@@D. World of Tank
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/936/D
Vitya loves programming and problem solving, but sometimes, to distract himself a little, he plays computer games. Once he found a new interesting game about tanks, and he liked it so much that he went through almost all levels in one day. Remained only the last level, which was too tricky. Then Vitya remembered that he is a programmer, and wrote a program that helped him to pass this difficult level. Try do the same.
The game is organized as follows. There is a long road, two cells wide and n cells long. Some cells have obstacles. You control a tank that occupies one cell. Initially, the tank is located before the start of the road, in a cell with coordinates (0, 1). Your task is to move the tank to the end of the road, to the cell (n + 1, 1)or (n + 1, 2).
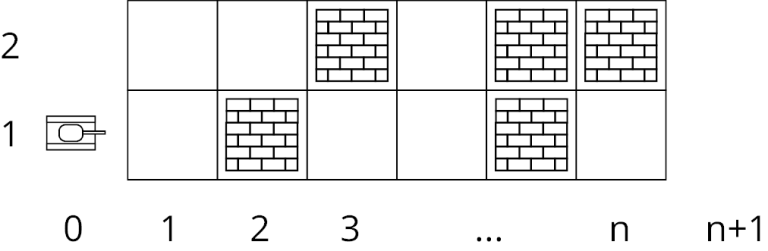
Every second the tank moves one cell to the right: the coordinate x is increased by one. When you press the up or down arrow keys, the tank instantly changes the lane, that is, the y coordinate. When you press the spacebar, the tank shoots, and the nearest obstacle along the lane in which the tank rides is instantly destroyed. In order to load a gun, the tank needs t seconds. Initially, the gun is not loaded, that means, the first shot can be made only after t seconds after the tank starts to move.
If at some point the tank is in the same cell with an obstacle not yet destroyed, it burns out. If you press the arrow exactly at the moment when the tank moves forward, the tank will first move forward, and then change the lane, so it will not be possible to move diagonally.
Your task is to find out whether it is possible to pass the level, and if possible, to find the order of actions the player need to make.
The first line contains four integers n, m1, m2 and t, the length of the field, the number of obstacles in the first lane, the number of obstacles in the second lane and the number of tank steps before reloading, respectively (1 ≤ n ≤ 109; 0 ≤ m1, m2 ≤ n; 0 ≤ m1 + m2 ≤ 106; 1 ≤ t ≤ n).
The next two lines contain a description of the obstacles. The first of these lines contains m1 numbers xi— the obstacle coordinates in the first lane (1 ≤ xi ≤ n; xi < xi + 1). The y coordinate for all these obstacles will be 1.
The second line contains m2 numbers describing the obstacles of the second lane in the same format. The y coordinate of all these obstacles will be 2.
In the first line print «Yes», if it is possible to pass the level, or «No», otherwise.
If it is possible, then in the second line print the number of times the tank moves from one lane to another, and in the next line print the coordinates of the transitions, one number per transition: the coordinate x(0 ≤ x ≤ n + 1). All transition coordinates coordinates must be distinct and should be output in strictly increasing order.The number of transitions should not exceed 2·106. If the tank can pass the level, then it can do it using no more than 2·106 transitions.
In the fourth line print the number of shots that the tank makes during the movement, in the following lines print two numbers, x and y coordinates of the point (1 ≤ x ≤ n, 1 ≤ y ≤ 2), from which the tank fired a shot, the number of shots must not exceed m1 + m2. Shots must be output in the order in which they are fired.
If there are several solutions, output any one.
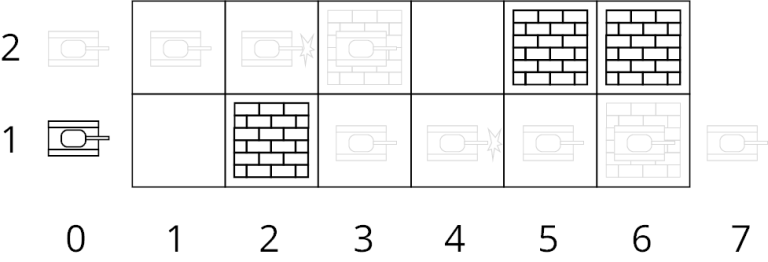
6 2 3 2
2 6
3 5 6
Yes
2
0 3
2
2 2
4 1
1 1 1 1
1
1
No
9 5 2 5
1 2 7 8 9
4 6
Yes
4
0 3 5 10
1
5 2
Picture for the first sample test.
附上tle垃圾代码


// 去吧!皮卡丘! 把AC带回来! // へ /| // /\7 ∠_/ // / │ / / // │ Z _,< / /`ヽ // │ ヽ / 〉 // Y ` / / // イ● 、 ● ⊂⊃〈 / // () へ | \〈 // >ー 、_ ィ │ // // / へ / ノ<| \\ // ヽ_ノ (_/ │// // 7 |/ // >―r ̄ ̄`ー―_ //************************************** #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000") #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; #define inf 2147483647 const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fll; #define ri register int template <class T> inline T min(T a, T b, T c) { return min(min(a, b), c); } template <class T> inline T max(T a, T b, T c) { return max(max(a, b), c); } template <class T> inline T min(T a, T b, T c, T d) { return min(min(a, b), min(c, d)); } template <class T> inline T max(T a, T b, T c, T d) { return max(max(a, b), max(c, d)); } #define pi acos(-1) #define mem(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x)); #define For(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++) #define FFor(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i >= b; i--) #define bug printf("***********\n"); #define mp make_pair #define pb push_back const int maxn = 3e5 + 10; // name******************************* struct pos { int x, y; }; int n, m1, m2, T; deque<int> q1, q2, c; deque<pos> p; int a[3][100000]; int pp[1000000]; // function****************************** int inv(int x) { if (x == 1) return 2; else return 1; } void dfs(int y, int x, int t, deque<int> c, deque<pos> p, deque<int> q1, deque<int> q2) { // cout<<"y:"<<y<<"x:"<<x<<"t:"<<t<<endl; if (a[y][x]) return; if (t > T) t = T; if (x == n + 1) { cout << "Yes" << endl; cout << c.size() << endl; for (int i : c) cout << i << " "; cout << endl; cout << p.size() << endl; for (pos i : p) cout << i.x << " " << i.y << endl; exit(0); } dfs(y, x + 1, t + 1, c, p, q1, q2); if (!a[inv(y)][x]) { c.push_back(x); dfs(inv(y), x + 1, t + 1, c, p, q1, q2); c.pop_back(); } if (t == T) { //不变道射击 if (y == 1) { for (int i : q1) if (i < x) q1.pop_front(); int tx = q1.front(); q1.pop_front(); a[y][tx] = 0; p.push_back(pos{x, y}); dfs(y, x + 1, 1, c, p, q1, q2); q1.push_front(tx); a[y][tx] = 1; p.pop_back(); } else { for (int i : q2) if (i < x) q2.pop_front(); int tx = q2.front(); q2.pop_front(); a[y][tx] = 0; p.push_back(pos{x, y}); dfs(y, x + 1, 1, c, p, q1, q2); q2.push_front(tx); a[y][tx] = 1; p.pop_back(); } //变道射击 y = inv(y); if (a[y][x]) return; if (y == 1) { for (int i : q1) if (i < x) q1.pop_front(); int tx = q1.front(); q1.pop_front(); a[y][tx] = 0; p.push_back(pos{x, y}); dfs(y, x + 1, 1, c, p, q1, q2); q1.push_front(tx); a[y][tx] = 1; p.pop_back(); } else { for (int i : q2) if (i < x) q2.pop_front(); int tx = q2.front(); q2.pop_front(); a[y][tx] = 0; p.push_back(pos{x, y}); dfs(y, x + 1, 1, c, p, q1, q2); q2.push_front(tx); a[y][tx] = 1; p.pop_back(); } } } //*************************************** int main() { // ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); // freopen("test.txt", "r", stdin); // freopen("outout.txt","w",stdout); cin >> n >> m1 >> m2 >> T; For(i, 1, n) a[1][i] = 0, a[2][i] = 0; int x; For(i, 1, m1) { cin >> x; a[1][x] = 1; q1.push_back(x); } For(i, 1, m2) { cin >> x; a[2][x]=1; q2.push_back(x); } dfs(1, 0, 0, c, p, q1, q2); cout << "No"; return 0; }
https://www.cnblogs.com/Blue233333/p/8520802.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号