学习狂神说CSS
2024-06-15
1.CSS快速入门示例及CSS导入及行内样式、本文件内style定义、外部css定义样式的优先级(就近原则)
CSS文件:
h1{ color: red; }
HTML文件:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 标签选择器 样式定义格式: 声明1; 声明2;*/ h1{ color: blue; } </style> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css"/> <!-- 行内样式、当前页面内定义style样式、外部引入style里定义样式 这3种优先级:就近原则 指 样式代码和这<h1>代码在物理上的远近 行内样式 肯定最近 本例子中,外部样式link标签在当前页面的<style>标签下面, 更靠近<h1>所以本例中外部样式的优先级高于内部<style>样式 --> </head> <body> <!--<h1 style="color: green;">我是标题</h1>--> <h1>我是标题</h1> </body> </html>
2.三种基本选择器及优先级
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> p{ color: red; } .practice-class{ color: blue; } #practice-id{ color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <p>段落1</p> <p class="practice-class">段落2</p> <!--<p id="practice-id">段落3</p>--> <!-- 3种基本选择器优先级: id选择器>类选择器>标签选择器 --> <p id="practice-id" class="practice-class">段落3</p> </body> </html>
2024-06-16
1.层次选择器
hierarchical /ˌhaɪəˈrɑː.kɪ.kəl/ 按等级划分的
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 不用id选择器、类选择器,来进行选择 */ /* 层次选择器 */ /* 1.后代选择器:选择所有后代: 太爷 爷爷 爸爸 孙子 对太爷来说,爷爷 爸爸 孙子 全是其后代 */ /*body p{ background: green; }*/ /*ul p{ background: blue; }*/ /* 2.子选择器:选直接后代 太爷 爷爷 爸爸 孙子 对太爷来说,爷爷是其直接后代 */ /*body>p{ background: red; }*/ /* 3.相邻兄弟选择器 我备注:也可以理解为相邻弟弟选择器, 选择直接相邻的那个弟弟 */ /*.practice-class + p{ background: orange; }*/ /* 4.通用选择器 我备注:也可以理解为全部弟弟选择器 */ .practice-class ~ p{ background: brown; } </style> </head> <body> <p>p0</p> <p>p1</p> <p class="practice-class">p2</p> <p>p3</p> <ul> <li> <p>p4</p> </li> <li> <p>p5</p> </li> <li> <p>p6</p> </li> </ul> <p>p7</p> </body> </html>
2024-06-17
1.结构伪类选择器
伪类:条件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 结构伪类选择器 伪类:条件 结构伪类选择器, 即在结构的基础上, 伪类 即条件 去选择 */ /* 在不用id、class选择器的基础上进行练习 */ /* 选择ul第一个子元素 */ ul li:first-child{ background: brown; } /* 选择ul最后一个子元素 */ ul li:last-child{ background: green; } /* 选中p1: 定位到父元素, 选择当前的第一个(子)元素。 注意:这个有个隐含条件是 要选的元素必须是p标签, 否则选不上, 即假设p的父级下的第一个元素为div, 则该div不会被选中 */ p:nth-child(1){ background: burlywood; } /* 选中p2: 定位到父元素, 选择当前的第二个类型为p的(子)元素, 即必须是其父元素的所有类型为p标签的元素 构成的列表中的第二个元素, 若没有这元素(例如父元素总共也没有两个p标签子元素), 则不会选中*/ p:nth-of-type(2){ background: blue; } /* 超链接鼠标移上去变色 */ a:hover{ background: darkorange; } </style> </head> <body> <a href="#">验证鼠标效果</a> <p>p1</p> <p>p2</p> <p>p3</p> <ul> <li>l1</li> <li>l2</li> <li>l3</li> </ul> </body> </html>
2024-06-18
1.属性选择器(重要)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* .test a 后代选择器 */ .test a{ background: dodgerblue; border-radius: 170px; /* 我一开始不会将其变成球 要设置浮动,否则是不会变成球的 float: left,向左浮动*/ float: left; width: 170px; height: 170px; /* 文字居中 */ text-align: center; color: red; /* 去掉下划线 */ text-decoration: none; /*font-style: italic; 斜体*/ /*font-variant: 这个不会,不用它*/ /*font-weight: bold;*/ /*font-stretch: 不会,不用它*/ font-size: large; /*line-height: 50px; 行高*/ /*font-family: Arial;字体*/ /* 我一开始写font: solid 10px 楷体;是错误的 font的顺序是: 下列字号font-size和font-family这俩是必须的 其余均可选 字号和行高用/分隔 1.font-style: italic; 斜体 2.font-weight: bold; 加粗 3.font-size: 50px; 字号 / line-height: 170px; 行高 4.font-family: Arial; 字体*/ font: italic bold 50px/170px Arial; /* 外边距提供间距 */ margin-left: 17px; } /*属性选择器:重要*/ /* 属性类似于id+class*/ /* 根据dom元素的属性,选择dom元素*/ /*1.选择含有id属性的*/ a[id]{ background: yellow; } /*2.选择class属性值为first的 = */ /* (完全等于)*/ /*下面这个选不到, 因为没有class完全等于first的*/ /*a[class='first']{ background: green; }*/ /* 这个能选到 */ /*a[class='links item first']{ background: green; }*/ /*3.选择class属性值包含first的 *= */ a[class*='first']{ background: darkorange; } /*4.选择href属性以http开头的 ^= */ a[href^='http']{ background: brown; } /*5.选择href属性以.pdf结尾的 $= */ a[href$='.pdf']{ background: darkorchid; } </style> </head> <body> <p class="test"> <a class="links item first">1</a> <a href="#" class="links item" id="second">2</a> <a href="http://www.cnblog.com" class="links item">3</a> <a href="https://www.baidu.com" class="links item">4</a> <a href="test.doc" class="links item">5</a> <a href="test.pdf" class="links item">6</a> <a href="test.jpg" class="links item">7</a> <a href="practice.pdf" class="links item">8</a> <a href="study.txt" class="links item">9</a> <a href="http://test.org" class="links item">10</a> </p> </body> </html>
2024-06-27
1.span标签及文字样式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .span-big{ /* font-weight粗细。bold加粗 */ font-weight: bold; /* font-family字体 */ /* 逗号分隔的, Centaur是英文字体则用于英文, 楷体则应用于中文 */ font-family: Centaur,'楷体'; /* font-size大小 */ font-size: 50px; /* color颜色 */ /*color: red;*/ /* rgb 红绿蓝 */ /*color: #00ff00;*/ /*color: rgb(0, 255, 0);*/ /* rgba a:透明度,取值0~1,由浅变深 */ color: rgba(0, 255, 0, 0.5); } </style> </head> <body> <!-- span通用标签,类似于div这种 --> 欢迎学习<span class="span-big">CSS课程</span>。 </body> </html>
2024-06-28
1.文本样式:对齐方式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 文本样式: 对齐方式:text-align */ .first-p{ text-align: center; /*text-align: left;*/ /*text-align: right;*/ font-size: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <!--对齐方式--> <h1>CSS基础</h1> <div> <p class="first-p">在Vue中,当你在模板中监听一个自定义事件时,通常你不需要在事件处理函数后面加上括号(),除非你想要在触发事件时立即执行某个方法并传递额外的参数(这通常不是从子组件传递的参数)。</p> </div> </body> </html>
2024-06-29
1.文本样式:首行缩进
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 首行缩进:text-indent 1em为(当前样式下)一个字的大小 */ .practice-text-indent{ text-indent: 2em; font-size: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>CSS基础</h1> <div> <p class="practice-text-indent">Tomcat使用这个目录来编译JSP页面和存放临时文件。删除work目录会清除所有编译的JSP页面和临时文件,这通常有助于解决一些运行时问题,尤其是与JSP相关的问题。</p> </div> </body> </html>
2024-06-30
1.文本样式:设置行高等于区域高度从而竖直方向居中、修饰(上中下划线)、两元素保持在水平方向上对齐
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 文本样式: 对齐方式:text-align */ .first-p{ text-align: center; /*text-align: left;*/ /*text-align: right;*/ font-size: 50px; } /* 首行缩进:text-indent 1em为(当前样式下)一个字的大小 */ .practice-text-indent{ text-indent: 2em; font-size: 50px; } /* 文本竖直方向上居中: 通过设置 行高line-height等于当前区域高度 来实现*/ .practice-line-height{ background: chartreuse; height: 500px; line-height: 500px; font-size: 50px; } /* 修饰:下、中、上划线 text-decoration text-decoration: underline:下划线 text-decoration: line-through:中划线 text-decoration: overline:上划线 */ .text-decoration-underline{ text-decoration: underline; font-size: 50px; } .text-decoration-line-through{ text-decoration: line-through; font-size: 50px; } .text-decoration-overline{ text-decoration: overline; font-size: 50px; } /* 实现两元素在水平方向上对齐 img,span 要对齐的两个元素 vertical-align: middle; */ img,span{ vertical-align: middle; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>CSS基础</h1> <div> <p class="first-p">在Vue中,当你在模板中监听一个自定义事件时,通常你不需要在事件处理函数后面加上括号(),除非你想要在触发事件时立即执行某个方法并传递额外的参数(这通常不是从子组件传递的参数)。</p> <p class="practice-text-indent">Tomcat使用这个目录来编译JSP页面和存放临时文件。删除work目录会清除所有编译的JSP页面和临时文件,这通常有助于解决一些运行时问题,尤其是与JSP相关的问题。</p> <p class="practice-line-height">从您提供的代码片段来看,您确实在第一次调用 this.$f7router.navigate 方法时遗漏了将 props 选项作为路由导航的第二个参数传递。在Framework7中(或类似的路由系统中),props 选项通常用于将自定义属性传递给路由的目标组件。</p> <p class="text-decoration-underline">修饰-下划线</p> <p class="text-decoration-line-through">修饰-中划线</p> <p class="text-decoration-overline">修饰-上划线</p> <p> <img src="images/sea.png" style="width: 100px; height: 100px;"/> <span>您错误地将 props 对象放在了字符串拼接的末尾,而不是作为 navigate 方法的第二个参数。这导致了 props 对象没有被正确地传递到路由中。</span> </p> </div> </body> </html>
2024-07-01
1.超链接伪类
a:hovor 当鼠标悬停时的样式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .book-img{ width: 200px; height: 300px; } /* 去掉超链接下划线 text-decoration: none;*/ a{ text-decoration: none; color: #000000; } /* 超链接伪类, 当鼠标悬停时的样式 a:hover */ a:hover{ color: orange; font-size: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <a href="#"> <img class="book-img" src="images/sea.png"/> </a> <p> <a href="#">码出高效</a> </p> <p> <a href="#">作者:孤尽老师</a> </p> <p> ¥99 </p> </body> </html>
2024-07-02
1.文本阴影
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 文本阴影 text-shadow 参数(h-shadow, v-shadow, blur, color) h-shadow x轴偏移 v-shadow y轴偏移 blur 模糊距离(模糊半径) 模糊半径越小越清楚 越大越模糊 color 阴影颜色 备注: 偏移,方向定义: 以窗口左上角为原点, 原点水平向右为x轴正向, 原点竖直向下为y轴正向 */ #price{ text-shadow: 50px 10px 3px red; } </style> </head> <body> <p id="price"> ¥99 </p> </body> </html>
2024-07-03
1.列表样式
页面:index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link href="css/style.css" rel="stylesheet"/> </head> <body> <div id="nav"> <h2 class="title">全部商品分类</h2> <ul> <li><a href="#">图书</a> <a href="#">音像</a> <a href="#">数字商品</a></li> <li><a href="#">家用电器</a> <a href="#">手机</a> <a href="#">数码</a></li> <li><a href="#">电脑</a> <a href="#">办公</a> <li><a href="#">家居</a> <a href="#">家装</a> <a href="#">厨具</a></li> <li><a href="#">服装鞋帽</a> <a href="#">个护化妆</a> <li><a href="#">礼品箱包</a> <a href="#">钟表</a> <a href="#">珠宝</a></li> <li><a href="#">食品饮料</a> <a href="#">保健食品</a> <li><a href="#">彩票</a> <a href="#">旅行</a> <a href="#">充值</a> <a href="#">票务</a></li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>
样式:css/style.css:
/* 通用规范是样式从最外层到内层写, 外层样式写在上方, 内层样式写在下方 */ #nav{ width: 300px; background: darkgray; } .title{ font-size: 18px; /* 加粗 */ font-weight: bold; text-indent: 1em; line-height: 35px; background: red; } /*ul{*/ /* background: darkgray;*/ /*}*/ /* 选中所有ul下的li 层次选择器里 的后代选择器ul li{} 列表项前‘.’的样式 list-style: none;不展示 list-style: circle;空心圆 list-style: decimal;(有序)数字 list-style: square;正方形*/ ul li{ /* height给个列表项之间的间距 */ height: 25px; list-style: none; font-size: 14px; text-indent: 1em; } a{ color: #000; /* 去下划线 */ text-decoration: none; } a:hover{ color: orange; text-decoration: underline; }
2024-07-04
1.背景(图片)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* border 设置边框 参数分别为: 边框粗细、边框样式、边框颜色 solid:实线*/ /* background-image 设置背景图片*/ div{ width: 1200px; height: 800px; border: 1px solid red; background-image: url("images/touXiang.png"); /* 默认是平铺,平铺满整个区域 */ /*background-repeat: repeat;*/ } .div1{ /* 水平平铺 */ background-repeat: repeat-x; } .div2{ /* 竖直平铺 */ background-repeat: repeat-y; } .div3{ /* 不平铺(只显示一个) */ background-repeat: no-repeat; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="div1"></div> <div class="div2"></div> <div class="div3"></div> </body> </html>
2024-07-05
1.接昨天代码,背景(图片),向菜单列表嵌入向下向右箭头图片,补充偏移相关内容:
style.css:
/* 菜单列表分别加向下和向右的箭头*/ .title{ font-size: 18px; /* 加粗 */ font-weight: bold; text-indent: 1em; line-height: 35px; /* css中都是用空格,而不是逗号分隔 直接合起来写background: 参数顺序: background-color background-image url里../ 取上一层目录 background-position 即position-x、position-y 相对于(左上角)原点的 水平(x)、竖直(y)偏移量 background-repeat repeat意思是重复*/ background: red url("../images/down.png") 260px 4px no-repeat; } ul li{ /* height给个列表项之间的间距 */ height: 25px; list-style: none; font-size: 14px; text-indent: 1em; /* 分开写background: url里../ 取上一层目录 background-position 相对于(左上角)原点的偏移量*/ background-image: url("../images/right.png"); background-position: 221px 2px; background-repeat: no-repeat; }
2024-07-06
1.border边框
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 盒子模型 border设置边框 参数顺序: 粗细、样式、颜色 粗细,例如2px; 样式,例如solid实线, dashed,类似于带间隔的线样式*/ #box{ width: 300px; border: 1px solid red; /*border: 1px dashed red;*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div id="box"> <h2>用户登录</h2> <form action="#"> <div> <span>用户名:</span> <input type="text" id="username"/> </div> <div> <span>密码:</span> <input type="text" id="pwd"/> </div> <div> <span>邮箱:</span> <input type="text" id="email"/> </div> </form> </div> </body> </html>
2024-07-07
1.接昨天的border边框,及新内容:margin外边距、padding内边距
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 去掉body默认的 8px的外边距 */ body{ margin: 0; } h2{ font-size: 16px; background: cadetblue; margin: 0; } /* 盒子模型 border设置边框 参数顺序: 粗细、样式、颜色 粗细,例如2px; 样式,例如solid实线, dashed,类似于带间隔的线样式 margin的一个妙用: 用于居中对齐 margin: 0 auto; margin和padding都是: 两个参数则:上下 左右 四个参数则: 顺时针 上右下左 */ #box{ width: 300px; border: 1px solid red; /*border: 1px dashed red;*/ margin: 0 auto; } form{ background: cadetblue; } /* 层次选择器:后代选择器 */ .username-div input{ border: 2px dashed black; } .pwd-div input{ border: 2px solid darkorchid; } .email-div input{ border: 2px solid darkorange; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="box"> <h2>用户登录</h2> <form action="#"> <div class="username-div"> <span>用户名:</span> <input type="text" id="username"/> </div> <div class="pwd-div"> <span>密码:</span> <input type="text" id="pwd"/> </div> <div class="email-div"> <span>邮箱:</span> <input type="text" id="email"/> </div> </form> </div> </body> </html>
2024-07-08
1.圆角边框
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .circle{ width: 500px; height: 500px; border: 10px solid red; /* border-radius 圆角边框 参数 顺时针 4个:左上 右上 右下 左下 2个:左上(及右下) 右上(及左下) 1个:所有 border-radius值 设置的是圆角的半径 当父级是正方形, 且border-radius等于 父级长宽一半时,就是个圆 border-radius: 250px;圆*/ /*border-radius: 30px 60px 40px 80px;*/ /*border-radius: 30px 80px;*/ border-radius: 250px; } /* (上)半圆 */ .banYuan{ width: 500px; height: 250px; border: 5px solid blue; border-radius: 250px 250px 0 0; } /* (右下)四分之一圆 */ .siFenZhiYiYuan{ width: 250px; height: 250px; border: 5px solid green; border-radius: 0 0 250px 0; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="circle"></div> <div class="banYuan"></div> <div class="siFenZhiYiYuan"></div> </body> </html>
2024-07-09
1.盒子阴影
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div{ width: 800px; height: 500px; border: 5px solid red; /* 盒子阴影box-shadow 参数:水平偏移 垂直偏移 模糊半径 阴影颜色 模糊半径越大,阴影越模糊 */ box-shadow: 80px 30px 2px yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <div></div> </body> </html>
2024-07-10
1.display 块级元素 行内元素
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 块级元素:独占一行: h1~h6 div p ul li 行内元素:不独占一行: span a input 块级元素内可以 嵌套行内元素, 但行内元素不能 嵌套行内元素。 display: block; 设置为块级元素 display: inline; 设置为行内元素 display: inline-block; 设置为 保持块级元素(的高度等) 且不独占一行 display: none; 设置为不显示*/ div{ width: 500px; height: 400px; border: 2px solid red; /*display: block;*/ display: inline-block; } span{ width: 500px; height: 400px; border: 2px dashed blue; /*display: block;*/ display: inline-block; } </style> </head> <body> <div>div内容</div> <span>span内容</span> </body> </html>
2024-07-11
1.float浮动
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css"/> </head> <body> <div id="father"> <div class="div1"> <img src="images/car2.png"/> </div> <div class="div2"> <img id="sea" src="images/sea.png"/> </div> <div class="div3"> <img src="images/touXiang.png"/> </div> <div class="div4"> <span>handleName(),Vue会尝试在渲染时就执行它,而不是在事件被触发时</span> </div> </div> </body> </html>
style.css:
div{ margin: 10px; padding: 5px; } #father{ border: 1px solid black; } /* float:浮动 left向左浮动 right向右浮动 clear: both; 清除浮动: 保持浮动的同时, 使其有块元素的效果。*/ .div1{ border: 1px dashed red; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } .div2{ border: 1px dashed blue; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: right; clear: both; } .div3{ border: 1px dashed green; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } .div4{ border: 1px dashed darkmagenta; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } #sea{ width: 200px; height: 400px; }
2024-07-12
1.float浮动:浮动的盒子可以向左浮动,也可以向右浮动,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动盒子为止
2.解决父级边框塌陷(共四种方法,这里先列出前两种)
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css"/> </head> <body> <div id="father"> <div class="div1"> <img src="images/car2.png"/> </div> <div class="div2"> <img id="sea" src="images/sea.png"/> </div> <div class="div3"> <img src="images/touXiang.png"/> </div> <div class="div4"> <span>浮动的盒子可以向左浮动,也可以向右浮动,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动盒子为止</span> </div> <div class="clear"></div> </div> </body> </html>
style.css:
div{ margin: 10px; padding: 5px; } #father{ border: 1px solid black; /*height: 1000px;*/ } /* float:浮动 left向左浮动 right向右浮动 浮动的盒子可以 向左浮动,也可以 向右浮动, 直到它的外边缘碰到 包含框或 另一个浮动盒子为止 clear: both; 清除浮动: 保持浮动的同时, 使其有块元素的效果。*/ /* 解决父级边框塌陷的方法: 1.给父级边框足够的高度 #father{ border: 1px solid black; height: 1000px; } 2.设置空的div, 且div设置如下3点: (1)左右清除浮动, (2)margin为0, (3)padding为0 备注: clear: left;清除左侧浮动 clear: right;清除右侧浮动 clear: both;清除两侧浮动 clear: none;不清除浮动 常用的是clear: both; */ .div1{ border: 1px dashed red; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } .div2{ border: 1px dashed blue; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: right; clear: both; } .div3{ border: 1px dashed green; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } .div4{ border: 1px dashed darkmagenta; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } #sea{ width: 200px; height: 400px; } .clear{ clear: both; margin: 0; padding: 0; }
2024-07-13
1.解决父级边框塌陷的第三种方式:设置父级元素overflow: hidden
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> img{ /*float: left;*/ } #content{ border: 1px solid black; width: 200px; height: 100px; /* 解决父级边框塌陷的第三种方式:设置父级元素overflow: hidden */ overflow: hidden; /* overflow: scroll; 滚动*/ /*overflow: scroll;*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div id="content"> <img src="images/car2.png"/> <div>哈哈,指一个人发出的笑声,高兴开心欢乐时的状态,抒发快乐的心情,表现一个人很开心快乐的状态。也指人通常用来开玩笑。一种很逗的心情。</div> </div> </body> </html>
2024-07-14
1.解决父级边框塌陷的第四种方式,也是最推荐的方式:对父级元素设置伪类
#father:after{ content: ''; display: block; clear: both; }
解决父级边框塌陷四种方式完整代码:
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css"/> </head> <body> <div id="father"> <div class="div1"> <img src="images/car2.png"/> </div> <div class="div2"> <img id="sea" src="images/sea.png"/> </div> <div class="div3"> <img src="images/touXiang.png"/> </div> <div class="div4"> <span>浮动的盒子可以向左浮动,也可以向右浮动,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动盒子为止</span> </div> <!-- <div class="clear"></div>--> </div> </body> </html>
style.css:
div{ margin: 10px; padding: 5px; } #father{ border: 1px solid black; /*height: 1000px;*/ /*overflow: hidden;*/ } /* float:浮动 left向左浮动 right向右浮动 浮动的盒子可以 向左浮动,也可以 向右浮动, 直到它的外边缘碰到 包含框或 另一个浮动盒子为止 clear: both; 清除浮动: 保持浮动的同时, 使其有块元素的效果。*/ /* 解决父级边框塌陷的方法: 1.给父级边框足够的高度 #father{ border: 1px solid black; height: 1000px; } 2.设置空的div, 且div设置如下3点: (1)左右清除浮动, clear: both; (2)margin为0, (3)padding为0 备注: clear: left;清除左侧浮动 clear: right;清除右侧浮动 clear: both;清除两侧浮动 clear: none;不清除浮动 常用的是clear: both; 3.设置父级元素overflow: hidden 4.对父元素设置伪类 这是最好的方式 #father:after{ content: ''; display: block; clear: both; } */ .div1{ border: 1px dashed red; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } .div2{ border: 1px dashed blue; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: right; clear: both; } .div3{ border: 1px dashed green; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } .div4{ border: 1px dashed darkmagenta; /*display: inline-block;*/ float: left; clear: both; } #sea{ width: 200px; height: 400px; } .clear{ clear: both; margin: 0; padding: 0; } #father:after{ content: ''; display: block; clear: both; }
2024-07-15
1.开始学习定位:相对定位、绝对定位、z-index
今天先是最开始的默认情况:index.html:
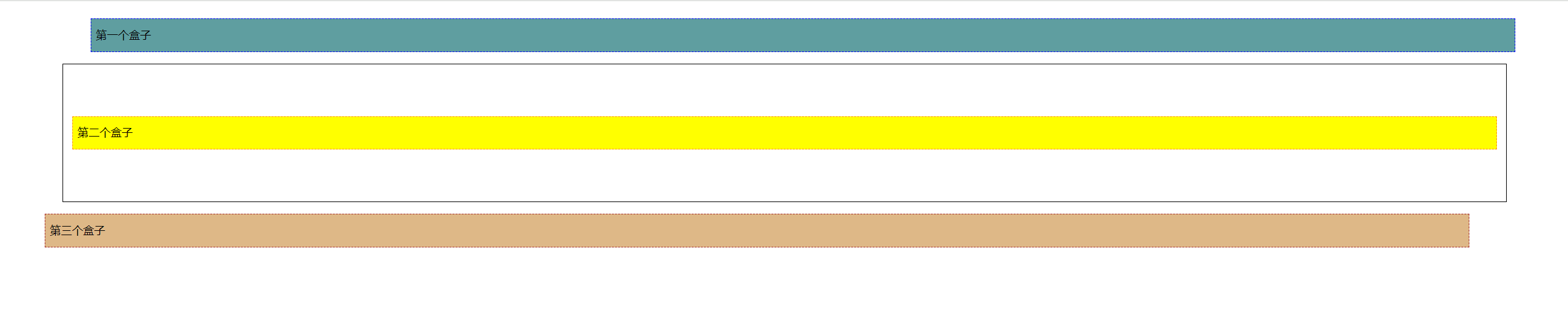
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div{ margin: 10px; padding: 5px; font-size: 12px; line-height: 25px; } #father{ border: 1px solid black; padding: 0; } #first{ background-color: cadetblue; border: 1px dashed blue; } #second{ background-color: yellow; border: 1px dashed darkorange; } #third{ background-color: burlywood; border: 1px dashed brown; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="father"> <div id="first">第一个盒子</div> <div id="second">第二个盒子</div> <div id="third">第三个盒子</div> </div> </body> </html>
2024-07-16
1.相对定位:
相对定位:相对于该元素原来的位置进行偏移
position: relative;
元素仍在文档流中,其原始位置仍被保留。
(所以示例中div3已经向下偏移出父级div了。但因为其原始位置仍被保留了,所以没出现父级边框塌陷
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> body{ padding: 50px; } div{ margin: 10px; padding: 5px; font-size: 12px; line-height: 25px; } #father{ border: 1px solid black; padding: 0; } /* 相对定位:相对于该元素原来的位置进行偏移 position: relative; 元素仍在文档流中,其原始位置仍被保留。 (所以示例中div3已经向下偏移出父级div了。但因为其原始位置仍被保留了,所以没出现父级边框塌陷) top right bottom left*/ #first{ background-color: cadetblue; border: 1px dashed blue; position: relative; top: -60px; left: 20px; } #second{ background-color: yellow; border: 1px dashed darkorange; } #third{ background-color: burlywood; border: 1px dashed brown; position: relative; right: 30px; bottom: -60px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="father"> <div id="first">第一个盒子</div> <div id="second">第二个盒子</div> <div id="third">第三个盒子</div> </div> </body> </html>
示例中div3已经向下偏移出父级div了。但因为其原始位置仍被保留了,所以没出现父级边框塌陷。效果:
2024-07-17
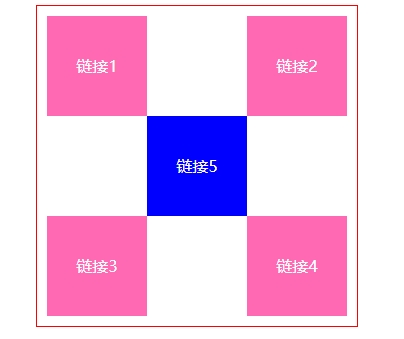
1.相对定位练习
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> #father{ text-align: center; } #sequar{ border: 1px solid red; width: 300px; margin: 0 auto; padding: 10px; /* 直接设置父级边框高度,来解决父级边框塌陷 */ height: 300px; } /* 父级正方形设置伪类,解决父级边框塌陷。但这里测试不好使。 改为直接设置父级边框高度,来解决父级边框塌陷 */ /*#sequar:after{ content: ''; display: block; clear: both; }*/ a{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: hotpink; color: white; /*display: inline-block;解决原默认inline设置width、height失效问题。 同时又因为通过设置父级高度解决了父级边框塌陷问题, 所以就不用担心我一开始练习时用block导致整体5行,不会解决父级塌陷的问题了。 而inline-block,左右会有间距。所以这里就用block。*/ display: block; line-height: 100px; text-decoration: none; } a:hover{ background-color: blue; } #a2{ position: relative; top: -100px; left: 200px; } #a4{ position: relative; top: -100px; left: 200px; } #a5{ position: relative; top: -300px; left: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="father"> <div id="sequar"> <!-- a标签一定要写上href="",才能有超链接(小手)效果 --> <a id="a1" href="#">链接1</a> <a id="a2" href="#">链接2</a> <a id="a3" href="#">链接3</a> <a id="a4" href="#">链接4</a> <a id="a5" href="#">链接5</a> </div> </div> </body> </html>
效果:
2024-07-18
1.绝对定位:position: absolute;
1.1相对于已定位的父级元素位置进行定位,如果没有已定位的父级元素,则相对于浏览器定位。
1.2脱离标准文档流,其在文档流中的原始位置不会被保留。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div{ margin: 10px; padding: 5px; font-size: 12px; line-height: 25px; } #father{ border: 1px solid black; padding: 0; position: relative; } #first{ background-color: cadetblue; border: 1px dashed blue; } /* 绝对定位:position: absolute; 1.相对于已定位的父级元素位置进行定位,如果没有已定位的父级元素,则相对于浏览器定位。 2.脱离标准文档流,其在文档流中的原始位置不会被保留。*/ #second{ background-color: yellow; border: 1px dashed darkorange; position: absolute; /*left: 100px;*/ /*top: 300px;*/ right: 300px; } #third{ background-color: burlywood; border: 1px dashed brown; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="father"> <div id="first">第一个盒子</div> <div id="second">第二个盒子</div> <div id="third">第三个盒子</div> </div> </body> </html>
2024-07-19
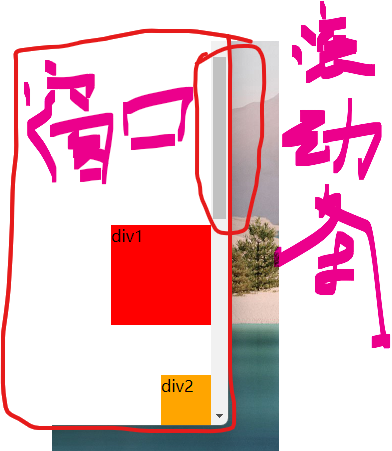
1.positon: fixed;固定定位。
1.1这里div1绝对定位因为所有父级都没有定位,所以根据浏览器定位,但浏览器有滚动效果,基于浏览器定位的绝对定位是受滚动条影响的。 随着页面滚动,该div1的位置也会动。
1.2position: fixed;固定定位。根据之前上网查,我的理解是可以认为是相对于浏览器的(可视)窗口进行定位。其不受页面是否有滚动影响。div2都会固定在浏览器可视窗口的最右下角。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* 这里将body高度设为高于屏幕实际高度,目的是测试滚动条对绝对定位、固定定位的影响。从而更好的理解两种定位。 */ body{ height: 1000px; } /* 这里div1绝对定位因为所有父级都没有定位,所以根据浏览器定位,但浏览器有滚动效果,基于浏览器定位的绝对定位是受滚动条影响的。 随着页面滚动,该div1的位置也会动。*/ div:nth-of-type(1){ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; position: absolute; right: 0; bottom: 0; } /* position: fixed;固定定位。根据之前上网查,我的理解是可以认为是相对于浏览器的(可视)窗口进行定位 其不受页面是否有滚动影响。div2都会固定在浏览器可视窗口的最右下角。*/ div:nth-of-type(2){ width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: orange; position: fixed; right: 0; bottom: 0; } </style> </head> <body> <div>div1</div> <div>div2</div> </body> </html>
效果:
2024-07-20
1.z-index设置图层高度,opacity设置透明度,取值在0~1之间
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link href="css/style.css" rel="stylesheet"> </head> <body> <div id="content"> <ul> <li><img src="images/SpringBootBackground.jpg"/></li> <li class="tipBackground"></li> <li class="tipText">学SpringBoot,找狂神说</li> <li>时间:2099-01-01</li> <li>地点:火星基地</li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>
style.css:
#content{ margin: 0; padding: 0; font-size: 12px; /* 字体12px,行高25px是常用的一个选择组合 */ line-height: 25px; border: 1px solid #000000; width: 140px; } ul{ margin: 0; padding: 0; list-style: none; /* 去掉列表项前符号 */ position: relative; /* 给url一个定位,用于子元素li“学SpringBoot,找狂神说"可以绝对定位 */ } img{ width: 141px; height: 117px; } .tipText, .tipBackground{ position: absolute; top: 90px; width: 140px; height: 25px; } .tipText{ z-index: 999; /* z-index设置图层高度 */ color: white; } .tipBackground{ background: #000000; opacity: 1; /* 透明度,取值在0~1之间 */ }
至此狂神说CSS教程已学完。



