python基础1--安装、package、数据类型
1、下载python
下载地址https://www.python.org/downloads/
2、Package以及数据类型
自带package和外部package
自带package举例: os; os.getwd()
import os
import requests
print(os.getcwd())
r = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
print(r.url)
print(r.encoding)
print(r.text)
外部package以及管理系统介绍: easy_install, pip
pip和easyinstall的区别:
1)pip会把插件及其相关的依赖一起安装而easyinstall只会安装制定的插件
2)pip继承easyinstall,即安装pip之前必须有easyinstall存在
Python 3.4以上版本已经带有,但在环境变量Path中配置相应路径,打开python安装目录中查看
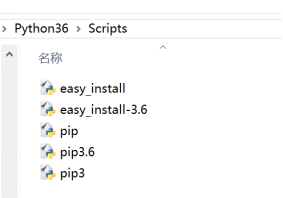
配置后,在cmd中测试easy_install
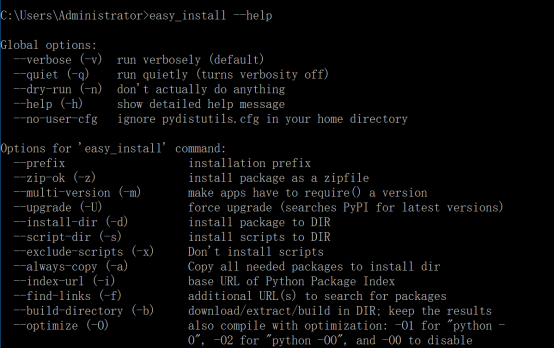
测试pip
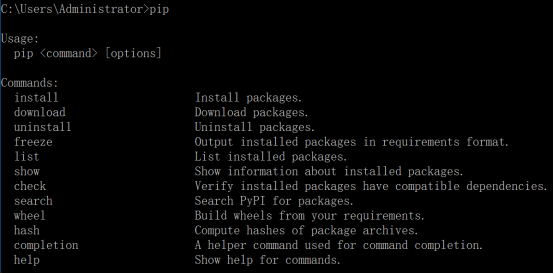
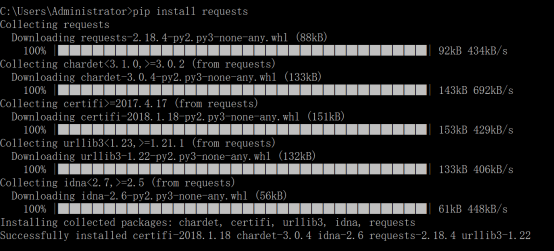
举例使用使用pip安装requests
3、Python数据类型
总体包含以下数据类型:numerics, sequences, mappings, classes, instances, and exceptions
Numeric Types包括 int (boolean类型被认为是int的一个特殊表现), float, complex(负数)
int: unlimited length
float: 对应的是C语言中的double类型, 可查看 sys.float_info
complex: real(实部) & imaginary(虚部),用z.real 和 z.imag来取两部分
具体运算以及法则参见:
|
Operation |
Result |
Full documentation |
|
x + y |
sum of x and y |
|
|
x - y |
difference of x and y |
|
|
x * y |
product of x and y |
|
|
x / y |
quotient of x and y |
|
|
x // y |
floored quotient of x and y |
|
|
x % y |
remainder of x / y |
|
|
-x |
x negated |
|
|
+x |
x unchanged |
|
|
abs(x) |
absolute value or magnitude of x |
|
|
int(x) |
x converted to integer |
|
|
float(x) |
x converted to floating point |
|
|
complex(re, im) |
a complex number with real part re, imaginary part im. im defaults to zero. |
|
|
c.conjugate() |
conjugate of the complex number c |
|
|
divmod(x, y) |
the pair (x // y, x % y) |
|
|
pow(x, y) |
x to the power y |
|
|
x ** y |
x to the power y |
|
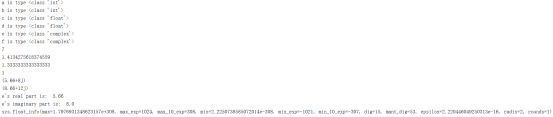
import sys
a = 3
b = 4
c = 5.66
d = 8.0
e = complex(c, d)
f = complex(float(a), float(b))
print ("a is type" , type(a))
print ("b is type" , type(b))
print ("c is type" , type(c))
print ("d is type" , type(d))
print ("e is type" , type(e))
print ("f is type" , type(f))
print(a + b)
print(d / c)
print (b / a)
print (b // a)
print (e)
print (e + f)
print ("e's real part is: " , e.real)
print ("e's imaginary part is: " , e.imag)
print (sys.float_info)
运行结果:
字符串:是指一串字符,示或者打印出来文字信息,不可变(immutable)。在python中有单引号,双引号,三引号的方式。Format字符串用于联合。换行符为" \n"
print("Hellow World")
print('Hellow World')
print('''This is 1 line
This is 2 line
this is 3 line
''')
age = 3
name = "Tom"
print("{0} was {1} years old.".format(name, age))
print(name + " was " + str(age) + " years old.")
运行结果:

字面常量(literal constant):
可以直接以字面的意义使用它们:
如:6,2.24,3.45e-3, "This is a string"
常量:不会被改变
变量:用于储存信息,属于identifier。其中identifier命名规则是第一个字符必须是字母或者下划线,其余字符可以是字母,数字,或者下划线。区分大小写。如:合法(i, name_3_4, big_bang)不合法(2people, this is tom, my-name, >123b_c2)
注释: #
缩进(Indentation):python的语法结构建立在缩进上

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号