【Spring 从0开始】IOC容器的Bean管理 - 基于XML,注入集合类型属性
一、定义数组、list、map、set类型属性
创建类、定义数组、list、map、set类型属性,生成对应set方法。
package com.pingguo.spring5.collectiontype;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Student {
// 1. 数组类型的属性
private String[] courses;
// 2. list集合类型属性
private List<String> list;
// 3. map集合类型属性
private Map<String, String> maps;
// 4. set集合类型属性
private Set<String> sets;
public void setCourses(String[] courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {
this.sets = sets;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(courses));
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(maps);
System.out.println(sets);
}
}
二、配置文件中进行对应配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--集合类型属性的注入-->
<bean id="student" class="com.pingguo.spring5.collectiontype.Student">
<!--数组类型的注入-->
<property name="courses">
<array>
<value>java开发课程</value>
<value>数据库课程</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--list类型的注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>大周</value>
<value>小毛</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--map类型的注入-->
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="班长" value="胖洪"></entry>
<entry key="采购" value="大周"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--set类型的注入-->
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>帅胡</value>
<value>小姜</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
写一个测试类,方便测试。
package com.pingguo.spring5.testdemo;
import com.pingguo.spring5.collectiontype.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestSpring5Demo2 {
@Test
public void testCollection() {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
Student student = context.getBean("student", Student.class);
student.test();
}
}
运行测试结果
[java开发课程, 数据库课程]
[大周, 小毛]
{班长=胖洪, 采购=大周}
[帅胡, 小姜]
Process finished with exit code 0
三、注入对象集合类型
在上面集合里的内容都是用的 String,如果现在里面是对象,要如何注入?
ok,现在新增一个类 Course:
package com.pingguo.spring5.collectiontype;
public class Course {
private String course_name;
public void setCourse_name(String course_name) {
this.course_name = course_name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Course{" +
"course_name='" + course_name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
接下来,在 Student 类里,加上这个 Course 对象属性,并且生成对应的 set 方法:
... ...
public class Student {
... ...
// 5. 学生所学多门课程
private List<Course> courseList;
public void setCourseList(List<Course> courseList) {
this.courseList = courseList;
}
... ...
public void test() {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(courses));
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(maps);
System.out.println(sets);
System.out.println(courseList);
}
}
操作配置文件。
在配置文件中可以新增多个 course 对象。
<!--创建多个 Course 对象-->
<bean id="course1" class="com.pingguo.spring5.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="course_name" value="胡氏面点课"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="course2" class="com.pingguo.spring5.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="course_name" value="毛氏面点课"></property>
</bean>
然后在 注入的时候使用 ref 标签。
<!--注入list类型,值是对象-->
<property name="courseList">
<list>
<ref bean="course1"></ref>
<ref bean="course2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
OK,现在运行测试类,看下结果:
[java开发课程, 数据库课程]
[大周, 小毛]
{班长=胖洪, 采购=大周}
[帅胡, 小姜]
[Course{course_name='胡氏面点课'}, Course{course_name='毛氏面点课'}]
注入成功。
四、提取注入集合的部分
上面集合注入的地方,当有多个值的时候感觉还是比较麻烦的,如果可以把这部分提取出来就更好了。
<property name="courseList">
<list>
<ref bean="course1"></ref>
<ref bean="course2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
现在新建一个类 Book 来演示:
package com.pingguo.spring5.collectiontype;
import java.util.List;
public class Book {
private List<String> list;
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
1. 引入名称空间 util
为了方便,新建一个 bean2.xml,在里面先引入名称空间 util。
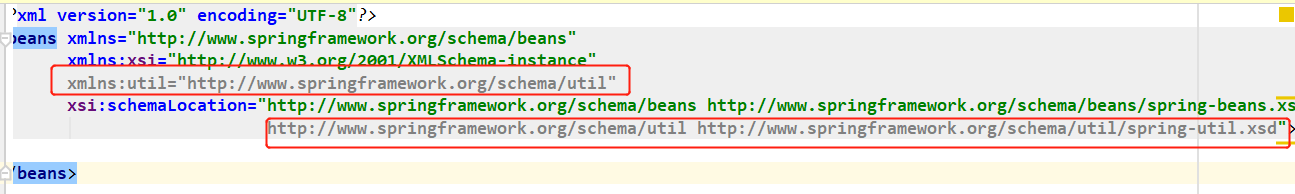
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
</beans>
增加的地方:
2. 使用 util 标签完成集合注入的提取
以提取 list 集合为例。
<!--提取 list 集合类型属性注入-->
<util:list id="bookList">
<value>mysql是怎样运行的</value>
<value>大数据测试</value>
<value>谷歌的软件测试之道</value>
</util:list>
然后,使用提取出来的集合,使用 ref 属性。
<bean id="book" class="com.pingguo.spring5.collectiontype.Book">
<property name="list" ref="bookList"></property>
</bean>
测试一下,新建一个测试方法 testCollection2() 。
@Test
public void testCollection2() {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
Book book = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
book.test();
}
运行测试方法:
[mysql是怎样运行的, 大数据测试, 谷歌的软件测试之道]
Process finished with exit code 0
注入成功。
--不要用肉体的勤奋,去掩盖思考的懒惰--



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号