8.3 credit sales(bad debt , ar)
method1:direct write off
method2:allowance method for bad debt allowance for doubtful accounts
8.4 inventories
The valuation method is the process by which the inventory is valued. GAAP requires inventory to be valued at the lower of cost to market (LCM) valuation. Market valuation is defined as replacement cost.
cogs= begining inventory + purchase - ending inventory
GAAP requires inventory to be valued at the lower of cost to market. LCM can be calculated by using the item-by-item method or the major-category method.
8.7
Rising Price (Inflationary) Environment
FIFO method
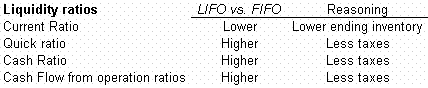
- COGS will be understated.
- Income will be overstated.
- The company will pay more income tax and have a lower cash flow.
- Assets on the balance sheet will be more reflective of the actual market value.
- Working capital and current ratio will be increased.
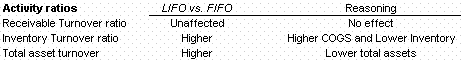
- Inventory turnover (COGS / average inventory) will worsen (decrease).
LIFO method
- COGS will be more reflective of current market environment.
- Income will be lower.
- The company will pay less income tax and cash flow will be higher.
- Assets will be understated and not reflective of its market value.
- Working capital and current ratio will be decreased.
- Inventory turnover (COGS / average inventory) will improve (increase).
Analysts should be aware that companies that operate in a rising-price environment and utilize the LIFO method could manipulate their earnings. To manipulate the earnings management could simply stop purchasing new inventory and start dipping into their old and cheap inventory. This is call "LIFO liquidation".
8.8
To make the conversion possible, U.S. GAAP requires companies that use LIFO to report a LIFO reserve (found in footnotes). The LIFO reserve is the difference between what their ending inventory would have been if they used FIFO.
Formula 8.2
| LIFO reserve = FIFO inventory - LIFO inventory |
COGS (FIFO) = COGS (LIFO) - change in LIFO reserve
A longer way to convert LIFO to FIFO is to calculate purchases, convert both beginning and ending inventory to FIFO levels, and then calculate COGS using the FIFO inventory levels and purchases.
COGS = beginning inventory + purchases - ending inventory
Rearrange the terms:
Purchases = ending inventory - beginning inventory + COGS (LIFO)
We also know that:
Ending inventory (FIFO) = Ending inventory (LIFO) + ending period LIFO reserve
Beginning inventory (FIFO) = Beginning inventory (LIFO) + Beginning LIFO reserve
Liquidity Ratio Changes
 |
Activity ratios
 |
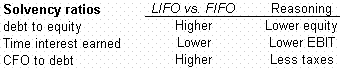
Solvency ratios
 |
8.11
LIFO reserves decline because a company is doing the following:
- liquidating its inventory (lower quantities / selling cheap/old stock)
- is purchasing inventory at lower prices (price decline)
| Look Out! |
Companies must report inventories at the lower of cost (determined by their LIFO, FIFO or other inventory accounting method) or market value.
Market value is essentially the net realizable value of the assets.
8.13
Depreciation is not a method of valuation but of cost allocation.
8.14
DDB in year i = 2 x (total acquisition cost - accumulated depreciation)
n
n = number of years
Note that changes in useful life and salvage value are considered changes in accounting estimates, not changes in accounting principle. The result is this: no need to restate past financial statements.
8.16 capitalizing and expensing
Expensing a cost indicates it is included on the income statement and subtracted from revenue to determine profit. Capitalizing indicates that the cost has been determined to be a capital expenditure and is accounted for on the balance sheet as an asset, with only the depreciationshowing up on the income statement.
The decision to capitalize interest will have an effect on a company's:
- Net income - In the current period earnings will be higher (overstated).
- CFO - In the current period, CFO will be higher (overstated) because the interest expense will be included in CFI.
- CFI - In the current period, CFI will be lower (understated).
- Assets - Total assets will be overstated because they include the capitalized interest.
- Solvency ratios - Since assets, EBIT and stockholders' equity will be higher, all solvency ratios will be overstated
8.18
capitalizing intangible assets
911
A defined-benefit pension plan promises a specific benefit at retirement to its employees. Since the benefits are defined, the employer is responsible for accumulating sufficient funds. Such plans insulate employees from investments that perform poorly, but it also prevents them from enjoying the entire upside potential of the pension if it does well.
That said, pension funds are governed by the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA), a more conservative investment approach, and large gains are unlikely to occur. Corporations refrain from setting up these types of plans because they can create enormous pension liabilities for a company if the pension's portfolio does not perform well.
A defined-contribution pension plan, by contrast, specifies how much the employer will contribute annually. The actual amount the employee will receive at retirement will depend on the overall performance of the pension fund. With such a plan, investments that perform poorly mean lower income in retirement, and vice versa. Under this plan the company does not carry any risk and does not create any pension liabilities if it pays its annual contribution amount. Contributions made are simply expenses on an annual basis and are usually discretionary.
Candidates should know that pension expenses are deducted from the income statement.

