pytorch通过unsqueeze和expand函数生成grid
示例:
import torch
h, w = 3, 5
x_ = torch.arange(w).unsqueeze(0).expand(h, -1) # torch.Size([h, w])
# expand(*size)函数可以实现对张量中单维度上数据的复制操作。
# 其中,*size分别指定了每个维度上复制的倍数。
# 对于不需要(或非单维度)进行复制的维度,对应位置上可以写上原始维度的大小或者直接写-1。
# 单维度怎么理解呢?
# 将张量中大小为1的维度称为单维度。例如,shape为[2,3]的张量就没有单维度,
# shape为[1,3]的张量,其第0个维度上的大小为1,因此第0个维度为张量的单维度。
# 例如,torch.arange(7)结果的shape为[7],没有单维度,因此需要先通过unsqueeze()进行维度增加,
# 参数为0表示在第0个维度进行维度增加操作,即在张量最外层加一个中括号变成第一维。
y_ = torch.arange(h).unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, w) # torch.Size([h, w])
grid = torch.stack([x_, y_], dim=0).float() # 将x_和y_沿维度0进行堆叠, torch.Size([2, h, w])
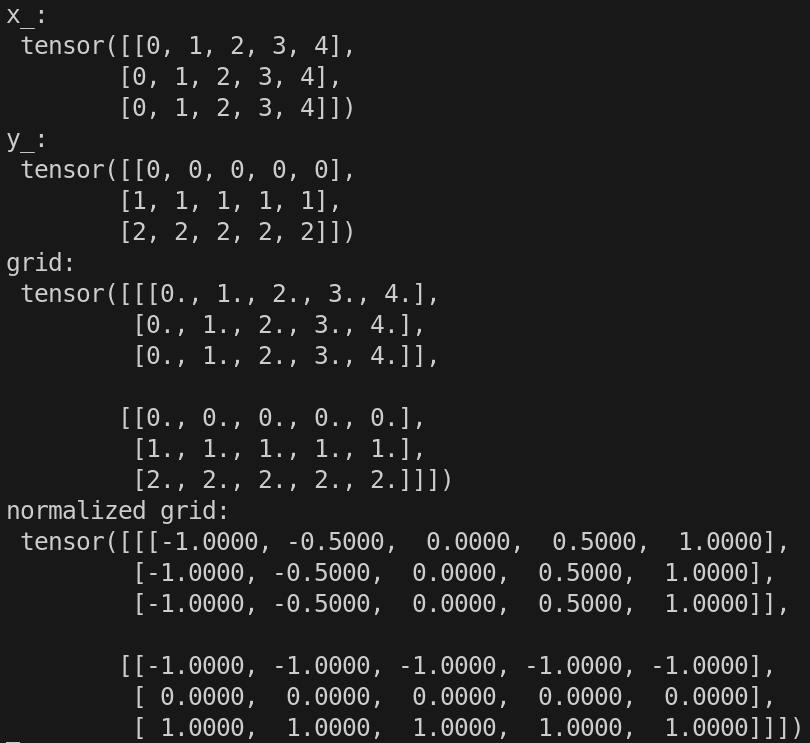
print('x_:\n', x_)
print('y_:\n', y_)
print('grid:\n', grid)
grid[0, :, :] = 2 * grid[0, :, :] / (w - 1) - 1 # 相当于对x轴坐标进行规范化操作 torch.Size([2, h, w])
grid[1, :, :] = 2 * grid[1, :, :] / (h - 1) - 1 # 相当于对y轴坐标进行规范化操作 torch.Size([2, h, w])
print('normalized grid:\n', grid)
输出:
或者:
import torch featSize = 5 #生成恒等网络采样grid gridY = torch.linspace(-1, 1, steps = featSize).view(1, -1, 1, 1).expand(1, featSize, featSize, 1) gridX = torch.linspace(-1, 1, steps = featSize).view(1, 1, -1, 1).expand(1, featSize, featSize, 1) grid = torch.cat((gridX, gridY), dim=3).type(torch.float32)
或者:
def get_reference_points(H=100,
W=240,
Z=8,
num_points_in_pillar=4,
dim='3d',
bs=1,
device='cuda',
dtype=torch.float):
"""Get the reference points used in SCA and TSA.
Args:
H, W: spatial shape of tpv.
Z: height of pillar.
device (obj:`device`): The device where
reference_points should be.
Returns:
Tensor: reference points used in decoder, has \
shape (bs, num_keys, num_levels, 2).
"""
# reference points in 3D space, used in spatial cross-attention (SCA)
zs = torch.linspace(
0.5, Z - 0.5, num_points_in_pillar,
dtype=dtype, device=device).view(-1, 1, 1).expand(
num_points_in_pillar, H, W) / Z # zs shape: ([4, 100, 240]). The height is [0.5000, 2.8333, 5.1667, 7.5000]
xs = torch.linspace(
0.5, W - 0.5, W, dtype=dtype, device=device).view(1, 1, -1).expand(
num_points_in_pillar, H, W) / W # xs shape: ([4, 100, 240]). x are [0.5, 1.5, 2.0, ..., 239.5]
ys = torch.linspace(
0.5, H - 0.5, H, dtype=dtype, device=device).view(1, -1, 1).expand(
num_points_in_pillar, H, W) / H # ys shape: ([4, 100, 240]). y are [0.5, 1.5, 2.0, ..., 99.5]
ref_3d = torch.stack((xs, ys, zs), -1) # ([4, 100, 240, 3])
ref_3d = ref_3d.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).flatten(2).permute(0, 2, 1) # ([4, 3, 100, 240]) --> ([4, 3, 24000]) --> ([4, 24000, 3])
return ref_3d
参考资料:
【通俗易懂】详解torch.nn.functional.grid_sample函数:可实现对特征图的水平/垂直翻转_gridsample-CSDN博客
一文彻底弄懂 PyTorch 的 `F.grid_sample`_pytorch grid sample-CSDN博客


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号