SpringBoot整合Elasticsearch
学习本章内容的前提:
1.能独立搭建SpringBoot项目。(SpringBoot的快速入门)
2.Elasticsearch环境搭建完毕。(Elasticsearch环境搭建和介绍(Windows))
1 前奏
Elasticsearch提供的Java客户端有一些不太方便的地方:
- 很多地方需要拼接Json字符串,在java中拼接字符串有多恐怖你应该懂的
- 需要自己把对象序列化为json存储
- 查询到结果也需要自己反序列化为对象
因此,我们这里就不讲解原生的Elasticsearch客户端API了。
而是学习Spring提供的套件:Spring Data Elasticsearch
1.1 简介
Spring Data Elasticsearch是Spring Data项目下的一个子模块。
查看 Spring Data的官网:http://projects.spring.io/spring-data/

Spring Data 的使命是给各种数据访问提供统一的编程接口,不管是关系型数据库(如MySQL),还是非关系数据库(如Redis),或者类似Elasticsearch这样的索引数据库。从而简化开发人员的代码,提高开发效率。
包含很多不同数据操作的模块:

Spring Data Elasticsearch的页面:https://projects.spring.io/spring-data-elasticsearch/

特征:
- 支持Spring的基于
@Configuration的java配置方式,或者XML配置方式 - 提供了用于操作ES的便捷工具类
ElasticsearchTemplate。包括实现文档到POJO之间的自动智能映射。 - 利用Spring的数据转换服务实现的功能丰富的对象映射
- 基于注解的元数据映射方式,而且可扩展以支持更多不同的数据格式
- 根据持久层接口自动生成对应实现方法,无需人工编写基本操作代码(类似mybatis,根据接口自动得到实现)。当然,也支持人工定制查询
1.2 Elasticsearch基本概念
Elasticsearch也是基于Lucene的全文检索库,本质也是存储数据,很多概念与MySQL类似的。
对比关系:
索引库(indices)--------------------------------Databases 数据库
类型(type)-----------------------------Table 数据表
文档(Document)----------------Row 行
字段(Field)-------------------Columns 列详细说明:
| 概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 索引库(indices) | indices是index的复数,代表许多的索引, |
| 类型(type) | 类型是模拟mysql中的table概念,一个索引库下可以有不同类型的索引,比如商品索引,订单索引,其数据格式不同。不过这会导致索引库混乱,因此未来版本中会移除这个概念 |
| 文档(document) | 存入索引库原始的数据。比如每一条商品信息,就是一个文档 |
| 字段(field) | 文档中的属性 |
| 映射配置(mappings) | 字段的数据类型、属性、是否索引、是否存储等特性 |
是不是与Lucene中的概念类似。
另外,在Elasticsearch有一些集群相关的概念:
- 索引集(Indices,index的复数):逻辑上的完整索引
- 分片(shard):数据拆分后的各个部分
- 副本(replica):每个分片的复制
注意:
Elasticsearch本身就是分布式的,因此即便你只有一个节点,Elasticsearch默认也会对你的数据进行分片和副本操作,当你向集群添加新数据时,数据也会在新加入的节点中进行平衡。
2.1 创建SpringBoot 项目
首先我们要新建一个SpringBoot项目,再进行Elasticsearch的整合。
pom依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.czxy</groupId> <artifactId>es-demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>es-demo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- elasticsearch启动器 (必须)--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
application.properties文件配置:
## Elasticsearch配置文件(必须) ## 该配置和Elasticsearch的elasticsearch.yml中的配置信息有关 spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-name=my-application spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes=127.0.0.1:9300
Elasticsearch的elasticsearch.yml中的配置信息如下:
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: my-application # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: node-1 # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # #path.data: /path/to/data # # Path to log files: # #path.logs: /path/to/logs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 0.0.0.0 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: # http.port: 9200 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # #discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["host1", "host2"] # # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): # #discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: # # For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Gateway ----------------------------------- # # Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started: # #gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3 # # For more information, consult the gateway module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*" node.master: true node.data: true
2.2 索引操作
2.2.1 创建索引和映射
SpringBoot-data-elasticsearch提供了面向对象的方式操作elasticsearch
业务:创建一个商品对象,有这些属性:
id,title,category,brand,price,图片地址
在SpringDataElasticSearch中,只需要操作对象,就可以操作elasticsearch中的数据实体类
首先我们准备好实体类:
public class Item { private Long id; private String title; //标题 private String category;// 分类 private String brand; // 品牌 private Double price; // 价格 private String images; // 图片地址 }
映射—注解
Spring Data通过注解来声明字段的映射属性,有下面的三个注解:
@Document作用在类,标记实体类为文档对象,一般有两个属性- indexName:对应索引库名称
- type:对应在索引库中的类型
- shards:分片数量,默认5
- replicas:副本数量,默认1
@Id作用在成员变量,标记一个字段作为id主键@Field作用在成员变量,标记为文档的字段,并指定字段映射属性:- type:字段类型,是枚举:FieldType,可以是text、long、short、date、integer、object等
- text:存储数据时候,会自动分词,并生成索引
- keyword:存储数据时候,不会分词建立索引
- Numerical:数值类型,分两类
- 基本数据类型:long、interger、short、byte、double、float、half_float
- 浮点数的高精度类型:scaled_float
- 需要指定一个精度因子,比如10或100。elasticsearch会把真实值乘以这个因子后存储,取出时再还原。
- Date:日期类型
- elasticsearch可以对日期格式化为字符串存储,但是建议我们存储为毫秒值,存储为long,节省空间。
- index:是否索引,布尔类型,默认是true
- store:是否存储,布尔类型,默认是false
- analyzer:分词器名称,这里的
ik_max_word即使用ik分词器
- type:字段类型,是枚举:FieldType,可以是text、long、short、date、integer、object等
示例:
@Document(indexName = "item",type = "docs", shards = 1, replicas = 0) public class Item { /** * @Description: @Id注解必须是springframework包下的 * org.springframework.data.annotation.Id *@Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Id private Long id; @Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word") private String title; //标题 @Field(type = FieldType.Keyword) private String category;// 分类 @Field(type = FieldType.Keyword) private String brand; // 品牌 @Field(type = FieldType.Double) private Double price; // 价格 @Field(index = false, type = FieldType.Keyword) private String images; // 图片地址 }
创建索引
ElasticsearchTemplate中提供了创建索引的API:
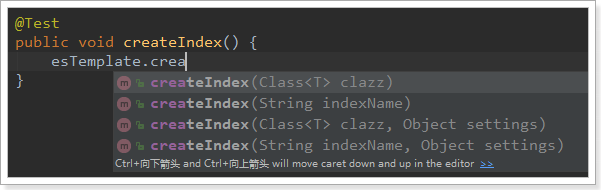
- 可以根据类的信息自动生成,也可以手动指定indexName和Settings
映射
映射相关的API:
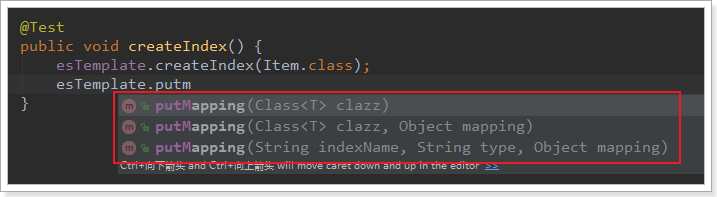
- 一样,可以根据类的字节码信息(注解配置)来生成映射,或者手动编写映射
我们这里采用类的字节码信息创建索引并映射,下面是测试类代码:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = EsDemoApplication.class) public class EsDemoApplicationTests { @Autowired private ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate; /** * @Description:创建索引,会根据Item类的@Document注解信息来创建 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 * @Date: 2018/9/29 0:51 */ @Test public void testCreateIndex() { elasticsearchTemplate.createIndex(Item.class); }
运行testCreateIndex(),索引创建成功后打开elasticsearch-head-master插件(es-head插件的安装)查看索引信息,
索引信息:

2.2.2 删除索引
删除索引的API:
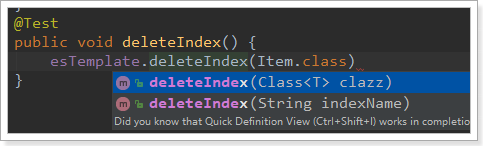
可以根据类名或索引名删除。
示例:
/** * @Description:删除索引 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 * @Date: 2018/9/29 0:50 */ @Test public void testDeleteIndex() { elasticsearchTemplate.deleteIndex(Item.class); }
运行testDeleteIndex(),索引删除成功后打开elasticsearch-head-master插件(es-head插件的安装)查看索引信息,发现item索引已经被删除。
2.3 新增文档数据
2.3.1 Repository接口
Spring Data 的强大之处,就在于你不用写任何DAO处理,自动根据方法名或类的信息进行CRUD操作。只要你定义一个接口,然后继承Repository提供的一些子接口,就能具备各种基本的CRUD功能。
来看下Repository的继承关系:

我们看到有一个ElasticsearchCrudRepository接口:
 .png)
.png)
所以,我们只需要定义接口,然后继承它就OK了。
/** * @Description:定义ItemRepository 接口 * @Param: * Item:为实体类 * Long:为Item实体类中主键的数据类型 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 * @Date: 2018/9/29 0:50 */ public interface ItemRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Item,Long> { }
接下来,我们测试新增数据:
2.3.2 新增一个对象
@Autowired private ItemRepository itemRepository; /** * @Description:定义新增方法 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void insert() { Item item = new Item(1L, "小米手机7", " 手机", "小米", 3499.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg"); itemRepository.save(item); }
运行insert(),去页面查询看看:

OK,新增成功!
2.3.3 批量新增
代码:
/** * @Description:定义批量新增方法 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void insertList() { List<Item> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Item(2L, "坚果手机R1", " 手机", "锤子", 3699.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg")); list.add(new Item(3L, "华为META10", " 手机", "华为", 4499.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg")); // 接收对象集合,实现批量新增 itemRepository.saveAll(list); }
再次去页面查询:

OK,批量新增成功!
2.3.4 修改
elasticsearch中本没有修改,它的修改原理是该是先删除在新增
修改和新增是同一个接口,区分的依据就是id。
/** * @Description:定义修改方法 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void update(){ Item item = new Item(1L, "苹果XSMax", " 手机", "小米", 3499.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg"); itemRepository.save(item); }
查看结果:

2.4 查询
2.4.1 基本查询
ElasticsearchRepository提供了一些基本的查询方法:

我们来试试查询所有:
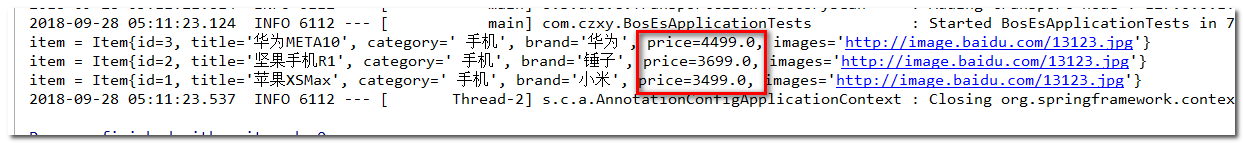
/** * @Description:定义查询方法,含对价格的降序、升序查询 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void testQueryAll(){ // 查找所有 //Iterable<Item> list = this.itemRepository.findAll(); // 对某字段排序查找所有 Sort.by("price").descending() 降序 // Sort.by("price").ascending():升序 Iterable<Item> list = this.itemRepository.findAll(Sort.by("price").ascending()); for (Item item:list){ System.out.println(item); } }
结果:
2.4.2 自定义方法
Spring Data 的另一个强大功能,是根据方法名称自动实现功能。
比如:你的方法名叫做:findByTitle,那么它就知道你是根据title查询,然后自动帮你完成,无需写实现类。
当然,方法名称要符合一定的约定:
| Keyword | Sample |
|---|---|
And |
findByNameAndPrice |
Or |
findByNameOrPrice |
Is |
findByName |
Not |
findByNameNot |
Between |
findByPriceBetween |
LessThanEqual |
findByPriceLessThan |
GreaterThanEqual |
findByPriceGreaterThan |
Before |
findByPriceBefore |
After |
findByPriceAfter |
Like |
findByNameLike |
StartingWith |
findByNameStartingWith |
EndingWith |
findByNameEndingWith |
Contains/Containing |
findByNameContaining |
In |
findByNameIn(Collection<String>names) |
NotIn |
findByNameNotIn(Collection<String>names) |
Near |
findByStoreNear |
True |
findByAvailableTrue |
False |
findByAvailableFalse |
OrderBy |
findByAvailableTrueOrderByNameDesc |
例如,我们来按照价格区间查询,定义这样的一个方法:
public interface ItemRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Item,Long> { /** * @Description:根据价格区间查询 * @Param price1 * @Param price2 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ List<Item> findByPriceBetween(double price1, double price2); }
然后添加一些测试数据:
/** * @Description:准备测试数据 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void insertList() { List<Item> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Item(1L, "小米手机7", "手机", "小米", 3299.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg")); list.add(new Item(2L, "坚果手机R1", "手机", "锤子", 3699.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg")); list.add(new Item(3L, "华为META10", "手机", "华为", 4499.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg")); list.add(new Item(4L, "小米Mix2S", "手机", "小米", 4299.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg")); list.add(new Item(5L, "荣耀V10", "手机", "华为", 2799.00, "http://image.baidu.com/13123.jpg")); // 接收对象集合,实现批量新增 itemRepository.saveAll(list); }
不需要写实现类,然后我们直接去运行:
/** * @Description:按照价格区间查询 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void queryByPriceBetween(){ List<Item> list = this.itemRepository.findByPriceBetween(2000.00, 3500.00); for (Item item : list) { System.out.println("item = " + item); } }
结果:

OK,测试成功!
2.4.3 自定义查询
先来看最基本的matchQuery:
/** * @Description:matchQuery底层采用的是词条匹配查询 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void testMatchQuery(){ // 构建查询条件 NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); // 添加基本分词查询 queryBuilder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "小米手机")); // 搜索,获取结果 Page<Item> items = this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build()); // 总条数 long total = items.getTotalElements(); System.out.println("total = " + total); for (Item item : items) { System.out.println(item); } }
-
NativeSearchQueryBuilder:Spring提供的一个查询条件构建器,帮助构建json格式的请求体
-
QueryBuilders.matchQuery(“title”, “小米手机”):利用QueryBuilders来生成一个查询。QueryBuilders提供了大量的静态方法,用于生成各种不同类型的查询:

-
Page<item>:默认是分页查询,因此返回的是一个分页的结果对象,包含属性:-
totalElements:总条数
-
totalPages:总页数
-
Iterator:迭代器,本身实现了Iterator接口,因此可直接迭代得到当前页的数据
-
其它属性:

-
结果:
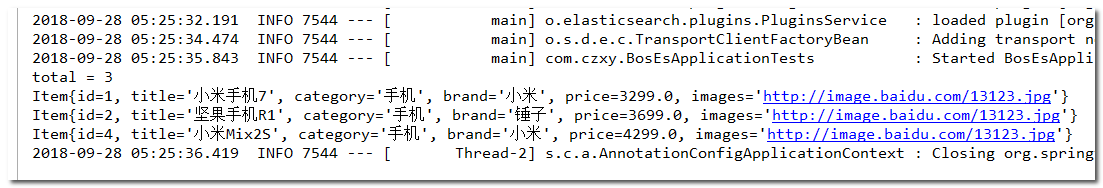
总的测试代码如下:
/** * * @Description:matchQuery *@Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void testMathQuery(){ // 创建对象 NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); // 在queryBuilder对象中自定义查询 //matchQuery:底层就是使用的termQuery queryBuilder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title","坚果")); //查询,search 默认就是分页查找 Page<Item> page = this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build()); //获取数据 long totalElements = page.getTotalElements(); System.out.println("获取的总条数:"+totalElements); for(Item item:page){ System.out.println(item); } } /** * @Description: * termQuery:功能更强大,除了匹配字符串以外,还可以匹配 * int/long/double/float/.... * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void testTermQuery(){ NativeSearchQueryBuilder builder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); builder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.termQuery("price",998.0)); // 查找 Page<Item> page = this.itemRepository.search(builder.build()); for(Item item:page){ System.out.println(item); } } /** * @Description:布尔查询 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void testBooleanQuery(){ NativeSearchQueryBuilder builder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); builder.withQuery( QueryBuilders.boolQuery().must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title","华为")) .must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("brand","华为")) ); // 查找 Page<Item> page = this.itemRepository.search(builder.build()); for(Item item:page){ System.out.println(item); } } /** * @Description:模糊查询 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void testFuzzyQuery(){ NativeSearchQueryBuilder builder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); builder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.fuzzyQuery("title","faceoooo")); Page<Item> page = this.itemRepository.search(builder.build()); for(Item item:page){ System.out.println(item); } }
2.4.4 分页查询
利用NativeSearchQueryBuilder可以方便的实现分页:
/** * @Description:分页查询 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void searchByPage(){ // 构建查询条件 NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); // 添加基本分词查询 queryBuilder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.termQuery("category", "手机")); // 分页: int page = 0; int size = 2; queryBuilder.withPageable(PageRequest.of(page,size)); // 搜索,获取结果 Page<Item> items = this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build()); // 总条数 long total = items.getTotalElements(); System.out.println("总条数 = " + total); // 总页数 System.out.println("总页数 = " + items.getTotalPages()); // 当前页 System.out.println("当前页:" + items.getNumber()); // 每页大小 System.out.println("每页大小:" + items.getSize()); for (Item item : items) { System.out.println(item); } }
结果:
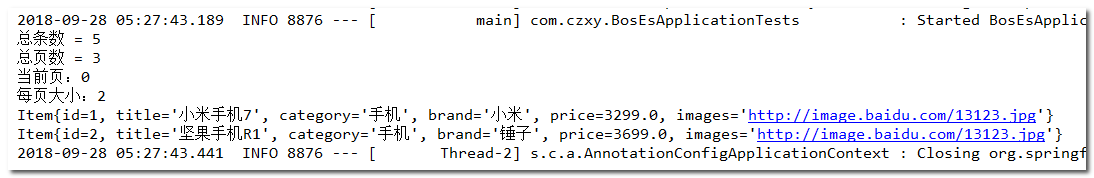
可以发现,Elasticsearch中的分页是从第0页开始。
2.4.5 排序
排序也通用通过NativeSearchQueryBuilder完成:
/** * @Description:排序查询 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void searchAndSort(){ // 构建查询条件 NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); // 添加基本分词查询 queryBuilder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.termQuery("category", "手机")); // 排序 queryBuilder.withSort(SortBuilders.fieldSort("price").order(SortOrder.ASC)); // 搜索,获取结果 Page<Item> items = this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build()); // 总条数 long total = items.getTotalElements(); System.out.println("总条数 = " + total); for (Item item : items) { System.out.println(item); } }
结果:

2.5 聚合(牛逼!!solr无此功能)
聚合可以让我们极其方便的实现对数据的统计、分析。例如:
- 什么品牌的手机最受欢迎?
- 这些手机的平均价格、最高价格、最低价格?
- 这些手机每月的销售情况如何?
实现这些统计功能的比数据库的sql要方便的多,而且查询速度非常快,可以实现近实时搜索效果。
2.5.1 聚合基本概念
Elasticsearch中的聚合,包含多种类型,最常用的两种,一个叫桶,一个叫度量:
桶(bucket)
桶的作用,是按照某种方式对数据进行分组,每一组数据在ES中称为一个桶,例如我们根据国籍对人划分,可以得到中国桶、英国桶,日本桶……或者我们按照年龄段对人进行划分:010,1020,2030,3040等。
Elasticsearch中提供的划分桶的方式有很多:
- Date Histogram Aggregation:根据日期阶梯分组,例如给定阶梯为周,会自动每周分为一组
- Histogram Aggregation:根据数值阶梯分组,与日期类似
- Terms Aggregation:根据词条内容分组,词条内容完全匹配的为一组
- Range Aggregation:数值和日期的范围分组,指定开始和结束,然后按段分组
- ……
综上所述,我们发现bucket aggregations 只负责对数据进行分组,并不进行计算,因此往往bucket中往往会嵌套另一种聚合:metrics aggregations即度量
度量(metrics)
分组完成以后,我们一般会对组中的数据进行聚合运算,例如求平均值、最大、最小、求和等,这些在ES中称为度量
比较常用的一些度量聚合方式:
- Avg Aggregation:求平均值
- Max Aggregation:求最大值
- Min Aggregation:求最小值
- Percentiles Aggregation:求百分比
- Stats Aggregation:同时返回avg、max、min、sum、count等
- Sum Aggregation:求和
- Top hits Aggregation:求前几
- Value Count Aggregation:求总数
- ……
注意:在ES中,需要进行聚合、排序、过滤的字段其处理方式比较特殊,因此不能被分词。这里我们将color和make这两个文字类型的字段设置为keyword类型,这个类型不会被分词,将来就可以参与聚合
2.5.2 聚合为桶
桶就是分组,比如这里我们按照品牌brand进行分组:
/** * @Description:按照品牌brand进行分组 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void testAgg(){ NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); // 不查询任何结果 queryBuilder.withSourceFilter(new FetchSourceFilter(new String[]{""}, null)); // 1、添加一个新的聚合,聚合类型为terms,聚合名称为brands,聚合字段为brand queryBuilder.addAggregation( AggregationBuilders.terms("brands").field("brand")); // 2、查询,需要把结果强转为AggregatedPage类型 AggregatedPage<Item> aggPage = (AggregatedPage<Item>) this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build()); // 3、解析 // 3.1、从结果中取出名为brands的那个聚合, // 因为是利用String类型字段来进行的term聚合,所以结果要强转为StringTerm类型 StringTerms agg = (StringTerms) aggPage.getAggregation("brands"); // 3.2、获取桶 List<StringTerms.Bucket> buckets = agg.getBuckets(); // 3.3、遍历 for (StringTerms.Bucket bucket : buckets) { // 3.4、获取桶中的key,即品牌名称 System.out.println(bucket.getKeyAsString()); // 3.5、获取桶中的文档数量 System.out.println(bucket.getDocCount()); } }
显示的结果:
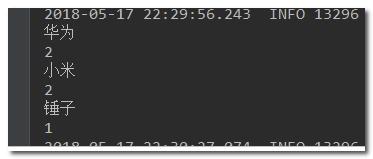
关键API:
AggregationBuilders:聚合的构建工厂类。所有聚合都由这个类来构建,看看他的静态方法:

(1)统计某个字段的数量 ValueCountBuilder vcb= AggregationBuilders.count("count_uid").field("uid"); (2)去重统计某个字段的数量(有少量误差) CardinalityBuilder cb= AggregationBuilders.cardinality("distinct_count_uid").field("uid"); (3)聚合过滤 FilterAggregationBuilder fab= AggregationBuilders.filter("uid_filter").filter(QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("uid:001")); (4)按某个字段分组 TermsBuilder tb= AggregationBuilders.terms("group_name").field("name"); (5)求和 SumBuilder sumBuilder= AggregationBuilders.sum("sum_price").field("price"); (6)求平均 AvgBuilder ab= AggregationBuilders.avg("avg_price").field("price"); (7)求最大值 MaxBuilder mb= AggregationBuilders.max("max_price").field("price"); (8)求最小值 MinBuilder min= AggregationBuilders.min("min_price").field("price"); (9)按日期间隔分组 DateHistogramBuilder dhb= AggregationBuilders.dateHistogram("dh").field("date"); (10)获取聚合里面的结果 TopHitsBuilder thb= AggregationBuilders.topHits("top_result"); (11)嵌套的聚合 NestedBuilder nb= AggregationBuilders.nested("negsted_path").path("quests"); (12)反转嵌套 AggregationBuilders.reverseNested("res_negsted").path("kps ");
AggregatedPage:聚合查询的结果类。它是Page<T>的子接口:
AggregatedPage在Page功能的基础上,拓展了与聚合相关的功能,它其实就是对聚合结果的一种封装。

而返回的结果都是Aggregation类型对象,不过根据字段类型不同,又有不同的子类表示

2.5.3 嵌套聚合,求平均值
代码:
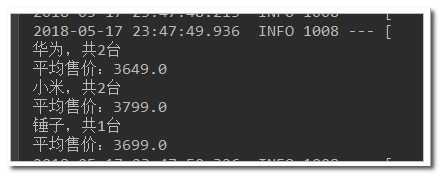
/** * @Description:嵌套聚合,求平均值 * @Author: https://blog.csdn.net/chen_2890 */ @Test public void testSubAgg(){ NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder(); // 不查询任何结果 queryBuilder.withSourceFilter(new FetchSourceFilter(new String[]{""}, null)); // 1、添加一个新的聚合,聚合类型为terms,聚合名称为brands,聚合字段为brand queryBuilder.addAggregation( AggregationBuilders.terms("brands").field("brand") .subAggregation(AggregationBuilders.avg("priceAvg").field("price")) // 在品牌聚合桶内进行嵌套聚合,求平均值 ); // 2、查询,需要把结果强转为AggregatedPage类型 AggregatedPage<Item> aggPage = (AggregatedPage<Item>) this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build()); // 3、解析 // 3.1、从结果中取出名为brands的那个聚合, // 因为是利用String类型字段来进行的term聚合,所以结果要强转为StringTerm类型 StringTerms agg = (StringTerms) aggPage.getAggregation("brands"); // 3.2、获取桶 List<StringTerms.Bucket> buckets = agg.getBuckets(); // 3.3、遍历 for (StringTerms.Bucket bucket : buckets) { // 3.4、获取桶中的key,即品牌名称 3.5、获取桶中的文档数量 System.out.println(bucket.getKeyAsString() + ",共" + bucket.getDocCount() + "台"); // 3.6.获取子聚合结果: InternalAvg avg = (InternalAvg) bucket.getAggregations().asMap().get("priceAvg"); System.out.println("平均售价:" + avg.getValue()); } }
结果:
ok,SpringBoot整合Spring Data Elasticsearch到此完结



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号