题意:给定n条在二维平面上的线段,写一个程序,判断是否存在一个直线,使得所有的线段投影到这根直线上,至少存在一个公共点。
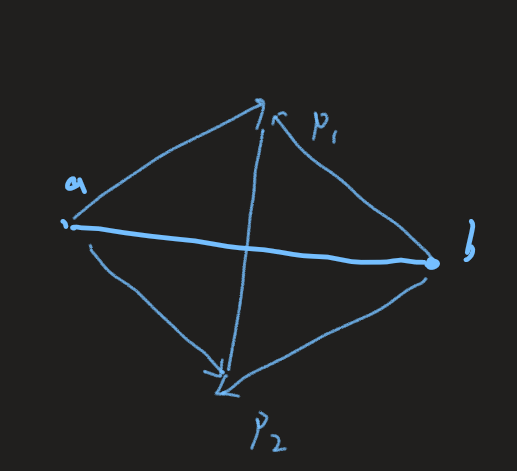
分析:从侧面考虑,如果存在一根直线,使得所有线段到这根直线上的投影至少有一个公共点,那么对所有投影的交集区域做一根垂线,可以穿过所有的线段。从而转换为找到一根直线,使得这根直线可以穿过所有线段的问题。对这根直线摆动,只要不超过任何一条线段的端点即可,然后摆动到不能摆动为止,会发现处于这条直线的端点两侧可以固定下来,所以我们可以枚举线段的任意两个端点作为一根直线,然后判断是否每一根线段的两个端点都在这根直线的两侧,这个可以用叉积判断。
只要线段的两个端点到直线的两侧端点的向量叉乘相乘 <= 0即可,\((\vec{ap1}\times\vec{ap2} * \vec{bp1}\times\vec{bp2})\),叉乘的两个向量具有符号,< 0表示在一根直线的左侧,> 0表示在一根直线的右侧,只要两个相乘 < 0即可。==0的情况表示这根线段在这根直线上,还有就是枚举的直线需要判断是否为一个点,这是一个特殊情况。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
//两个点之间的距离<1e-8就表示相等
const double eps = 1e-8;
int dcmp(double x)
{
if (fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
else return x < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
struct Point
{
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
};
typedef Point Vector;
//向量 + 向量 = 向量, 点 + 向量 = 点
Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B) { return Vector(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); }
//点 - 点 = 向量
Vector operator - (Point A, Point B) { return Vector(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y); }
//向量 * 标量 = 向量
Vector operator * (Vector A, double p) { return Vector(A.x * p, A.y * p); }
//向量 / 数 = 向量
Vector operator / (Vector A, double p) { return Vector(A.x / p, A.y / p); }
bool operator<(const Point& a, const Point& b)
{
return dcmp(a.x - b.x) < 0 || dcmp(a.x - b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y - b.y) < 0;
}
bool operator == (const Point& a, const Point& b)
{
return dcmp(a.x - b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y - b.y) == 0;
}
double Dot(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y; }
double Cross(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x; }
double Length(Vector A) { return sqrt(Dot(A, A)); }
//求A的单位法线,垂直于A
Vector Normal(Vector A)
{
double L = Length(A);
return Vector(-A.y / L, A.x / L);
}
struct Line{
Point p;
Vector v;
Line(Point p, Vector v) :p(p), v(v) { }
//直线上的点坐标
Point point(double t) {
return p + v * t;
}
//平移直线d距离
Line move(double d) {
return Line(p + Normal(v) * d, v);
}
};
const int N = 105;
Point a[N], b[N];
Point c[2 * N];
bool check(Point q1, Point q2, Point a, Point b)
{
Vector bq1(q1 - b);
Vector bq2(q2 - b);
Vector aq1(q1 - a);
Vector aq2(q2 - a);
if (dcmp(Cross(bq1, bq2) * Cross(aq1, aq2)) <= 0) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &a[i].x, &a[i].y, &b[i].x, &b[i].y);
c[i].x = a[i].x, c[i].y = a[i].y, c[i + n].x = b[i].x, c[i + n].y = b[i].y;
}
bool f = false;
//枚举任意两个端点
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; ++i)
for (int j = i + 1; j <= 2 * n; ++j)
{
Point q1(c[i].x, c[i].y);
Point q2(c[j].x, c[j].y);
if (q1 == q2) continue;
bool flag = true;
for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k)
{
if (!check(q1, q2, a[k], b[k]))
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag)
{
f = true;
break;
}
}
if (f) puts("Yes!");
else puts("No!");
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号