20162308 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》第六周学习总结
20162308 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》第六周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
学习目标
- 理解queue抽象数据类型
- 会用queue解决问题
- 掌握queue的实现(数组,链表)
- 分析Java Collections API中queue相关的类
学习内容
- Queue抽象类源码分析
package java.util;
public abstract class AbstractQueue<E>
extends AbstractCollection<E>
implements Queue<E> {
/**
* Constructor for use by subclasses.
*/
protected AbstractQueue() {
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this queue if it is possible to do so
* immediately without violating capacity restrictions, returning
* {@code true} upon success and throwing an {@code IllegalStateException}
* if no space is currently available.
*
* <p>This implementation returns {@code true} if {@code offer} succeeds,
* else throws an {@code IllegalStateException}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws IllegalStateException if the element cannot be added at this
* time due to capacity restrictions
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this queue does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
if (offer(e))
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. This method differs
* from {@link #poll poll} only in that it throws an exception if this
* queue is empty.
*
* <p>This implementation returns the result of {@code poll}
* unless the queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
public E remove() {
E x = poll();
if (x != null)
return x;
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. This method
* differs from {@link #peek peek} only in that it throws an exception if
* this queue is empty.
*
* <p>This implementation returns the result of {@code peek}
* unless the queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
public E element() {
E x = peek();
if (x != null)
return x;
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this queue.
* The queue will be empty after this call returns.
*
* <p>This implementation repeatedly invokes {@link #poll poll} until it
* returns {@code null}.
*/
public void clear() {
while (poll() != null)
;
}
/**
* Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this
* queue. Attempts to addAll of a queue to itself result in
* {@code IllegalArgumentException}. Further, the behavior of
* this operation is undefined if the specified collection is
* modified while the operation is in progress.
*
* <p>This implementation iterates over the specified collection,
* and adds each element returned by the iterator to this
* queue, in turn. A runtime exception encountered while
* trying to add an element (including, in particular, a
* {@code null} element) may result in only some of the elements
* having been successfully added when the associated exception is
* thrown.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this queue
* @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of the specified
* collection prevents it from being added to this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains a
* null element and this queue does not permit null elements,
* or if the specified collection is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of an element of the
* specified collection prevents it from being added to this
* queue, or if the specified collection is this queue
* @throws IllegalStateException if not all the elements can be added at
* this time due to insertion restrictions
* @see #add(Object)
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (c == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
boolean modified = false;
for (E e : c)
if (add(e))
modified = true;
return modified;
}
}
在Java Collections API源码分析中,娄老师介绍了Java Collection源码分析的一些方法,在过去几周的实践中,我发现阅读Java内这些高质量的源码能够在很大程度上发现自己源代码中存在的问题,包括变量的命名和代码的拆分、整合等。近日,阿里巴巴推出了阿里巴巴Java开发规范自动化检测插件,也能够在一定程度上实现代码的规范化。
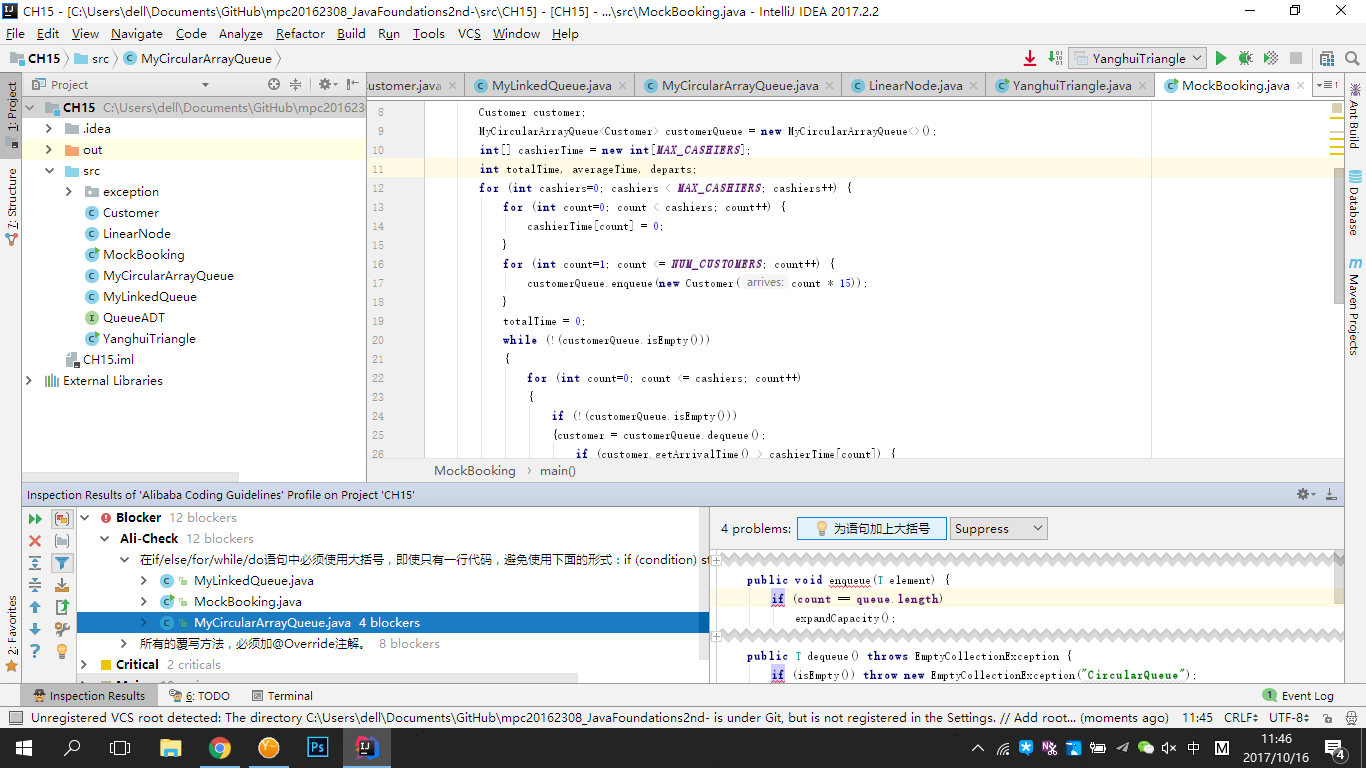
阿里巴巴的编程规范中规定了for,if后面不省略花括号,王垠也在博客中介绍了这种设定的优势,他说,永远不要省略花括号。很多语言允许你在某种情况下省略掉花括号,比如C,Java都允许你在if语句里面只有一句话的时候省略掉花括号:
if (...)
action1();
咋一看少打了两个字,多好。可是这其实经常引起奇怪的问题。比如,你后来想要加一句话action2()到这个if里面,于是你就把代码改成:
if (...)
action1();
action2();
为了美观,你很小心的使用了action1()的缩进。咋一看它们是在一起的,所以你下意识里以为它们只会在if的条件为真的时候执行,然而action2()却其实在if外面,它会被无条件的执行。我把这种现象叫做“光学幻觉”(optical illusion),理论上每个程序员都应该发现这个错误,然而实际上却容易被忽视。
那么你问,谁会这么傻,我在加入action2()的时候加上花括号不就行了?可是从设计的角度来看,这样其实并不是合理的作法。首先,也许你以后又想把action2()去掉,这样你为了样式一致,又得把花括号拿掉,烦不烦啊?其次,这使得代码样式不一致,有的if有花括号,有的又没有。况且,你为什么需要记住这个规则?如果你不问三七二十一,只要是if-else语句,把花括号全都打上,就可以想都不用想了,就当C和Java没提供给你这个特殊写法。这样就可以保持完全的一致性,减少不必要的思考。
有人可能会说,全都打上花括号,只有一句话也打上,多碍眼啊?然而经过实行这种编码规范几年之后,我并没有发现这种写法更加碍眼,反而由于花括号的存在,使得代码界限明确,让我的眼睛负担更小了。
但是看完这些就会发现Java源代码中存在一些问题。
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (c == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
boolean modified = false;
for (E e : c)
if (add(e))
modified = true;
return modified;
}
在Queue的addAll方法中,Java的开发者并没有严格执行这种编程规范,而是基于缩进体现代码逻辑上的关系,这样写虽然省略了两个花括号,使代码看起来更加清爽,但是还是觉得有些问题。
- 使用Queue解决问题
在队列课下作业中,我们基于队列实现了一个模拟售票员买票的程序,能够模拟多售票员的情况下,客户的排队等候时间。
队列比较多地出现在多线程的程序中,比如生产者-消费者的多线程模型,就是利用Redis维护了一个分布式队列,并由生产者线程在队列中添加任务,消费者线程从队列中获取任务,在一定程度上降低程序的逻辑耦合度。
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
没有问题
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
没有问题
代码托管
- 代码提交过程 & 代码量截图:
![2017-04-30.png]()
结对及互评
点评模板:
- 博客中值得学习的或问题:
其他
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | - | 1 | 10 | |
| 第二周 | - | 2 | 20 | |
| 第三周 | - | 3 | 30 | |
| 第四周 | - | 4 | 40 | |
| 第五周 | - | 5 | 50 | |
| 第六周 | - | 6 | 60 |
-
计划学习时间:20小时
-
实际学习时间:10小时
-
改进情况:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号