struts2的ActionProxy
ctinoProxy的全名是com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionProxy,
ActionProxy = Action + Proxy,从字面意思来解释:Action的代理。
在Struts中,ActionContext、ActionInvocation、ActionProxy、ActionConfig联系的很紧密。
|
1
|
ActionContext<-->ActionInvocation<-->ActionProxy-->ActionConfig |
(1.1)从ActionContext对象可以得到ActionInvocation对象
(1.2)从ActionInvocation对象可以得到ActionContext对象
(2.1)从ActionInvocation对象可以得到ActionProxy对象
(2.2)从ActionProxy对象可以得到ActionInvocation对象
(3.1)从ActionProxy对象可以得到ActionConfig对象
在搜索的时候 ,遇到一句描述ActionInvocation和ActionProxy关系的话,感觉非常切中要害:
Essentially, ActionProxy encapsulates how an Action can be obtained. ActionInvocation encapsulates how the Action is executed when a request is invoked.
本质上来,ActionProxy对如何获取Action对象进行了封装,而ActionInvocation对如何执行Action进行了封装。
原话地址:https://struts.apache.org/docs/action-proxy-actionproxy-factory.html
Typically, an ActionProxy will utilize the ActionInvocation to encapsulate the execution of a particular request.
The ActionInvocation determines how an Action is handled: Is it being intercepted? Is there a PreResultListener acting on it?
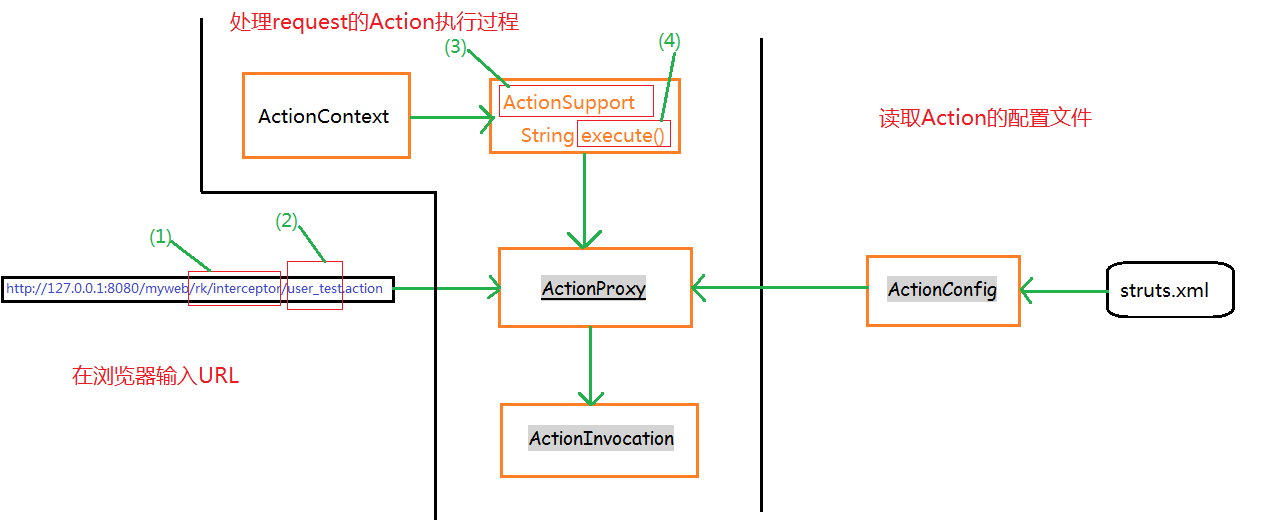
在上面图中,
ActionConfig,负责从struts.xml文件中读取配置;
ActionSupport,我们自己实现的Action类一般都继承ActionSupport类;
ActionContext,是Action运行的环境,为Action类提供一些信息;
ActionProxy,是如何获取Action;
ActionInvocation是如何执行Action。
上面标的(1)至(4),都能通过ActionProxy来获得:
(1)表示当前Action类在struts.xml文件中对应的<action>标签所在的<package>标签的namespace属性
(2)表示<action>标签的name属性
(3)表示真实的Action类的实例,不是字符串类型,而<action>标签的class属性对应的类的实例化。
(4)<action>标签的method属性
从一些java培训机构的视频来看,ActionProxy实现了URL和真正Action类之间的映射。
1、如何获取ActionProxy对象
|
1
|
ActionProxy proxy = invocation.getProxy(); |
2、如何获取ActionProxy中的值
(1)获取当前<action>所在的命名空间
|
1
|
String namespace = proxy.getNamespace(); |
(2)获取<action>的名字
|
1
|
String actionName = proxy.getActionName(); |
(3)获取Action类的实例
|
1
|
Object action = proxy.getAction(); |
(4)获取<action>执行的方法
|
1
|
String method = proxy.getMethod(); |
(5)得到ActionInvocation和ActionConfig对象
|
1
2
3
|
ActionConfig config = proxy.getConfig();ActionInvocation invocation2 = proxy.getInvocation(); |
3、ActionProxy的源代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
|
package com.opensymphony.xwork2;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.config.entities.ActionConfig;/** * ActionProxy is an extra layer between XWork and the action so that different proxies are possible. * <p/> * An example of this would be a remote proxy, where the layer between XWork and the action might be RMI or SOAP. * * @author Jason Carreira */public interface ActionProxy { /** * Gets the Action instance for this Proxy. * * @return the Action instance */ Object getAction(); /** * Gets the alias name this ActionProxy is mapped to. * * @return the alias name */ String getActionName(); /** * Gets the ActionConfig this ActionProxy is built from. * * @return the ActionConfig */ ActionConfig getConfig(); /** * Sets whether this ActionProxy should also execute the Result after executing the Action. * * @param executeResult <tt>true</tt> to also execute the Result. */ void setExecuteResult(boolean executeResult); /** * Gets the status of whether the ActionProxy is set to execute the Result after the Action is executed. * * @return the status */ boolean getExecuteResult(); /** * Gets the ActionInvocation associated with this ActionProxy. * * @return the ActionInvocation */ ActionInvocation getInvocation(); /** * Gets the namespace the ActionConfig for this ActionProxy is mapped to. * * @return the namespace */ String getNamespace(); /** * Execute this ActionProxy. This will set the ActionContext from the ActionInvocation into the ActionContext * ThreadLocal before invoking the ActionInvocation, then set the old ActionContext back into the ThreadLocal. * * @return the result code returned from executing the ActionInvocation * @throws Exception can be thrown. * @see ActionInvocation */ String execute() throws Exception; /** * Gets the method name to execute, or <tt>null</tt> if no method has been specified (meaning <code>execute</code> will be invoked). * * @return the method to execute */ String getMethod(); /** * Gets status of the method value's initialization. * * @return true if the method returned by getMethod() is not a default initializer value. */ boolean isMethodSpecified(); |



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号