树上DP - 最大连通子树 - CodeForces - Maximum White Subtree
写在前面:在看这篇题解前,首先需要学会基本的树型dp是什么,推荐一道题,是本题的简单版。 传送门
本题:题目链接
这是我第一次接触最大连通子树的题。
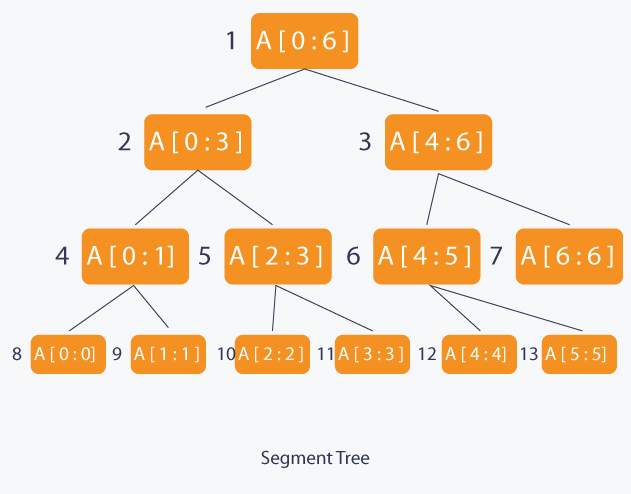
常规的树型DP,是先dfs求取子树的最优解,再回溯更新父节点的最优解。比如构造一棵最值线段树的过程就是这样:
每一个节点的最优解只受到子节点的影响,而与父节点无关。
然而,本题不能简单这么做。因为一个节点所对应的最优解可能需要从父节点继续向上拓展。
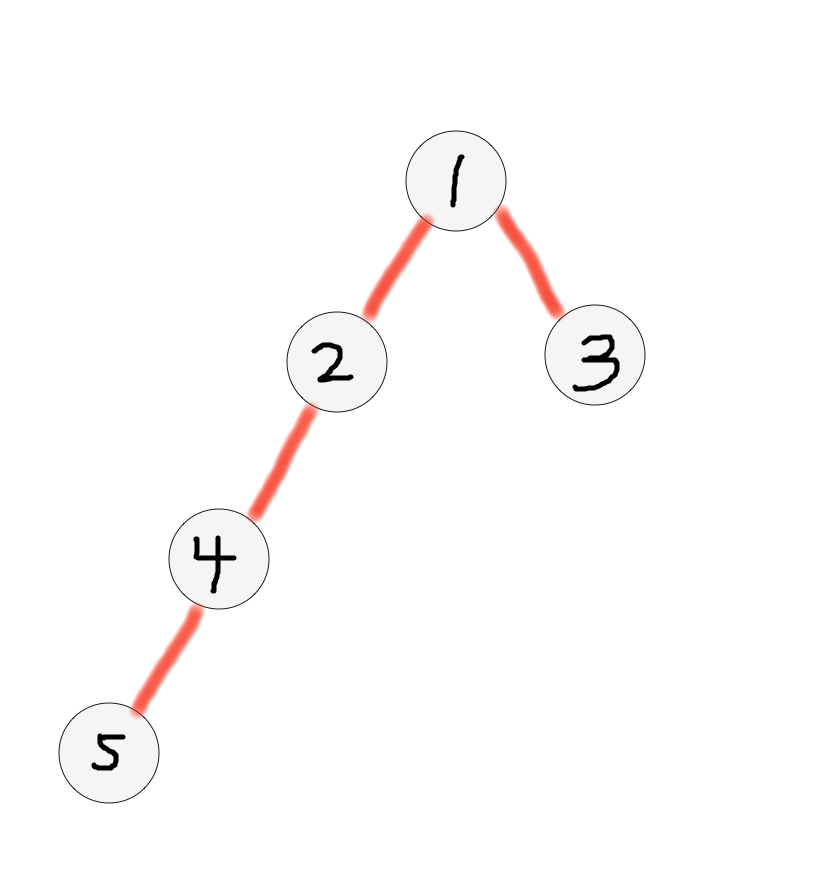
比如下图的这棵树,我们假设每个点均为白色。那么对于 ' 4 ' 号节点的最优解,不仅包含子节点 ' 5 ' , 还要包含父节点 ' 2 ' -> ' 1 ' -> ' 3 ' 的拓展。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #define MAX(a,b) (a>b?a:b) 4 #define Maxsize 200000+1 5 using namespace std; 6 int n; // 节点数目 7 int ans[Maxsize]; // ans[i]表示包含 i 节点的最大连通子树,即 i 号的最终答案 8 int nex[Maxsize]; // nex 即 next , nex[i] 表示 以 i 号节点为根,向下(子树)拓展所得到的最优解 9 int val[Maxsize]; // val[i] 记录每个点的权值,即 1 或 -1 ,这个数组其实可以省略,直接记录到 nex[i]上 10 vector<int> vec[Maxsize]; // 存边 11 void init(){ // 初始化 12 int a,b; 13 cin >> n; 14 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 15 cin >> val[i]; 16 if(val[i] == 0) 17 val[i] = -1; 18 } 19 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { 20 cin >> a >> b; 21 vec[a].push_back(b); 22 vec[b].push_back(a); 23 } 24 } 25 void push_up(int root,int f){ // 常规的树形dp,自底而上更新每一个nex[i] 26 for (auto it = vec[root].begin(); it != vec[root].end(); it++) { 27 if(*it != f) 28 push_up(*it,root); 29 } 30 nex[root] = val[root]; 31 for (auto it = vec[root].begin(); it != vec[root].end(); it++) { 32 if(*it != f) 33 nex[root] += MAX(0,nex[*it]); 34 } 35 } 36 37 void push_down(int root,int f){ // 自顶而下更新每一个ans[i] 38 ans[root] = MAX(0,ans[f] - MAX(0,nex[root])) + nex[root]; 39 for (auto it = vec[root].begin(); it != vec[root].end(); it++) { 40 if(*it != f) 41 push_down(*it,root); 42 } 43 } 44 int main(){ 45 init(); 46 push_up(1,0); 47 push_down(1,0); 48 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 49 cout << ans[i] <<' '; 50 } 51 return 0; 52 }
这里唯一需要解释的,应该就是 push_down 函数的状态转移方程:
ans[root] = MAX(0,ans[f] - MAX(0,nex[root])) + nex[root];
依然拿这个图说明。

第一步,我们求1号节点的答案 : ans[ 1 ] 等于什么? 由于1根本就没有父节点,因此 ans[ 1 ] = nex[ 1 ] + 0
假设现在 root = 2, 我们正在求包含2号节点的最大连通子树的值为多少。
此时我们已知哪些条件? 我们知道了 nex[ 2 ] , ans[ 1 ] 。
ans[ 1 ] 是怎么构成的呢? 它可以包含 1->2->4->5 这个方向的拓展,也可以包含 1->3 这个方向的拓展。
如果 nex[ 2 ] <= 0, 那么 ans[ 1 ] 一定不会包括1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5这个方向。反之,如果nex[ 2 ] > 0,那么ans[ 1 ] 一定包括了 1->2->4->5这个方向的拓展。
那么,我们现在要借助ans[ 1 ]求解ans [ 2 ] ,就要想办法求这样的值: 1号节点的最优解,且为了避免重复计算不包含 1->2->4->5方向的拓展。也即 ans[ 1 ] - MAX(0,nex[ 2 ])
但是,这个值并不一定是正数。如果是正数,表明 2号节点向 1 号节点拓展可以让答案增大;如果是负数,那么就不能向 1号节点拓展。
因此得到最终2号节点的状态转移方程 : ans[ 2 ] = nex[ 2 ] + MAX( 0 , ans[ 1 ] - MAX( 0,nex[ 2 ] ) )
以此类推,状态转移方程的通式就是:
ans[root] = MAX(0,ans[f] - MAX(0,nex[root])) + nex[root];


