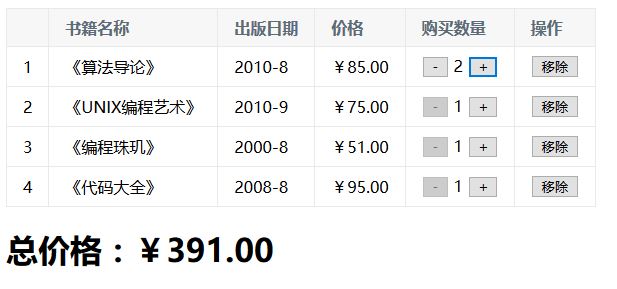
1 html

<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <title>购物车</title> <script src="vue.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css" /> </head> <body > <div id="app"> <div v-if="books.length"> <table> <thead> <tr> <th></th> <th>书籍名称</th> <th>出版日期</th> <th>价格</th> <th>购买数量</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for="(item,index) in books"> <td>{{item.id}}</td> <td>{{item.name}}</td> <td>{{item.date}}</td> <td>{{item.price | getFinalPriceF}}</td> <td> <button @click='decrement(index)' v-bind:disabled=" item.count > 1 ? false :true">-</button> {{item.count}} <button @click='increment(index)'>+</button> </td> <td> <button @click="removeHandle(index)">移除</button> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> <h1>总价格:{{totalPrice |getFinalPriceF}}</h1> </div> <h2 v-else>购物车为空</h2> </div> </body> <!--js要加载在最后面!!--> <script src="mian.js" type="text/javascript"> </script> </html>
2 main.js

const app=new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ books:[ { id:1, name:'《算法导论》', date:'2010-8', price:85.00, count:1 }, { id:2, name:'《UNIX编程艺术》', date:'2010-9', price:75.00, count:1 }, { id:3, name:'《编程珠玑》', date:'2000-8', price:51.00, count:1 }, { id:4, name:'《代码大全》', date:'2008-8', price:95.00, count:1 } ], }, computed:{ totalPrice(){ let totalPrice=0 for(let i=0;i<this.books.length;i++){ totalPrice += this.books[i].price * this.books[i].count } return totalPrice } }, methods:{ getFinalPrice(price){ return '¥'+ price.toFixed(2) }, decrement(index){ if(this.books[index].count>=1){ this.books[index].count-- } }, increment(index){ this.books[index].count++ }, removeHandle(index){ this.books.splice(index,1) } }, filters:{ //过滤器 getFinalPriceF(price){ return '¥'+ price.toFixed(2) } } })
3 style.css

table { border:1px solid #e9e9e9; border-collapse:collapse; border-spacing:0; } th,td { padding:8px 16px; border:1px solid #e9e9e9; text-align:left; } th { background-color:#f7f7f7; color:#5c6b77; }
过滤器
filters:{ //过滤器
getFinalPriceF(price){
return '¥'+ price.toFixed(2)
}
}
使用方法
<h1>总价格:{{totalPrice |getFinalPriceF}}</h1>
idsabled属性
v-bind:disabled=" item.count > 1 ? false :true"
当数量小于等于1时 按钮不可用
循环的简略写法 in of
//1 普通的for循环 totalPrice(){ let totalPrice=0 for(let i=0;i<this.books.length;i++){ totalPrice += this.books[i].price * this.books[i].count } return totalPrice }, //2 in 拿到i totalPrice2(){ let totalPrice=0 for(let i in this.books){ totalPrice += this.books[i].price * this.books[i].count } return totalPrice }, //3 of 拿到item totalPrice3(){ let totalPrice=0 for(let item of this.books){ totalPrice += item.price *item.count } return totalPrice }
三种写法效果相同,推荐使用3
高阶函数与箭头函数//filter /map/reduce

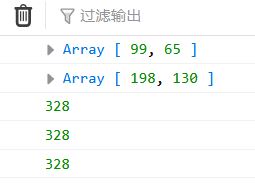
//filter也是一个常用的操作,它用于把Array的某些元素过滤掉,然后返回剩下的元素。和map()类似,Array的filter()也接收一个函数。和map()不同的是,filter()把传入的函数依次作用于每个元素,然后根据返回值是true还是false决定保留还是丢弃该元素。 const nums = [10,99,22,3,44,34,24,65] newNums = nums.filter(function(n){ // if(n>50){ // return true //返回true 则加到新的数组里 // }else{ // return false //返回false 则 // } return n>50 }) console.log(newNums) //map每次返回 值会作为新的值 newNums2 = newNums.map(function(n){ return n*2 }) console.log(newNums2) //reduce 对数组中的所有数据进行汇总 //preValue 上一次返回的值 // 第一次时 初始化值为0 所以preValue为0 // 第二次时 初始化值为上一次的返回值 newNums3 = newNums2.reduce(function(preValue,n){ return preValue+n },0) console.log(newNums3)
链式写法

//链式写法 let total = nums.filter(function(n){ return n>50 }).map(function(n){ return n*2 }).reduce(function(preValue,n){ return preValue+n },0) console.log(total)
箭头函数写法
//更简洁的箭头函数 let total2 = nums.filter(n => n>50).map(n=> n*2).reduce((pre,n)=>pre +n) console.log(total2)
将总价格改成高阶函数的形式
totalPrice(){ return this.books.reduce(function(preValue,book){ return preValue + book.price * book.count },0) }
totalPrice(){ return this.books.reduce((preValue,book) => (preValue + book.price * book.count),0) }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号