logger(一)slf4j简介及其实现原理
一、slf4j简介
slf4j(Simple logging facade for Java)是对所有日志框架制定的一种规范、标准、接口,并不是一个框架的具体的实现,因为接口并不能独立使用,需要和具体的日志框架实现配合使用
slf4j是门面模式的典型应用,外部与一个子系统的通信必须通过一个统一的外观对象进行,使得子系统更易于使用。用一张图来表示门面模式的结构为
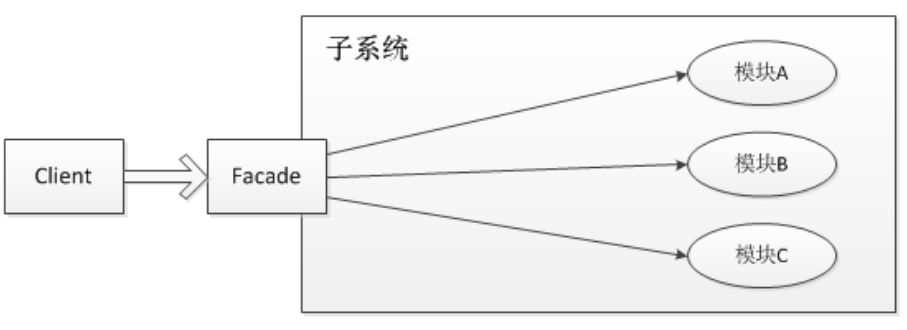
日志实现(log4j、logback、log4j2)
- log4j是apache实现的一个开源日志组件
- logback同样是由log4j的作者设计完成的,拥有更好的特性,用来取代log4j的一个日志框架,是slf4j的原生实现
- log4j2是log4j 1.x和logback的改进版,据说采用了一些新技术(无锁异步、等等),使得日志的吞吐量、性能比log4j 1.x提高10倍,并解决了一些死锁的bug,而且配置更加简单灵活。
为什么要使用slf4j
- SLF4J提供了统一的记录日志的接口,对不同日志系统的具体实现进行了抽象化,只要按照其提供的方法记录即可,最终日志的格式、记录级别、输出方式等通过绑定具体的日志系统来实现。在项目中使用了SLF4J记录日志,并且绑定了log4j,则日志会以log4j的风格输出;后期需要改为以logback的风格输出日志,只需要将jar包log4j替换成logback即可,不用修改项目中的代码。
- SLF4J支持
{}作为占位符,等价于C语言中的%s,而不必再进行字符串的拼接,效率有显著的提升
maven jar包
<dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>1.7.21</version> </dependency>
如下图所示,slf4j不能单独使用,比如要使用logback实现,需要导入logback的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.1.7</version>
</dependency>
比如要使用log4j或者 jdk自带的logging,需要使用桥接包如slf4j-jdk14.jar包
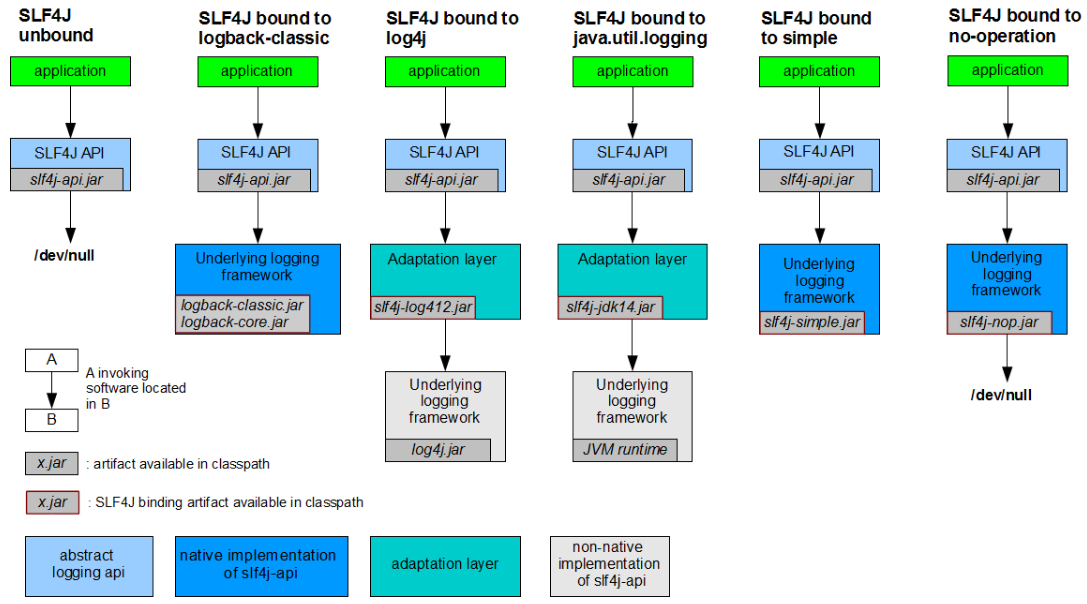
二、实现原理
slf4j只是一个日志标准,并不是日志系统的具体实现。slf4j只提做两件事情:Logger类用来打日志,LoggerFactory类用来获取Logger;
- 提供日志接口 (Logger.class)
- 提供获取具体日志对象的方法 (LoggerFactory.class)
Logger.class

public interface Logger { /** * Case insensitive String constant used to retrieve the name of the root logger. * * @since 1.3 */ final public String ROOT_LOGGER_NAME = "ROOT"; /** * Return the name of this <code>Logger</code> instance. * @return name of this logger instance */ public String getName(); /** * Is the logger instance enabled for the TRACE level? * * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the TRACE level, * false otherwise. * @since 1.4 */ public boolean isTraceEnabled(); /** * Log a message at the TRACE level. * * @param msg the message string to be logged * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(String msg); /** * Log a message at the TRACE level according to the specified format * and argument. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the TRACE level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(String format, Object arg); /** * Log a message at the TRACE level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the TRACE level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * Log a message at the TRACE level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger * is disabled for the TRACE level. However, this variant incurs the hidden * (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method, * even if this logger is disabled for TRACE. The variants taking {@link #trace(String, Object) one} and * {@link #trace(String, Object, Object) two} arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p> * * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(String format, Object... arguments); /** * Log an exception (throwable) at the TRACE level with an * accompanying message. * * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(String msg, Throwable t); /** * Similar to {@link #isTraceEnabled()} method except that the * marker data is also taken into account. * * @param marker The marker data to take into consideration * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the TRACE level, * false otherwise. * * @since 1.4 */ public boolean isTraceEnabled(Marker marker); /** * Log a message with the specific Marker at the TRACE level. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param msg the message string to be logged * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(Marker marker, String msg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #trace(String, Object)} method except that the * marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object arg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #trace(String, Object, Object)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * This method is similar to {@link #trace(String, Object...)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param argArray an array of arguments * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object... argArray); /** * This method is similar to {@link #trace(String, Throwable)} method except that the * marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log * @since 1.4 */ public void trace(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t); /** * Is the logger instance enabled for the DEBUG level? * * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the DEBUG level, * false otherwise. */ public boolean isDebugEnabled(); /** * Log a message at the DEBUG level. * * @param msg the message string to be logged */ public void debug(String msg); /** * Log a message at the DEBUG level according to the specified format * and argument. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the DEBUG level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument */ public void debug(String format, Object arg); /** * Log a message at the DEBUG level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the DEBUG level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument */ public void debug(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * Log a message at the DEBUG level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger * is disabled for the DEBUG level. However, this variant incurs the hidden * (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method, * even if this logger is disabled for DEBUG. The variants taking * {@link #debug(String, Object) one} and {@link #debug(String, Object, Object) two} * arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p> * * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments */ public void debug(String format, Object... arguments); /** * Log an exception (throwable) at the DEBUG level with an * accompanying message. * * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log */ public void debug(String msg, Throwable t); /** * Similar to {@link #isDebugEnabled()} method except that the * marker data is also taken into account. * * @param marker The marker data to take into consideration * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the DEBUG level, * false otherwise. */ public boolean isDebugEnabled(Marker marker); /** * Log a message with the specific Marker at the DEBUG level. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param msg the message string to be logged */ public void debug(Marker marker, String msg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #debug(String, Object)} method except that the * marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument */ public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object arg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #debug(String, Object, Object)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument */ public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * This method is similar to {@link #debug(String, Object...)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments */ public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments); /** * This method is similar to {@link #debug(String, Throwable)} method except that the * marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log */ public void debug(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t); /** * Is the logger instance enabled for the INFO level? * * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the INFO level, * false otherwise. */ public boolean isInfoEnabled(); /** * Log a message at the INFO level. * * @param msg the message string to be logged */ public void info(String msg); /** * Log a message at the INFO level according to the specified format * and argument. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the INFO level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument */ public void info(String format, Object arg); /** * Log a message at the INFO level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the INFO level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument */ public void info(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * Log a message at the INFO level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger * is disabled for the INFO level. However, this variant incurs the hidden * (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method, * even if this logger is disabled for INFO. The variants taking * {@link #info(String, Object) one} and {@link #info(String, Object, Object) two} * arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p> * * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments */ public void info(String format, Object... arguments); /** * Log an exception (throwable) at the INFO level with an * accompanying message. * * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log */ public void info(String msg, Throwable t); /** * Similar to {@link #isInfoEnabled()} method except that the marker * data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker The marker data to take into consideration * @return true if this logger is warn enabled, false otherwise */ public boolean isInfoEnabled(Marker marker); /** * Log a message with the specific Marker at the INFO level. * * @param marker The marker specific to this log statement * @param msg the message string to be logged */ public void info(Marker marker, String msg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #info(String, Object)} method except that the * marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument */ public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object arg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #info(String, Object, Object)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument */ public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * This method is similar to {@link #info(String, Object...)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments */ public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments); /** * This method is similar to {@link #info(String, Throwable)} method * except that the marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data for this log statement * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log */ public void info(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t); /** * Is the logger instance enabled for the WARN level? * * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the WARN level, * false otherwise. */ public boolean isWarnEnabled(); /** * Log a message at the WARN level. * * @param msg the message string to be logged */ public void warn(String msg); /** * Log a message at the WARN level according to the specified format * and argument. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the WARN level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument */ public void warn(String format, Object arg); /** * Log a message at the WARN level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger * is disabled for the WARN level. However, this variant incurs the hidden * (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method, * even if this logger is disabled for WARN. The variants taking * {@link #warn(String, Object) one} and {@link #warn(String, Object, Object) two} * arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p> * * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments */ public void warn(String format, Object... arguments); /** * Log a message at the WARN level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the WARN level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument */ public void warn(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * Log an exception (throwable) at the WARN level with an * accompanying message. * * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log */ public void warn(String msg, Throwable t); /** * Similar to {@link #isWarnEnabled()} method except that the marker * data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker The marker data to take into consideration * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the WARN level, * false otherwise. */ public boolean isWarnEnabled(Marker marker); /** * Log a message with the specific Marker at the WARN level. * * @param marker The marker specific to this log statement * @param msg the message string to be logged */ public void warn(Marker marker, String msg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #warn(String, Object)} method except that the * marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument */ public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object arg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #warn(String, Object, Object)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument */ public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * This method is similar to {@link #warn(String, Object...)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments */ public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments); /** * This method is similar to {@link #warn(String, Throwable)} method * except that the marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data for this log statement * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log */ public void warn(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t); /** * Is the logger instance enabled for the ERROR level? * * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the ERROR level, * false otherwise. */ public boolean isErrorEnabled(); /** * Log a message at the ERROR level. * * @param msg the message string to be logged */ public void error(String msg); /** * Log a message at the ERROR level according to the specified format * and argument. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the ERROR level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument */ public void error(String format, Object arg); /** * Log a message at the ERROR level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger * is disabled for the ERROR level. </p> * * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument */ public void error(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * Log a message at the ERROR level according to the specified format * and arguments. * <p/> * <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger * is disabled for the ERROR level. However, this variant incurs the hidden * (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method, * even if this logger is disabled for ERROR. The variants taking * {@link #error(String, Object) one} and {@link #error(String, Object, Object) two} * arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p> * * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments */ public void error(String format, Object... arguments); /** * Log an exception (throwable) at the ERROR level with an * accompanying message. * * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log */ public void error(String msg, Throwable t); /** * Similar to {@link #isErrorEnabled()} method except that the * marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker The marker data to take into consideration * @return True if this Logger is enabled for the ERROR level, * false otherwise. */ public boolean isErrorEnabled(Marker marker); /** * Log a message with the specific Marker at the ERROR level. * * @param marker The marker specific to this log statement * @param msg the message string to be logged */ public void error(Marker marker, String msg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #error(String, Object)} method except that the * marker data is also taken into consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg the argument */ public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object arg); /** * This method is similar to {@link #error(String, Object, Object)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arg1 the first argument * @param arg2 the second argument */ public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2); /** * This method is similar to {@link #error(String, Object...)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param format the format string * @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments */ public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments); /** * This method is similar to {@link #error(String, Throwable)} * method except that the marker data is also taken into * consideration. * * @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement * @param msg the message accompanying the exception * @param t the exception (throwable) to log */ public void error(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t); }
LoggerFactory.class

public final class LoggerFactory { static final String CODES_PREFIX = "http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html"; static final String NO_STATICLOGGERBINDER_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#StaticLoggerBinder"; static final String MULTIPLE_BINDINGS_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#multiple_bindings"; static final String NULL_LF_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#null_LF"; static final String VERSION_MISMATCH = CODES_PREFIX + "#version_mismatch"; static final String SUBSTITUTE_LOGGER_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#substituteLogger"; static final String LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#loggerNameMismatch"; static final String REPLAY_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#replay"; static final String UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#unsuccessfulInit"; static final String UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG = "org.slf4j.LoggerFactory in failed state. Original exception was thrown EARLIER. See also " + UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_URL; static final int UNINITIALIZED = 0; static final int ONGOING_INITIALIZATION = 1; static final int FAILED_INITIALIZATION = 2; static final int SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION = 3; static final int NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION = 4; static volatile int INITIALIZATION_STATE = UNINITIALIZED; static final SubstituteLoggerFactory SUBST_FACTORY = new SubstituteLoggerFactory(); static final NOPLoggerFactory NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY = new NOPLoggerFactory(); // Support for detecting mismatched logger names. static final String DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_PROPERTY = "slf4j.detectLoggerNameMismatch"; static final String JAVA_VENDOR_PROPERTY = "java.vendor.url"; static boolean DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH = Util.safeGetBooleanSystemProperty(DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_PROPERTY); /** * It is LoggerFactory's responsibility to track version changes and manage * the compatibility list. * <p/> * <p/> * It is assumed that all versions in the 1.6 are mutually compatible. */ static private final String[] API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST = new String[] { "1.6", "1.7" }; // private constructor prevents instantiation private LoggerFactory() { } /** * Force LoggerFactory to consider itself uninitialized. * <p/> * <p/> * This method is intended to be called by classes (in the same package) for * testing purposes. This method is internal. It can be modified, renamed or * removed at any time without notice. * <p/> * <p/> * You are strongly discouraged from calling this method in production code. */ static void reset() { INITIALIZATION_STATE = UNINITIALIZED; } private final static void performInitialization() { bind(); if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION) { versionSanityCheck(); } } private static boolean messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(String msg) { if (msg == null) return false; if (msg.contains("org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder")) return true; if (msg.contains("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder")) return true; return false; } private final static void bind() { try { Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = null; // skip check under android, see also // http://jira.qos.ch/browse/SLF4J-328 if (!isAndroid()) { staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(); reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(staticLoggerBinderPathSet); } // the next line does the binding StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton(); INITIALIZATION_STATE = SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION; reportActualBinding(staticLoggerBinderPathSet); fixSubstituteLoggers(); replayEvents(); // release all resources in SUBST_FACTORY SUBST_FACTORY.clear(); } catch (NoClassDefFoundError ncde) { String msg = ncde.getMessage(); if (messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(msg)) { INITIALIZATION_STATE = NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION; Util.report("Failed to load class \"org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder\"."); Util.report("Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation"); Util.report("See " + NO_STATICLOGGERBINDER_URL + " for further details."); } else { failedBinding(ncde); throw ncde; } } catch (java.lang.NoSuchMethodError nsme) { String msg = nsme.getMessage(); if (msg != null && msg.contains("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton()")) { INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION; Util.report("slf4j-api 1.6.x (or later) is incompatible with this binding."); Util.report("Your binding is version 1.5.5 or earlier."); Util.report("Upgrade your binding to version 1.6.x."); } throw nsme; } catch (Exception e) { failedBinding(e); throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected initialization failure", e); } } private static void fixSubstituteLoggers() { synchronized (SUBST_FACTORY) { SUBST_FACTORY.postInitialization(); for (SubstituteLogger substLogger : SUBST_FACTORY.getLoggers()) { Logger logger = getLogger(substLogger.getName()); substLogger.setDelegate(logger); } } } static void failedBinding(Throwable t) { INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION; Util.report("Failed to instantiate SLF4J LoggerFactory", t); } private static void replayEvents() { final LinkedBlockingQueue<SubstituteLoggingEvent> queue = SUBST_FACTORY.getEventQueue(); final int queueSize = queue.size(); int count = 0; final int maxDrain = 128; List<SubstituteLoggingEvent> eventList = new ArrayList<SubstituteLoggingEvent>(maxDrain); while (true) { int numDrained = queue.drainTo(eventList, maxDrain); if (numDrained == 0) break; for (SubstituteLoggingEvent event : eventList) { replaySingleEvent(event); if (count++ == 0) emitReplayOrSubstituionWarning(event, queueSize); } eventList.clear(); } } private static void emitReplayOrSubstituionWarning(SubstituteLoggingEvent event, int queueSize) { if (event.getLogger().isDelegateEventAware()) { emitReplayWarning(queueSize); } else if (event.getLogger().isDelegateNOP()) { // nothing to do } else { emitSubstitutionWarning(); } } private static void replaySingleEvent(SubstituteLoggingEvent event) { if (event == null) return; SubstituteLogger substLogger = event.getLogger(); String loggerName = substLogger.getName(); if (substLogger.isDelegateNull()) { throw new IllegalStateException("Delegate logger cannot be null at this state."); } if (substLogger.isDelegateNOP()) { // nothing to do } else if (substLogger.isDelegateEventAware()) { substLogger.log(event); } else { Util.report(loggerName); } } private static void emitSubstitutionWarning() { Util.report("The following set of substitute loggers may have been accessed"); Util.report("during the initialization phase. Logging calls during this"); Util.report("phase were not honored. However, subsequent logging calls to these"); Util.report("loggers will work as normally expected."); Util.report("See also " + SUBSTITUTE_LOGGER_URL); } private static void emitReplayWarning(int eventCount) { Util.report("A number (" + eventCount + ") of logging calls during the initialization phase have been intercepted and are"); Util.report("now being replayed. These are subject to the filtering rules of the underlying logging system."); Util.report("See also " + REPLAY_URL); } private final static void versionSanityCheck() { try { String requested = StaticLoggerBinder.REQUESTED_API_VERSION; boolean match = false; for (String aAPI_COMPATIBILITY_LIST : API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST) { if (requested.startsWith(aAPI_COMPATIBILITY_LIST)) { match = true; } } if (!match) { Util.report("The requested version " + requested + " by your slf4j binding is not compatible with " + Arrays.asList(API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST).toString()); Util.report("See " + VERSION_MISMATCH + " for further details."); } } catch (java.lang.NoSuchFieldError nsfe) { // given our large user base and SLF4J's commitment to backward // compatibility, we cannot cry here. Only for implementations // which willingly declare a REQUESTED_API_VERSION field do we // emit compatibility warnings. } catch (Throwable e) { // we should never reach here Util.report("Unexpected problem occured during version sanity check", e); } } // We need to use the name of the StaticLoggerBinder class, but we can't // reference // the class itself. private static String STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH = "org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class"; static Set<URL> findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet() { // use Set instead of list in order to deal with bug #138 // LinkedHashSet appropriate here because it preserves insertion order // during iteration Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = new LinkedHashSet<URL>(); try { ClassLoader loggerFactoryClassLoader = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader(); Enumeration<URL> paths; if (loggerFactoryClassLoader == null) { paths = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH); } else { paths = loggerFactoryClassLoader.getResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH); } while (paths.hasMoreElements()) { URL path = paths.nextElement(); staticLoggerBinderPathSet.add(path); } } catch (IOException ioe) { Util.report("Error getting resources from path", ioe); } return staticLoggerBinderPathSet; } private static boolean isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(Set<URL> binderPathSet) { return binderPathSet.size() > 1; } /** * Prints a warning message on the console if multiple bindings were found * on the class path. No reporting is done otherwise. * */ private static void reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(Set<URL> binderPathSet) { if (isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(binderPathSet)) { Util.report("Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings."); for (URL path : binderPathSet) { Util.report("Found binding in [" + path + "]"); } Util.report("See " + MULTIPLE_BINDINGS_URL + " for an explanation."); } } private static boolean isAndroid() { String vendor = Util.safeGetSystemProperty(JAVA_VENDOR_PROPERTY); if (vendor == null) return false; return vendor.toLowerCase().contains("android"); } private static void reportActualBinding(Set<URL> binderPathSet) { // binderPathSet can be null under Android if (binderPathSet != null && isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(binderPathSet)) { Util.report("Actual binding is of type [" + StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactoryClassStr() + "]"); } } /** * Return a logger named according to the name parameter using the * statically bound {@link ILoggerFactory} instance. * * @param name * The name of the logger. * @return logger */ public static Logger getLogger(String name) { ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory(); return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name); } /** * Return a logger named corresponding to the class passed as parameter, * using the statically bound {@link ILoggerFactory} instance. * * <p> * In case the the <code>clazz</code> parameter differs from the name of the * caller as computed internally by SLF4J, a logger name mismatch warning * will be printed but only if the * <code>slf4j.detectLoggerNameMismatch</code> system property is set to * true. By default, this property is not set and no warnings will be * printed even in case of a logger name mismatch. * * @param clazz * the returned logger will be named after clazz * @return logger * * * @see <a * href="http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#loggerNameMismatch">Detected * logger name mismatch</a> */ public static Logger getLogger(Class<?> clazz) { Logger logger = getLogger(clazz.getName()); if (DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH) { Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass = Util.getCallingClass(); if (autoComputedCallingClass != null && nonMatchingClasses(clazz, autoComputedCallingClass)) { Util.report(String.format("Detected logger name mismatch. Given name: \"%s\"; computed name: \"%s\".", logger.getName(), autoComputedCallingClass.getName())); Util.report("See " + LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_URL + " for an explanation"); } } return logger; } private static boolean nonMatchingClasses(Class<?> clazz, Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass) { return !autoComputedCallingClass.isAssignableFrom(clazz); } /** * Return the {@link ILoggerFactory} instance in use. * <p/> * <p/> * ILoggerFactory instance is bound with this class at compile time. * * @return the ILoggerFactory instance in use */ public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() { if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) { synchronized (LoggerFactory.class) { if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) { INITIALIZATION_STATE = ONGOING_INITIALIZATION; performInitialization(); } } } switch (INITIALIZATION_STATE) { case SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION: return StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory(); case NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION: return NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY; case FAILED_INITIALIZATION: throw new IllegalStateException(UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG); case ONGOING_INITIALIZATION: // support re-entrant behavior. // See also http://jira.qos.ch/browse/SLF4J-97 return SUBST_FACTORY; } throw new IllegalStateException("Unreachable code"); } }
这里看下获取getLogger函数的源码,我们发现LoggerFactory.getLogger()首先获取一个ILoggerFactory接口,然后使用该接口获取具体的Logger。获取ILoggerFactory的时候用到了一个StaticLoggerBinder类,仔细研究我们会发现StaticLoggerBinder这个类并不是slf4j-api这个包中的类,而是实现日志框架里的类,所有的实现框架都需要定义该类,提供具体的Logger实现。
接下来具体分析日志实现框架 logback和log4j2。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号