SpringBoot集成JPA及基本使用
参考地址: https://blog.csdn.net/JingAi_jia917/article/details/138159418
前言
在讲解SpringBoot集成JPA之前,先简单了解一下几个概念,JDBC、ORM、JPA以及Spring Data JPA。
1.1 JDBC
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity),是java连接数据库操作的原生接口API,为开发者访问数据库提供标准的接口。各数据库厂商依照JDBC规范,实现规范中的接口,实现数据库的连接。Java开发者使用同样的访问代码,配置不同的Driver、url以及账号,即可实现不同数据库厂家的数据库连接。
当数据库连接之后,通过拼接SQL语句,发送到数据库,达到对数据库中数据的操作。
缺点: 1)业务代码耦合SQL字符串拼接语句,维护比较麻烦; 2)不符合Java面向对象的编程思想;
1.2 ORM
对象-关系映射(Object-Relational Mapping,简称ORM),是一种描述对象与关系数据库之间映射的规范,采用面向对象编程的思想,操作数据库。
在Java中,ORM就是将Java类与DB中的Table表进行映射,代码中对相关Java类的操作,关联到数据库后,即体现为DB中关联的Table表的操作。
1.3 JPA
JPA是Java Persistence API的简称,中文名Java持久层API,是JDK5.x版本引入的。JPA的宗旨是为POJO提供持久化标准规范。
JPA采用ORM对象关系映射,以Java面向对象的编程思想,在javax.persistence包下提供对实体对象的CRUD操作,将开发者从繁琐的JDBC和SQL代码中解脱出来。
1.4 Spring Data JPA
Spring Data JPA是Spring提供的一套简化JPA开发的框架,按照约定好的方法名命规则写DAO层接口,可以在不写接口实现的情况下,实现对数据库中Table的操作,同时提供了除CRUD操作之外的许多功能,如分页、复杂查询等。
SpringBoot集成Spring Data JPA
2.1 引入依赖
在SpringBoot项目的pom.xml中引入相关依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 参数校验 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- JPA是针对数据库的操作,需要引入对应的数据库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.22</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
2.2 参数配置
在application.yml中配置数据库连接信息。
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false&allowMultiQueries=true username: root password: 123456 druid: stat-view-servlet: login-username: druid login-password: 123456 url-pattern: /druid/* enabled: true filters: stat,wall web-stat-filter: url-pattern: / enabled: true exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*' filter: wall: config: #支持单个事物多条sql语句执行 multi-statement-allow: true none-base-statement-allow: true enabled: true jpa: hibernate: naming: #Java代码实体字段命名与数据库表结构字段之间的名称映射策略 #当没有使用@Table和@Column注解时,implicit-strategy配置项才会被使用,当对象模型中已经指定时, #implicit-strategy并不会起作用。 #implicit-strategy: org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.ImplicitNamingStrategyLegacyJpaImpl #physical-strategy一定会被应用,与对象模型中是否显式地指定列名或者已经被隐式决定无关, #SpringPhysicalNamingStrategy:表名,字段为小写,当有大写字母的时候会添加下划线分隔符号,默认值。 #PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl:直接映射,不会做过多的处理,会禁止将驼峰转为下划线 #physical-strategy: org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl # 用于指定 Session 是否在视图渲染完成后自动关闭,默认为false,意味着在视图渲染完成后,session会自动关闭 open-in-view: false # 控制是否打印运行时的SQL语句与参数信息 show-sql: true
说明:
spring.jpa.open-in-view通常设置为false,即当视图渲染完成后,Session自动关闭。Spring使用AOP(面向切面编程思想)管理事务,在方法调用前和调用后插入事务处理逻辑。如果open-in-view设置为true时,由于Session保持打开状态,可能导致事务的隔离性问题。另外,在多线程环境中,如果多个线程共享同一个Session,并且该Session的open-in-view设置为true,也可能导致事务的隔离性问题。
2.3 添加数据库表实体类Entity
package com.jingai.jpa.dao.entity; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import javax.persistence.*; import java.util.Date; @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Data @Entity @JsonIgnoreProperties(value = { "hibernateLazyInitializer"}) @Table(name = "tb_product") public class ProductEntity { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long pid; private String name; private String deliveryNo; private String customer; private String securityCode; private Date createTime; private Date validateTime; private int validateNum; }
说明:如果数据库访问时报com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.InvalidDefinitionException异常,是因为在转化成json的时候,fasterxml.jackson将对象转换为json报错,发现有字段值为null。底层的hibernate会给被管理的Entity加入一个hibernateLazyInitializer属性,jsonplugin会把hibernateLazyInitializer也拿出来操作,并读取里面一个不能被反射操作的属性就产生了这个异常。
@GeneratedValue注解用于提供主键的生成策略规范。GenerationType有四种标准用法,分别为为:
1)TABLE:使用一个特定的数据库表格来保存主键。该策略通常和@TableGenerator注解一起使用,@TableGenerator注解指定生成主键的表(可以在实体类上指定,也可以在主键字段或属性上指定),JPA将会根据主键内容自动生成一张表作为系列表(或使用现有的系列表)。
2)SEQUENCE:使用底层数据库的序列来生成主键,前提是数据库支持序列。MySql数据库不支持序列。该策略通常与@SequenceGenerator主键一起使用,@SequenceGenerator注解指定了生成主键的系列。
3)IDENTITY:主键由数据库自动生成(主要是自动增长型)。比如MySql可以在创建表时声明auto_increment来指定主键自增长,在实体类中使用该策略。
4)AUTO:主键由程序控制,把主键生成策略较给持久化引擎,持久化引起会根据数据库在以上三种主键生成策略中选择其中一种。
2.4 添加Repository
继承JpaRepository接口,自动提供了基本的CRUD、分页、批量保存接口。
package com.jingai.jpa.dao; import com.jingai.jpa.dao.entity.ProductEntity; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query; import java.util.List; public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<ProductEntity, Long> { List<ProductEntity> findByPidBetween(long startPid, long endPid); @Query("from ProductEntity where name like ?1") List<ProductEntity> searchByName(String name); }
在Repository接口中,除了JpaRepository自动提供的接口以外,可以自定义接口。
1)通过Spring Data JPA的命名规范,直接定义接口,无需写Sql语句;
2)使用自定义的SQL语句;
2.5 添加Service
package com.jingai.jpa.service; import com.jingai.jpa.dao.entity.ProductEntity; import java.util.List; public interface ProductService { ProductEntity save(ProductEntity entity); ProductEntity getById(long id); List<ProductEntity> findByPidBetween(long start, long end); List<ProductEntity> searchByName(String name); int batchSave(List<ProductEntity> list) }
2.6 添加Service实现类
在Service实现类中,引入Repository对象,对数据库表进行操作。在此处,不仅可以使用ProductRepository中定义的searchByName和findByIdBetween(),而且还可以访问save、getById以及saveAll,这些是在JpaRespository中提供的实现。
package com.jingai.jpa.service.impl; import com.jingai.jpa.dao.ProductRepository; import com.jingai.jpa.dao.entity.ProductEntity; import com.jingai.jpa.service.ProductService; import org.apache.logging.log4j.util.Strings; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport; import javax.annotation.Resource; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.Query; import java.util.List; @Service public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService { @Resource private ProductRepository productRepository; @Override public ProductEntity save(ProductEntity entity) { return productRepository.save(entity); } @Override public ProductEntity getById(long id) { return productRepository.getById(id); } @Override public List<ProductEntity> findByPidBetween(long startPid, long endPid) { return productRepository.findByPidBetween(startPid, endPid); } @Override public List<ProductEntity> searchByName(String name) { return productRepository.searchByName("%" + name + "%"); } @Override public int batchSave(List<ProductEntity> list) { return productRepository.saveAll(list).size(); } }
2.7 添加Controller
package com.jingai.jpa.controller; import com.jingai.jpa.dao.entity.ProductEntity; import com.jingai.jpa.service.ProductService; import com.jingai.jpa.util.ResponseUtil; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import javax.annotation.Resource; import javax.persistence.EntityNotFoundException; import javax.validation.constraints.Min; import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; import java.util.Map; @Slf4j @Validated @RestController @RequestMapping("product") public class ProductController { @Resource private ProductService productService; @GetMapping("get") public Map<String, Object> get(@NotNull(message = "id不能为空") @Min(value = 1, message = "id无效") Long id) { ProductEntity entity = productService.getById(id); try { if (entity == null || !StringUtils.hasText(entity.getSecurityCode())) { log.info(String.format("id为%d的记录不存在", id)); } } catch(EntityNotFoundException e) { return ResponseUtil.fail(String.format("id为%d的记录不存在", id)); } return ResponseUtil.success(entity); } }
在Controller类中引入Service,访问Service的提供的接口,实现对数据库的操作。其他接口的访问也是使用类似的方法,此处就不在贴代码了。
说明:@Validated、@NotNull、@Min为参数校验,详见:Spring validation参数校验基本使用_spring validate 参数-CSDN博客
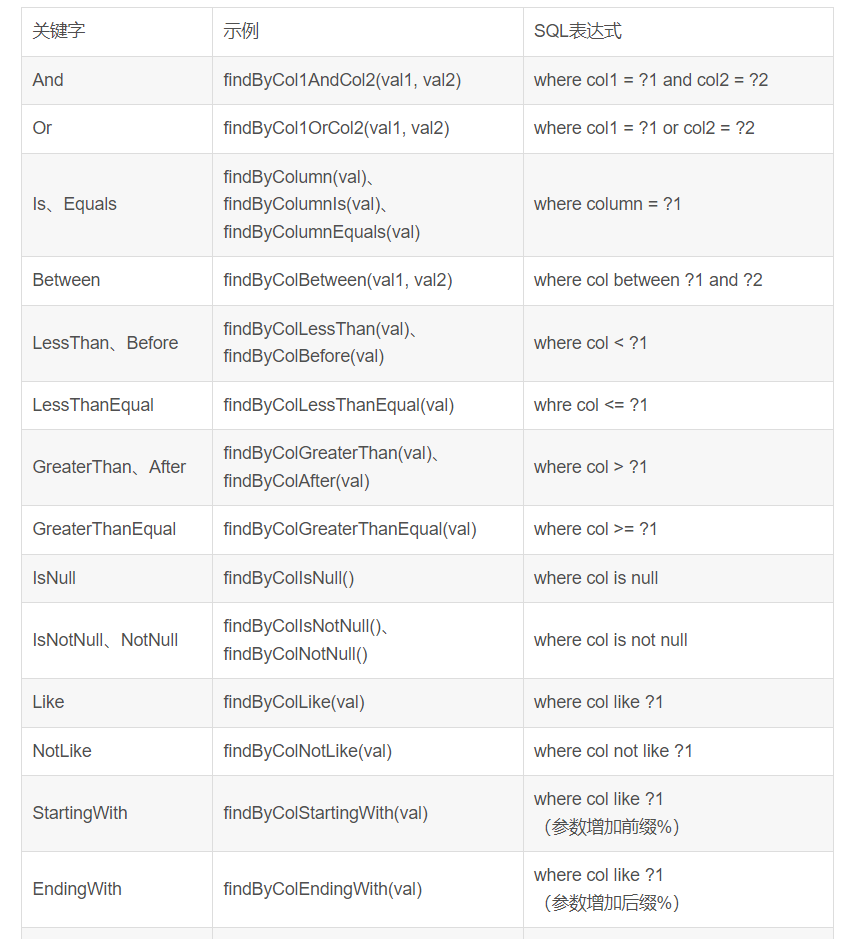
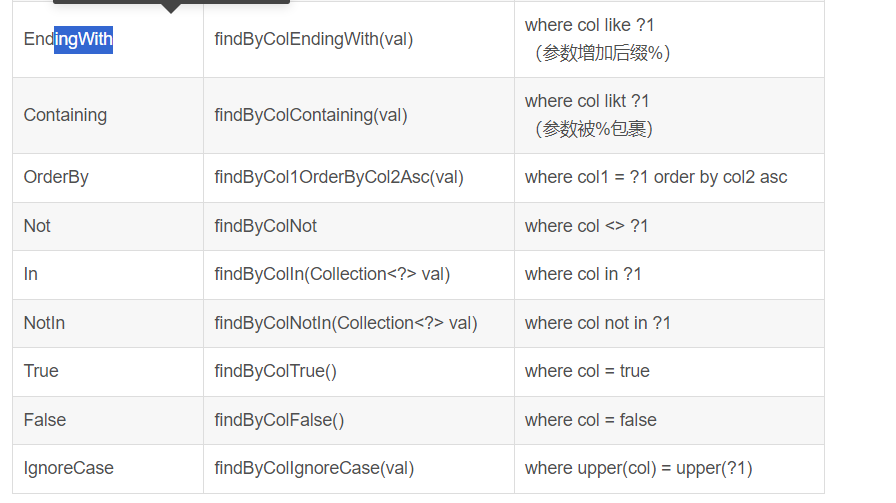
Repository方法命名规则
规则:findBy(关键字)+ 属性名称(属性名称的首字母大写)+ 查询条件(首字母大写)
方法名词命名规范表






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix