js模拟call,apply,bind以及应用场景
js模拟call,apply,bind以及应用场景
call,apply,bind定义及日常用法
实现原理
各种应用场景详解
一、call,apply,bind定义及日常用法
call的日常用法
Function.prototype.call()
call() 方法使用一个指定的 this 值和单独给出的一个或多个参数来调用一个函数。
注意:该方法的语法和作用与 apply() 方法类似,只有一个区别,就是 call() 方法接受的是一个参数列表,而 apply() 方法
接受的是一个包含多个参数的数组。
function Product(name, price) { this.name = name; this.price = price; console.log('Product-->') } function Food(name, price) { Product.call(this, name, price); this.category = 'food'; } console.log(new Food('cheese', 5).name);
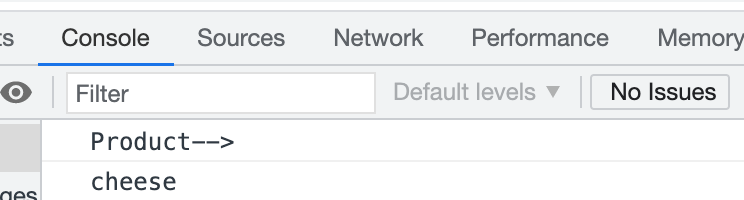
const a = { user:"桃子吃桃子", fn:function(num1, num2){ console.log(this.user); // 桃子吃桃子 console.log(num1+num2); // 3 } } const b = a.fn; b.call(a,1,2);

使用 call 方法调用函数并且不指定第一个参数(argument)
在下面的例子中,我们调用了 display 方法,但并没有传递它的第一个参数。如果没有传递第一个参数,this 的值将会被绑定为全局对象。
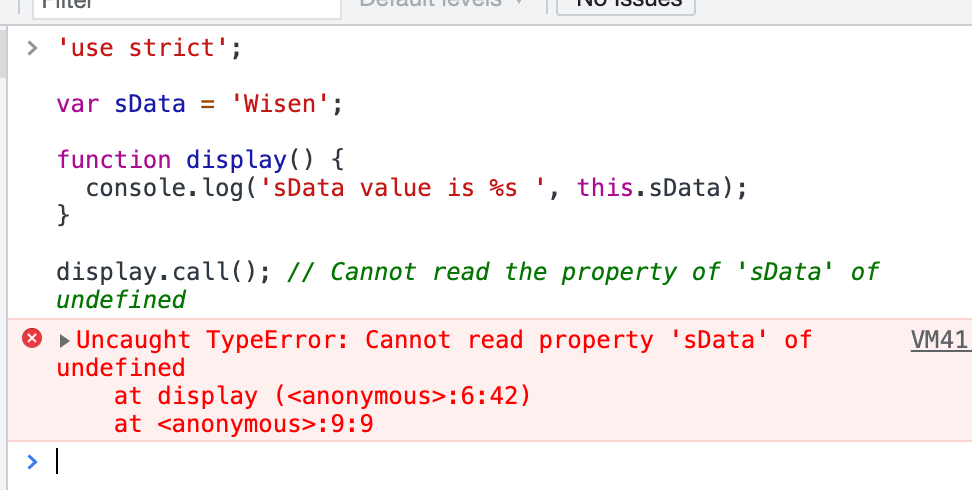
var sData = 'Wisen'; function display() { console.log('sData value is %s ', this.sData); } display.call(); // sData value is Wisen
注意:在严格模式下,this 的值将会是 undefined。见下文。
'use strict'; var sData = 'Wisen'; function display() { console.log('sData value is %s ', this.sData); } display.call(); // Cannot read the property of 'sData' of undefined
二、实现原理
call的实现原理
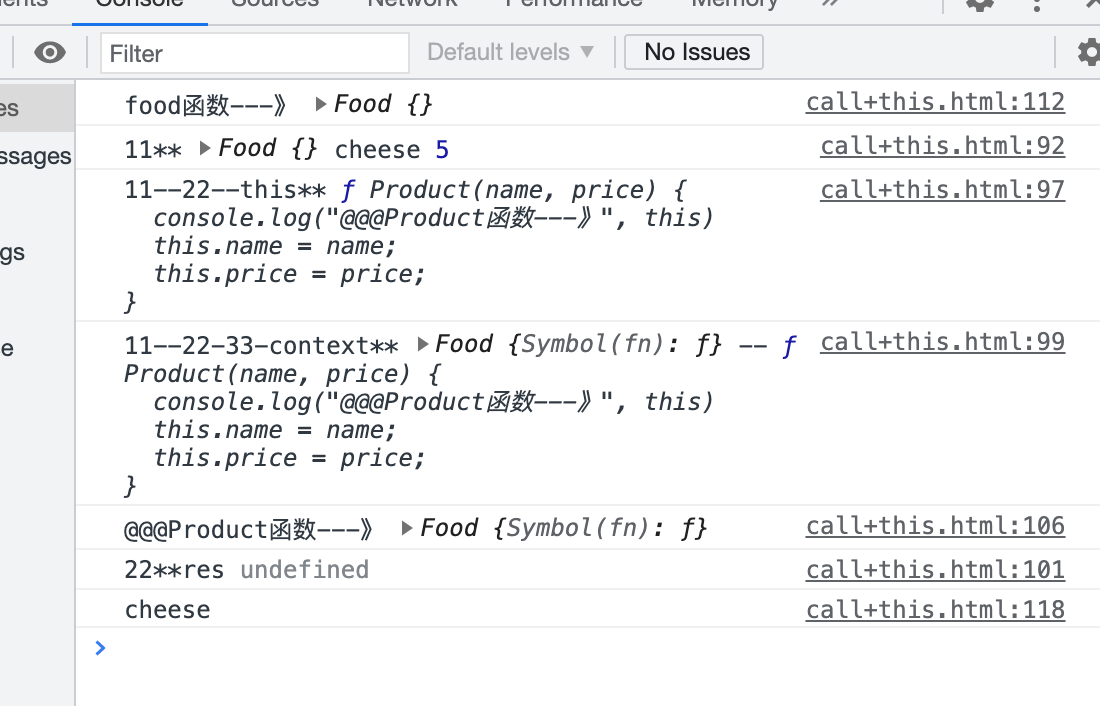
// 实现原理 结合下图logs数据分一下原理 Function.prototype.callDemo = function(context = window, ...args) { console.log("11**", context, ...args) // Product在Food函数内传入this应该是Food内的this if (typeof this !== 'function') { throw new TypeError('Type Error'); } const fn = Symbol('fn'); console.log("11--22--this**", this) // callDemo方法是function prototype方法当前this指向当前函数Product(){} // 下面几行核心代码 context[fn] = this;// Product当前的this赋给Food函数 console.log("11--22-33-context**", context,'--',context[fn], ) const res = context[fn](...args); // 当前存在Food函数的Product函数复制给res变量 console.log("22**res", res) delete context[fn]; // 删除当前Product函数 return res; // 返回 }
来看看例子
function Product(name, price) { console.log("@@@Product函数---》", this) this.name = name; this.price = price; } function Food(name, price) { console.log("food函数---》", this) Product.callDemo(this, name, price); this.category = 'food'; } console.log(new Food('cheese', 5).name);
// 大概思路写成下面是不是好理解一些, 然后保存Product(name, price)的值返回,在删除Product函数 function Food(name, price) { console.log("food函数---》", this) // Product.callDemo(this, name, price); function Product(name, price) { console.log("@@@Product函数---》", this) this.name = name; this.price = price; } Product(name, price) this.category = 'food'; }
三、 各种应用场景详解
call的应用场景
下面用call模拟实现filter的功能,先来看看filter基本用法以及参数
Array.prototype.filter() filter参数及主要有两个callball回调函数(回调函数有三个参数分别是element当前元素, index索引和array当前的数组)和this(可可选)
filter() 方法创建一个新数组, 其包含通过所提供函数实现的测试的所有元素。

const words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present']; const result = words.filter(word => word.length > 6); console.log(result); // expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'grapes', 'mango', 'orange']; /** * Array filters items based on search criteria (query) */ const filterItems = (query) => { return fruits.filter((el) => el.toLowerCase().indexOf(query.toLowerCase()) > -1 ); } console.log(filterItems('ap')); // ['apple', 'grapes'] console.log(filterItems('an')); // ['banana', 'mango', 'orange']
打印一下值加深一下
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'grapes', 'mango', 'orange']; function filterItems(query) { return fruits.filter(function(el, index, arr) { console.log('el--',el, 'index--',index, 'arr--',arr) return el.toLowerCase().indexOf(query.toLowerCase()) > -1; }) } console.log(filterItems('ap')); // ['apple', 'grapes']

Array.prototype.filterDemo = function(callback, thisArg) { if (this == undefined) { throw new TypeError('this is null or not undefined'); } if (typeof callback !== 'function') { throw new TypeError(callback + 'is not a function'); } const res = []; // 让O成为回调函数的对象传递(强制转换对象) console.log(typeof this,Object.prototype.toString.call(this), 'this--', this) const O = Object(this); // >>>0 保证len为number,且为正整数 console.log(typeof O,Object.prototype.toString.call(O), 'O--', O, 'callback--', callback) const len = O.length >>> 0; for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { // 检查i是否在O的属性(会检查原型链) console.log('--for--', i, i in O ,O) if (i in O) { // 回调函数调用传参 console.log('****', callback.call(thisArg, O[i], i, O)) // 函数的返回值 if (callback.call(thisArg, O[i], i, O)) { // 符合返回值为true的值输入res的数组中返回一个符合条件的新数组 console.log('####res', i, O[i]) res.push(O[i]); } } } return res; } function isBigEnough(element) { console.log("ele", element) return element >= 10; } const filtered = [12, 5, 8, 130, 44].filterDemo(isBigEnough); console.log('filtered--'. filtered)

更新中


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号