数学建模 - 状态转移问题
人狼羊菜过河问题

-
定义状态:人、狼、羊、菜表示为四维向量 \([i,j,k,w]\) 。\(0\) 表示在左岸,\(1\) 表示在右岸。最终需要从 \([0,0,0,0]\) 转移到 \([1,1,1,1]\)
-
不合法状态:由于人不在时,狼会吃羊,羊会吃菜,故这些状态不合法:
i != j and j == k # 狼吃羊 i != k and k == w # 羊吃菜获取全部合法状态的函数:
def get_state(): cnt = 0 state = {} for i in range(2): for j in range(2): for k in range(2): for w in range(2): if (i != j and j == k) or (i != k and k == w): continue else: state[cnt] = [i,j,k,w] cnt += 1 return cnt, state -
状态转移:
船每一次需从左岸到右岸,或从右岸到左岸,运送至多两样,且人必须在船上。故对于某一个状态转移\([I_1, J_1, K_1, W_1]\to [I_2, J_2, K_2, W_2]\) 需要满足下列条件:
- \(I_1 \neq I2\)。即人必须在船上,即转移前后人处于岸的不同侧
- 一次至多运送两样
- 运送的物品都是从\(A\)侧到\(B\)侧,不能是一个从\(A\)到\(B\),一个从\(B\)到A
获取全部合法状态转移的函数:
def get_trans(cnt, state): trans = [] for i in range(cnt): for j in range(i+1, cnt): m = state[i] n = state[j] # count diff diff = sum([m[x]^n[x] for x in range(4)]) sub = sum([m[x]-n[x] for x in range(4)]) if diff > 2 or m[0] == n[0] or sub == 0: continue else: # print(str(m) + " => " + str(n)) trans.append((i,j)) return trans -
转化为无向图最短路问题,求解\([0,0,0,0] \to [1,1,1,1]\) 的最短路
import networkx as nx import numpy as np # [ human, wolf, sheep, veg] def get_state(): cnt = 0 state = {} for i in range(2): for j in range(2): for k in range(2): for w in range(2): if (i != j and j == k) or (i != k and k == w): continue else: state[cnt] = [i,j,k,w] cnt += 1 return cnt, state def get_trans(cnt, state): trans = [] for i in range(cnt): for j in range(i+1, cnt): m = state[i] n = state[j] # count diff diff = sum([m[x]^n[x] for x in range(4)]) sub = sum([m[x]-n[x] for x in range(4)]) if diff > 2 or m[0] == n[0] or sub == 0: continue else: # print(str(m) + " => " + str(n)) trans.append((i,j)) return trans if __name__ == '__main__': num_node, tot_state = get_state() tot_trans = get_trans(num_node, tot_state) G = nx.Graph() for node in range(num_node): G.add_node(node) for edge in tot_trans: G.add_edge(edge[0], edge[1]) tot_shortest_path = nx.all_shortest_paths(G=G, source=0, target=num_node-1) dic = {0:"人", 1:"狼", 2:"羊", 3:"菜"} cnt = 0 for shortest_path in tot_shortest_path: for i in range(len(shortest_path)): cur = tot_state[shortest_path[i]] print('[' + str(i+1) + '] ', end='') print("左岸: ", end='') for j in range(4): if cur[j] == 0: print(dic[j], end='') print(" | ",end='') print("右岸: ", end='') for j in range(4): if cur[j] == 1: print(dic[j], end='') print('\n') print('------------------------') cnt += 1 print('总方案数' + str(cnt)) -
结果
[1] 左岸: 人狼羊菜 | 右岸: [2] 左岸: 狼菜 | 右岸: 人羊 [3] 左岸: 人狼菜 | 右岸: 羊 [4] 左岸: 狼 | 右岸: 人羊菜 [5] 左岸: 人狼羊 | 右岸: 菜 [6] 左岸: 羊 | 右岸: 人狼菜 [7] 左岸: 人羊 | 右岸: 狼菜 [8] 左岸: | 右岸: 人狼羊菜 ------------------------ [1] 左岸: 人狼羊菜 | 右岸: [2] 左岸: 狼菜 | 右岸: 人羊 [3] 左岸: 人狼菜 | 右岸: 羊 [4] 左岸: 菜 | 右岸: 人狼羊 [5] 左岸: 人羊菜 | 右岸: 狼 [6] 左岸: 羊 | 右岸: 人狼菜 [7] 左岸: 人羊 | 右岸: 狼菜 [8] 左岸: | 右岸: 人狼羊菜 ------------------------ 总方案数2
商人仆人过河问题

-
本题思路和上一题类似,定义状态\([i,j,k,w,p]\)。 \(i\) 表示左岸商人数量,\(j\)表示左岸仆人数量,\(k\)表示右岸商人数量,\(w\)表示右岸仆人数量,\(p\)表示当前船所在的侧。
-
所有状态即
for i in range(4): for j in range(4): [i,j,3-i,3-j,0] 和 [i,j,3-i,e-j,1]依题意,不合法状态包括
(i != 0 and i < j) or (k != 0 and k < w)故求所有合法状态的函数如下:
def get_state(): cnt = 0 tot_state = {} for i in range(4): for j in range(4): k = 3-i w = 3-j if (i != 0 and i < j) or (k != 0 and k < w): continue else: tot_state[cnt] = [i,j,k,w,0] cnt += 1 tot_state[cnt] = [i,j,k,w,1] cnt += 1 return cnt, tot_state -
状态转移
由于船从一侧驶向另一侧,故转移前后船位置一定是 \(0 \to 1\) 或 \(1 \to 0\)
假设当前转移为\([I_1, J_1, K_1, W_1, P] \to [I_2, J_2, K_2, W_2, \overline{P}]\)
- \(P = 0\) 时,需满足 \(I_2 \geq I_1\) 且 \(J_2 \geq J_1\)
- \(P = 1\) 时,需满足 \(K_2 \geq K_1\) 且 \(W_2 \geq W_1\)
此外,每一次船一定是载客的,即不能出现空船的情况。
综上,求所有合法状态转移的函数如下:
def get_trans(cnt, tot_state): tot_trans = [] for i in range(cnt): for j in range(i+1, cnt): x = tot_state[i] y = tot_state[j] if x[4] == y[4]: continue p = 0 q = 0 for k in range(2): if x[k] > y[k]: p = 1 elif x[k] < y[k]: q = 1 if p == 1 and y[4] == 1: continue elif q == 1 and y[4] == 0: continue elif p == 0 and q == 0: continue else: trans_num = abs(sum([x[p]-y[p] for p in range(2)])) if trans_num <= 2: # print(str(tot_state[i]) + ' =>> ' + str(tot_state[j])) tot_trans.append((i,j)) return tot_trans -
转化为无向图最短路问题,从 \([3,3,0,0,1]\) 转移到 \([0,0,3,3,0]\)
import networkx as nx import numpy as np def get_state(): cnt = 0 tot_state = {} for i in range(4): for j in range(4): k = 3-i w = 3-j if (i != 0 and i < j) or (k != 0 and k < w): continue else: tot_state[cnt] = [i,j,k,w,0] cnt += 1 tot_state[cnt] = [i,j,k,w,1] cnt += 1 return cnt, tot_state def get_trans(cnt, tot_state): tot_trans = [] for i in range(cnt): for j in range(i+1, cnt): x = tot_state[i] y = tot_state[j] if x[4] == y[4]: continue p = 0 q = 0 for k in range(2): if x[k] > y[k]: p = 1 elif x[k] < y[k]: q = 1 if p == 1 and y[4] == 1: continue elif q == 1 and y[4] == 0: continue elif p == 0 and q == 0: continue else: trans_num = abs(sum([x[p]-y[p] for p in range(2)])) if trans_num <= 2: # print(str(tot_state[i]) + ' =>> ' + str(tot_state[j])) tot_trans.append((i,j)) return tot_trans if __name__ == '__main__': cnt, tot_state = get_state() tot_trans = get_trans(cnt, tot_state) G = nx.Graph() for i in range(cnt): G.add_node(i) for edge in tot_trans: # print(edge) G.add_edge(edge[0], edge[1]) tot_shortest_paths = nx.all_shortest_paths(G=G, source=cnt-1, target=0) t = 1 for shortest_path in tot_shortest_paths: print('方案{0}:'.format(t)) for i in shortest_path: node = tot_state[i] print('左岸: 商人:{0}, 仆人:{1} | 右岸: 商人:{2}, 仆人:{3} | 船在{4}边'.format( node[0], node[1], node[2], node[3], '左' if node[4] == 1 else '右')) t += 1 print('--------------') -
结果
方案1: 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:3 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:0 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:0 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:3 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:3 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:0 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:0 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:3 | 船在右边 -------------- 方案2: 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:3 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:0 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:0 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:3 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:3 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:0 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:0 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:3 | 船在右边 -------------- 方案3: 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:3 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:0 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:0 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:3 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:3 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:0 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:0 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:3 | 船在右边 -------------- 方案4: 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:3 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:0 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:0 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:3 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:2 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:1 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:3 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:0 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:2 | 船在右边 左岸: 商人:1, 仆人:1 | 右岸: 商人:2, 仆人:2 | 船在左边 左岸: 商人:0, 仆人:0 | 右岸: 商人:3, 仆人:3 | 船在右边 --------------
等分酒问题

-
定义状态:
\([i,j,k]\) 定义为三个杯子(8容量杯,5容量杯,3容量杯)中酒水含量
-
有效状态:
\([i,j,k]\) 有效状态:
\[i+j+k=8 \\ 0 \leq i \leq 8 \\ 0 \leq j \leq 5 \\ 0 \leq k \leq 3 \]求全部合法状态函数如下:
def get_state(): source = -1 target = -1 cnt = 0 tot_state = {} for i in range(9): for j in range(6): for k in range(4): if i + j + k != 8: continue else: if i == 8: source = cnt elif i == 4 and j == 4: target = cnt tot_state[cnt] = [i,j,k] cnt += 1 return cnt, tot_state, source, target -
状态转移:
不借助其他工具,单次倒酒的衡量方式只有两种:
- 将杯子 \(A\) 内的酒全部倒进杯子 \(B\) 中
- 将杯子 \(A\) 内的酒注满杯子 \(B\)
状态转移判断函数如下:
def try_path(a, b): # 注满 8 if b[0]==8 and a[0]!=8: if a[1]-b[1]==b[0]-a[0] or a[2]-b[2]==b[0]-a[0]: return True # 注满 5 elif b[1]==5 and a[1]!=5: if a[0]-b[0]==b[1]-a[1] or a[2]-b[2]==b[1]-a[1]: return True # 注满 3 elif b[2]==3 and a[2]!=3: if a[0]-b[0]==b[2]-a[2] or a[1]-b[1]==b[2]-a[2]: return True # 不能通过注满转移到,尝试排空 # 排空 8 if b[0]==0 and a[0]!=0: if b[1]-a[1]==a[0]-b[0] or b[2]-a[2]==a[0]-b[0]: return True # 排空 5 elif b[1]==0 and a[1]!=0: if b[0]-a[0]==a[1]-b[1] or b[2]-a[2]==a[1]-b[1]: return True # 排空 3 elif b[2]==0 and a[2]!=0: if b[0]-a[0]==a[2]-b[2] or b[1]-a[1]==a[2]-b[2]: return True # 无法转移 return False求解所有状态转移函数如下:
def get_trans(cnt, tot_state): tot_trans = [] for i in range(cnt): for j in range(cnt): if i == j: continue else: x = tot_state[i] y = tot_state[j] if try_path(x, y): tot_trans.append((i,j)) return tot_trans -
转化为有向图(之所以是有向图,是因为 \(A \to B\) 不一定有 \(B \to A\)),求解从 \([8,0,0]\) 转移到 \([4,4,0]\) 的最短路
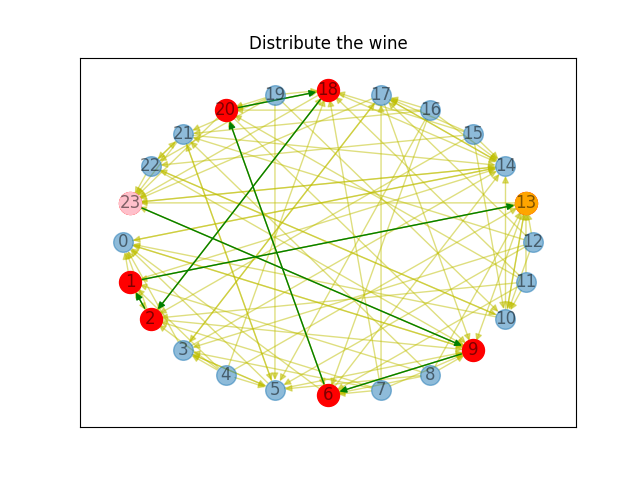
import networkx as nx import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # ( a, b, c) # ( 8, 0, 0) => ( 4, 4, 0) def try_path(a, b): # 注满 8 if b[0]==8 and a[0]!=8: if a[1]-b[1]==b[0]-a[0] or a[2]-b[2]==b[0]-a[0]: return True # 注满 5 elif b[1]==5 and a[1]!=5: if a[0]-b[0]==b[1]-a[1] or a[2]-b[2]==b[1]-a[1]: return True # 注满 3 elif b[2]==3 and a[2]!=3: if a[0]-b[0]==b[2]-a[2] or a[1]-b[1]==b[2]-a[2]: return True # 不能通过注满转移到,尝试排空 # 排空 8 if b[0]==0 and a[0]!=0: if b[1]-a[1]==a[0]-b[0] or b[2]-a[2]==a[0]-b[0]: return True # 排空 5 elif b[1]==0 and a[1]!=0: if b[0]-a[0]==a[1]-b[1] or b[2]-a[2]==a[1]-b[1]: return True # 排空 3 elif b[2]==0 and a[2]!=0: if b[0]-a[0]==a[2]-b[2] or b[1]-a[1]==a[2]-b[2]: return True # 无法转移 return False def get_state(): source = -1 target = -1 cnt = 0 tot_state = {} for i in range(9): for j in range(6): for k in range(4): if i + j + k != 8: continue else: if i == 8: source = cnt elif i == 4 and j == 4: target = cnt tot_state[cnt] = [i,j,k] cnt += 1 return cnt, tot_state, source, target def get_trans(cnt, tot_state): tot_trans = [] for i in range(cnt): for j in range(cnt): if i == j: continue else: x = tot_state[i] y = tot_state[j] if try_path(x, y): tot_trans.append((i,j)) return tot_trans if __name__ == '__main__': cnt, tot_state,source,target = get_state() tot_trans = get_trans(cnt, tot_state) G = nx.DiGraph() for i in range(cnt): G.add_node(i) for edge in tot_trans: G.add_edge(edge[0], edge[1]) tot_shortest_paths = nx.all_shortest_paths(G=G, source=source, target=target) t = 1 for shortest_path in tot_shortest_paths: if t != 1 : print('') print('方案{0}:'.format(t)) t += 1 first = 1 for node in shortest_path: if first == 1: first = 0 else: print(' => ', end='') print(tot_state[node],end='') plt.figure() pos = nx.shell_layout(G) edgelist = [] for i in range(len(shortest_path)-1): edgelist.append((shortest_path[i], shortest_path[i+1])) nx.draw_networkx(G=G, pos=pos, node_size=200, alpha=0.5, edge_color='y') nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G=G, pos=pos, nodelist=shortest_path, node_color='r', node_size=250) nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G=G, pos=pos, nodelist=[source], node_color='pink', node_size=250) nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G=G, pos=pos, nodelist=[target], node_color='orange', node_size=250) nx.draw_networkx_edges(G=G, pos=pos, edgelist=edgelist, edge_color='g') plt.title('Distribute the wine') plt.show() -
结果
方案1: [8, 0, 0] => [3, 5, 0] => [3, 2, 3] => [6, 2, 0] => [6, 0, 2] => [1, 5, 2] => [1, 4, 3] => [4, 4, 0]