神经网络模型的参数量和计算量FLOPs的计算,torchstat,thop,循环神经网络RNN
概念
FLOPS和FLOPs的区别:
- FLOPS:注意全大写,是floating point operations per second的缩写,意指每秒浮点运算次数,理解为计算速度。是一个衡量硬件性能的指标。
- FLOPs:注意s小写,是floating point operations的缩写(s表复数),意指浮点运算数,理解为计算量。可以用来衡量算法/模型的复杂度。
卷积的FLOPs的计算过程可参考:CNN 模型所需的计算力flops是什么?怎么计算? - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
在介绍torchstat包和thop包之前,先总结一下:
- torchstat包可以统计卷积神经网络和全连接神经网络的参数和计算量。
- thop包可以统计统计卷积神经网络、全连接神经网络以及循环神经网络的参数和计算量,程序示例等详见下文。
torchstat包
在实际操作中,我们可以调用torchstat包,帮助我们统计模型的parameters和FLOPs。如果不修改这个包里面的一些代码,那么这个包只适用于输入为3通道的图像的模型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | import torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom torchstat import statclass Simple(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3, 1, padding=1, bias=False) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3, 1, padding=1, bias=False) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x = self.conv2(x) return xmodel = Simple()stat(model, (3, 244, 244)) # 统计模型的参数量和FLOPs,(3,244,244)是输入图像的size |
运行结果:

如果把torchstat包中的一行程序进行一点点改动,那么这个包可以用来统计全连接神经网络的参数量和计算量。当然手动计算全连接神经网络的参数量和计算量也很快 =_= 。进入torchstat源代码之后,如下图所示,注释掉圈红的地方,就可以用torchstat包统计全连接神经网络的参数量和计算量了。
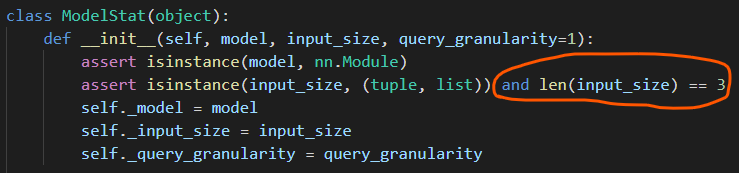
程序示例二,用torchstat统计全连接神经网络的参数量和计算量::
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | import torch.nn as nnfrom torchstat import statclass Simple(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(10, 10) def forward(self, x): x = self.fc1(x) return xnet = Simple()stat(net, (10,)) |
运行结果:

我本来想把torchstat源码改一下,使得它可以用来统计循环神经网络的参数量和计算量,但好像稍微有点麻烦,然后网上找到thop包,可以用来统计循环神经网络的参数量和计算量,所以改torchstat源码的动力就...没有了 =_=。
thop包
除了torchstat包之外,thop也可以统计神经网络模型的参数量。thop的安装可以参考:GitHub - Lyken17/pytorch-OpCounter: Count the MACs / FLOPs of your PyTorch model.
程序示例三,用thop统计全连接神经网络的参数量和计算量:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | import torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom thop import profileclass Simple(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(10, 10) def forward(self, x): x = self.fc1(x) return xnet = Simple()input = torch.randn(1, 10) # batchsize=1, 输入向量长度为10macs, params = profile(net, inputs=(input, ))print(' FLOPs: ', macs*2) # 一般来讲,FLOPs是macs的两倍print('params: ', params) |
运行结果:

程序示例四,用thop统计循环神经网络的参数量和计算量:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | import torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom thop import profileclass Simple(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=100, hidden_size=100, num_layers=1) def forward(self, x): x = self.lstm(x) return xnet = Simple()input = torch.randn(1, 10, 100) # batchsize=1,序列长度为10,序列中每个时间步的向量长度为100macs, params = profile(net, inputs=(input, ))print(' FLOPs: ', macs*2) # 一般来讲,FLOPs是macs的两倍print('params: ', params) |
运行结果:

分类:
Deep Learning
标签:
参数量





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
2020-06-05 relint, 相对内点集的理解