从Flux到Redux详解单项数据流
从Flux到Redux是状态管理工具的演变过程,但两者还是有细微的区别的。但是最核心的都还是观察者模式的应用。
一、Flux
1. Flux的处理逻辑
通俗来讲,应用的状态被放到了store中,组件是store状态的一个映射,用户通过事件触发action,再通过Dispatcher根据不同的actionType进行分发,并做不同的逻辑处理,但核心都是通过直接改变store的状态,再触发emitChange间接改变组件中的数据。(后面会上代码)

从代码层面来讲,store中的数据通过EventEmitter注册监听,并通知引入此store的组件状态变化,view中的数据实时通过store获取,action中则是通过AppDispatcher分发,而注册后的AppDispatcher则根据对应的actionTypes做不通的逻辑处理。
常规方法使用Flux需要引入的库有:Dispatcher,EventEmitter
2. Flux的劣势:
1.Flux可以有多个store,而当逻辑复杂时,多个store的依赖会非常繁琐。异步操作也不是很友好。
2. 难以进行服务端渲染,同构成本较高。
3. store混杂了处理逻辑与状态。
3. Flux项目的关联核心代码:
js/countPanel.js
类的构造函数初始化store的数据:
constructor (props) {
super(props);
this.state = {max: 15, fluxData: CounterValues};
this.setMax = this.setMax.bind(this);
this.totalChange = this.totalChange.bind(this);
this.fluxTest = this.fluxTest.bind(this);
}
在事件中调用action
<button onClick={this.fluxTest}>click flux</button>
fluxTest () {
increment();
}
./Action.js
import * as ActionTypes from './ActionTypes.js';
import AppDispatcher from './AppDispatcher.js';
export const increment = (counterCaption) => {
AppDispatcher.dispatch({
type: ActionTypes.INCREMENT,
counterCaption: counterCaption
})
}
export const decrement = (counterCaption) => {
AppDispatcher.dispatch({
type: ActionTypes.DECREMENT,
counterCaption: counterCaption
})
}
./AppDispatcher.js
import {Dispatcher} from 'flux';
import * as ActionTypes from './ActionTypes.js';
import CounterStore from './store/CounterStore.js';
let AppDispatcher = new Dispatcher();
AppDispatcher.register((actions) => {
if (actions.type === ActionTypes.INCREMENT) {
// CounterValues[actions.counterCaption]++;
CounterStore.doChange('First', 1000)
CounterStore.emitChange();
} else if (actions.type === ActionTypes.DECREMENT) {
// doSomthing
}
})
export default AppDispatcher;
./store/CounterStore.js
通过EventEmitter(观察者模式最典型的应用)注册数据监听与处理:
import {EventEmitter} from 'events';
const CounterValues = {
First: 0,
Second: 10,
Third: 30
}
const CounterStore = Object.assign({}, EventEmitter.prototype, {
doChange (counterKey, CounterVal) {
CounterValues[counterKey] = CounterVal;
},
getCounterValues: function () {
return CounterValues;
},
emitChange: function () {
this.emit('change');
},
addChangeListener: function (callBack) {
this.on('change', callBack);
},
removeChangeListener: function (callBack) {
this.removeChangeListener('change', callBack)
}
})
export {CounterValues};
export default CounterStore;
二、Redux
1. Redux的三条原则:
(1)唯一数据源
(2)保持状态只读
(3)通过纯函数改变数据
ps: 纯函数:1.不得改写参数 2. 不得调用系统的IO 3. 不能调用Date.now()或Math.random()等方法,因为每次获取的结果都不同。
2. Redux的逻辑处理
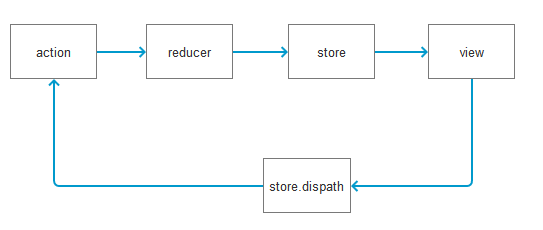
与Flux的区别在于:
(1)Flux中对action的处理没有返回值,只是通过Dispatcher分发动作,由Dispatcher的注册函数中做逻辑处理;而Redux中则取消了Dispatcher对象,action只是通过store的dispatch方法提交动作,再由store注册的reducer根据对应的ActionTypes做逻辑处理。
(2)Flux中的逻辑处理是直接对现有的state做处理,而Redux则是通过纯函数进行处理,在原有的state基础上返回新生成的state,不会对原有数据产生副作用。
3. Redux实际使用的核心代码:
./counter.js
在事件处理函数中通过store.dispatch分发动作:
onIncrement() {
store.dispatch(Actions.increment(this.props.caption));
}
通过subscribe进行监听:
componentDidMount() {
store.subscribe(this.onChange);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
store.unsubscribe(this.onChange);
}
./action.js
对应的dispatch处理函数中,返回一个action对象:
export const increment = (counterCaption) => {
return {
type: ActionTypes.INCREMENT,
counterCaption: counterCaption
};
};
./reducer.js
通过纯函数处理对应的action
export default (state, action) => {
const {counterCaption} = action;
switch (action.type) {
case ActionTypes.INCREMENT:
return {...state, [counterCaption]: state[counterCaption] + 1};
case ActionTypes.DECREMENT:
return {...state, [counterCaption]: state[counterCaption] - 1};
default:
return state
}
}
./store.js
通过createStore将reducer与store数据联系起来
import {createStore} from 'redux';
import reducer from './reducer.js';
const initValues = {
'First': 0,
'Second': 10,
'Third': 20
};
const store = createStore(reducer, initValues);
export default store;
