;
判断平面和球体相交,只需要计算球中心点到平面的距离(非有符号距离,因为即在平面负方向也会相交)与球体半径的关系即可。同样球体也定义了与射线的相交检测函数如下图,分别是射线原点在球外(上)和球内(下)的情况,这里要计算的是点b的位置。
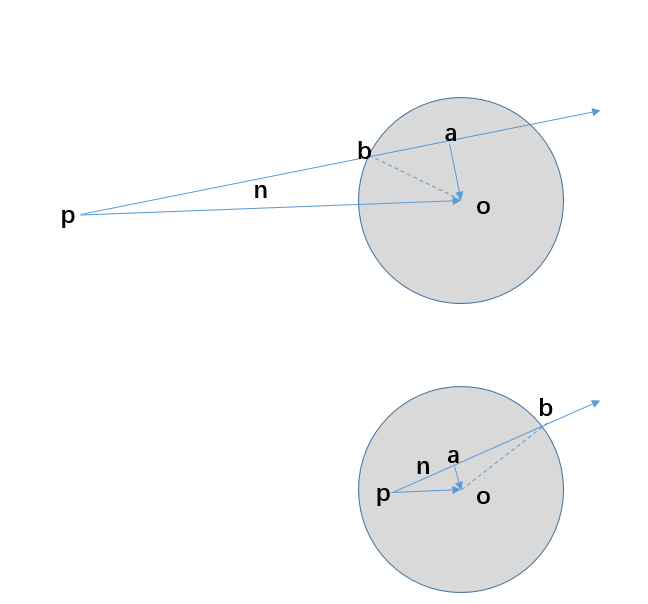
从图中可以看到,射线原点到点b的距离等于射线原点到球心的向量在射线方向上的投影距离加(p在球内)或减(p在球外)ab之间的距离,这里ob的距离为球的半径,通过三角函数即求得ab距离的大小。
另一个常用的图元是AABB(Axis Aligned Bounding Box,轴对齐包围盒),它的每一面都平行于坐标平面,其实现非常简单,只需要指定最小点和最大点即可表示这个包围盒。
1 template <typename T> 2 class AABBox 3 { 4 public: 5 AABBox(const Vector3<T> &min, const Vector3<T> &max); 6 void Union(const Vector3<T> &point); 7 void Union(const AABBox<T> &box); 8 inline Vector3<T> Size() const; 9 inline Vector3<T> Center() const; 10 Vector3<T> ClosestPointTo(const Vector3<T> &point) const; 11 bool Contains(const Vector3<T> &point) const; 12 bool Intersect(const Sphere<T> &sphere) const; 13 bool Intersect(const Ray<T> &ray, float *maxDistance = nullptr, Vector3<T> *intersection = nullptr) const; 14 bool Intersect(const AABBox<T> &box, AABBox<T> *intersection = nullptr) const; 15 16 template <typename T1> 17 friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const AABBox<T1> &v); 18 private: 19 Vector3<T> _Min; 20 Vector3<T> _Max; 21 }; 22 23 template <typename T> 24 AABBox<T>::AABBox(const Vector3<T> &min, const Vector3<T> &max) 25 { 26 //保证传值不正确时得到合法的aabbox 27 for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) 28 { 29 _Min[i] = MIN(min[i], max[i]); 30 _Max[i] = MAX(min[i], max[i]); 31 } 32 } 33 34 template <typename T> 35 void AABBox<T>::Union(const Vector3<T> &point) 36 { 37 for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) 38 { 39 _Min[i] = MIN(_Min[i], point[i]); 40 _Max[i] = MAX(_Max[i], point[i]); 41 } 42 } 43 44 template <typename T> 45 void AABBox<T>::Union(const AABBox<T> &box) 46 { 47 for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) 48 { 49 _Min[i] = MIN(_Min[i], box._Min[i]); 50 _Max[i] = MAX(_Max[i], box._Max[i]); 51 } 52 } 53 54 template <typename T> 55 Vector3<T> AABBox<T>::Size() const 56 { 57 return _Max - _Min; 58 } 59 60 template <typename T> 61 Vector3<T> AABBox<T>::Center() const 62 { 63 return (_Max + _Min) * (T)0.5; 64 } 65 66 template <typename T> 67 Vector3<T> AABBox<T>::ClosestPointTo(const Vector3<T> &point) const 68 { 69 Vector3<T> result; 70 for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) 71 { 72 if (point[i] < _Min[i]) 73 result[i] = _Min[i]; 74 else if (point[i] > _Max[i]) 75 result[i] = _Max[i]; 76 else 77 result[i] = point[i]; 78 } 79 return result; 80 } 81 82 template <typename T> 83 bool AABBox<T>::Contains(const Vector3<T> &point) const 84 { 85 return point.x >= _Min.x && point.y >= _Min.y && point.z >= _Min.z && point.x <= _Max.x && point.y <= _Max.y && point.z <= _Max.z; 86 } 87 88 template <typename T> 89 bool AABBox<T>::Intersect(const Sphere<T> &sphere) const 90 { 91 const Vector3<T> &sphereCenter = sphere.Center(); 92 Vector3<T> closestPoint = ClosestPointTo(sphereCenter); 93 return (closestPoint - sphereCenter).SqrLength() < sphere.Radius(); 94 } 95 96 template <typename T> 97 bool AABBox<T>::Intersect(const Ray<T> &ray, float *maxDistance, Vector3<T> *intersection) const 98 { 99 Plane<T> planes[6] = {Plane<T>(-Vector3<T>::right, _Min), Plane<T>(-Vector3<T>::up, _Min), Plane<T>(-Vector3<T>::forward, _Min), 100 Plane<T>(Vector3<T>::right, _Max), Plane<T>(Vector3<T>::up, _Max), Plane<T>(Vector3<T>::forward, _Max)}; 101 102 for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) 103 { 104 Vector3<T> intersectPoint; 105 if (planes[i].Intersect(ray, maxDistance, &intersectPoint)) 106 { 107 bool contains = Contains(intersectPoint); 108 if (contains) 109 { 110 if (intersection) *intersection = intersectPoint; 111 return true; 112 } 113 } 114 } 115 116 return false; 117 } 118 119 template <typename T> 120 bool AABBox<T>::Intersect(const AABBox<T> &box, AABBox *intersection) const 121 { 122 for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) 123 { 124 if (_Min[i] > box._Max[i]) 125 return false; 126 } 127 128 if (intersection) 129 { 130 for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) 131 { 132 intersection->_Min[i] = MAX(_Min[i], box._Min[i]); 133 intersection->_Max[i] = MIN(_Max[i], box._Max[i]); 134 } 135 } 136 137 return true; 138 } 139 140 template <typename T> 141 ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const AABBox<T> &v) 142 { 143 out << v._Min << ", " << v._Max; 144 return out; 145 }
上面代码中Union方法可以点或另一个AABB合并到当前AABB,当计算一个模型的AABB时,通过Union模型的每一个顶点,可以最终模型的AABB;ClosestPointTo是通过将点推向AABB的各平面计算出点到包含上最近的位置;Contains计算点是否在包含盒内;Intersect的几的个函数是用来计算与球、射线 、其它包围盒的相交性。AABB与球的相交检测是通过计算球心到AABB上最近的点的距离和球的半径来判断的。射线与AABB的相交检测首先计算射线与AABB的哪一个正平面相交,然后判断相交点是否在包围盒上。两个AABB之间的相交检测只需要判断最小点和最大点之间的关系就可以了,同时,将相交部分生成一个新的AABB。
最后在我们还会经常用到三角形,Triangle类代码如下:
/** * _V0 * /\ * e2/ \e1 * / \ * _V1/______\ _V2 * e0 **/ template <typename T> class Triangle { public: Triangle(const Vector3<T> &v0, const Vector3<T> &v1, const Vector3<T> v2); bool Contains(const Vector3<T> &point) const; bool BarycentricCoord(const Vector3<T> &point, Vector3<T> &out) const; bool Intersect(const Ray<T> &ray, float *maxDistance = nullptr, Vector3<T> *intersection = nullptr) const; Vector3<T> &operator[](int i); const Vector3<T> &operator[](int i) const; template <typename T1> friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Triangle<T1> &tri); private: union { struct { Vector3<T> _V0, _V1, _V2; }; Vector3<T> _V[3]; }; }; template <typename T> Triangle<T>::Triangle(const Vector3<T> &v0, const Vector3<T> &v1, const Vector3<T> v2) : _V0(v0), _V1(v1), _V2(v2) { } template <typename T> bool Triangle<T>::BarycentricCoord(const Vector3<T> &point, Vector3<T> &out) const { Vector3<T> e0 = _V2 - _V1; Vector3<T> e1 = _V0 - _V2; Vector3<T> e2 = _V1 - _V0; Vector3<T> v0p = point - _V0; Vector3<T> v1p = point - _V1; Vector3<T> v2p = point - _V2; Vector3<T> dir = e2.CrossProduct(-e1); T area012_2 = e2.CrossProduct(-e1).DotProduct(dir); // 退化三角形,面积为0 if (FLOAT_EQUAL(area012_2, 0)) return false; //点在三角形外部时,至少有一个重心坐标值为负, T areaP01_2 = e2.CrossProduct(v0p).DotProduct(dir); T areaP12_2 = e0.CrossProduct(v1p).DotProduct(dir); T areaP20_2 = e1.CrossProduct(v2p).DotProduct(dir); T area012_2_inv = (T)1 / area012_2; out.x = areaP01_2 * area012_2_inv; out.y = areaP12_2 * area012_2_inv; out.z = areaP20_2 * area012_2_inv; return true; } template <typename T> bool Triangle<T>::Contains(const Vector3<T> &point) const { Vector3<T> e0 = _V2 - _V1; Vector3<T> e1 = _V0 - _V2; Vector3<T> e2 = _V1 - _V0; T area012_2 = e2.CrossProduct(-e1).Length(); // 退化三角形,面积为0 if (FLOAT_EQUAL(area012_2, 0)) return false; Vector3<T> v0p = point - _V0; Vector3<T> v1p = point - _V1; Vector3<T> v2p = point - _V2; T areaP01_2 = e2.CrossProduct(v0p).Length(); T areaP12_2 = e0.CrossProduct(v1p).Length(); T areaP20_2 = e1.CrossProduct(v2p).Length(); return FLOAT_EQUAL(areaP01_2 + areaP12_2 + areaP20_2 - area012_2, 0); } template <typename T> bool Triangle<T>::Intersect(const Ray<T> &ray, float *maxDistance, Vector3<T> *intersection) const { Vector3<T> e1 = _V2 - _V0; Vector3<T> e2 = _V1 - _V0; Vector3<T> normal = e2.CrossProduct(e1); Plane<T> plane(normal, _V0); Vector3<T> intersectionPoint; bool intersetWithPlane = plane.Intersect(ray, maxDistance, &intersectionPoint); if (intersetWithPlane) { bool result = Contains(intersectionPoint); if (result && intersection) { *intersection = intersectionPoint; } return result; } return false; } template <typename T> Vector3<T> &Triangle<T>::operator[](int i) { return _V[i]; } template <typename T> const Vector3<T> &Triangle<T>::operator[](int i) const { return _V[i]; } template <typename T> ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Triangle<T> &tri) { return out << tri._V0 << ", " << tri._V1 << ", " << tri._V2; } typedef Triangle<double> Triangled; typedef Triangle<float> Trianglef; }
这里主要定义了三个函数,分别用来计算点是否在三角形上(Contains)、求点在三角形上的重心坐标(BarycentricCoord)和射线之间的相交检测(Intersect),Contains函数的原理是三角形内任意一点到三个顶点所组成的子三角形面积和等于原三角形的面积。
BarycentricCoord函数用到了子三角形的面积与原角形面积的比来计算重心坐标,三角形平面内任意一点可以用重心坐标来表示,即p = b0v0 + b1v1 + b2v2,如果点不在三角形所在的平面,计算出的为点在三角形所在平面投影点的重心坐标。
以上就是常用的一些基本图元,游戏中还会用到OBB、圆柱、胶囊体内几何图元,这些内容会在将来游戏物理章节用到时再进行补充。
本文来自博客园,作者:毅安,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/primarycode/p/16514246.html,文章内容同步更新微信公众号:“游戏开发实战”或“GamePrimaryCode”


