pytorch lstm 预测航空旅客数目
airflights passengers dataset下载地址https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jbrownlee/Datasets/master/airline-passengers.csv
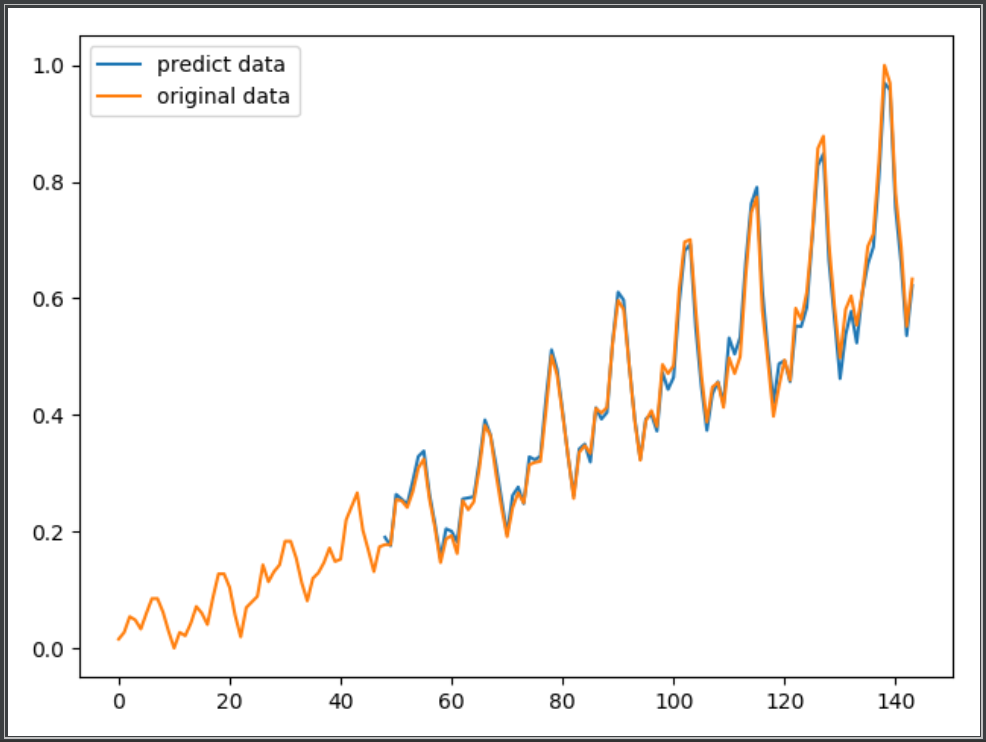
这个dataset包含从1949年到1960年每个月的航空旅客数目,共12*12=144个数字。
下面的程序中,我们以1949-1952的数据预测1953的数据,以1950-1953的数据预测1954的数据,以此类推,训练模型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 | import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pdimport torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerimport os# super parametersEPOCH = 400learning_rate = 0.01seq_length = 4 # 序列长度n_feature = 12 # 序列中每个元素的特征数目。本程序采用的序列元素为一年的旅客,一年12个月,即12维特征。# datadata = pd.read_csv('airline-passengers.csv') # 共 "12年*12个月=144" 个数据data = data.iloc[:, 1:5].values # dataFrame, shape (144,1)data = np.array(data).astype(np.float32)sc = MinMaxScaler()data = sc.fit_transform(data) # 归一化data = data.reshape(-1, n_feature) # shape (12, 12)trainData_x = []trainData_y = []for i in range(data.shape[0]-seq_length): tmp_x = data[i:i+seq_length, :] tmp_y = data[i+seq_length, :] trainData_x.append(tmp_x) trainData_y.append(tmp_y)# modelclass Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_dim=12, hidden_dim=10, output_dim=12, n_layer=1): super(Net, self).__init__() self.in_dim = in_dim self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim self.output_dim = output_dim self.n_layer = n_layer self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=in_dim, hidden_size=hidden_dim, num_layers=n_layer, batch_first=True) self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim) def forward(self, x): _, (h_out, _) = self.lstm(x) # h_out是序列最后一个元素的hidden state # h_out's shape (batchsize, n_layer*n_direction, hidden_dim), i.e. (1, 1, 10) # n_direction根据是“否为双向”取值为1或2 h_out = h_out.view(h_out.shape[0], -1) # h_out's shape (batchsize, n_layer * n_direction * hidden_dim), i.e. (1, 10) h_out = self.linear(h_out) # h_out's shape (batchsize, output_dim), (1, 12) return h_outtrain = Trueif train: model = Net() loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) # train for epoch in range(EPOCH): total_loss = 0 for iteration, X in enumerate(trainData_x): # X's shape (seq_length, n_feature) X = torch.tensor(X).float() X = torch.unsqueeze(X, 0) # X's shape (1, seq_length, n_feature), 1 is batchsize output = model(X) # output's shape (1,12) output = torch.squeeze(output) loss = loss_func(output, torch.tensor(trainData_y[iteration])) optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training iteration loss.backward() # computing gradients optimizer.step() # update weights total_loss += loss if (epoch+1) % 20 == 0: print('epoch:{:3d}, loss:{:6.4f}'.format(epoch+1, total_loss.data.numpy())) # torch.save(model, 'flight_model.pkl') # 这样保存会弹出UserWarning,建议采用下面的保存方法,详情可参考https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/129948825 torch.save({'state_dict': model.state_dict()}, 'checkpoint.pth.tar')else: # model = torch.load('flight_model.pth') model = Net() checkpoint = torch.load('checkpoint.pth.tar') model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])# predictmodel.eval()predict = []for X in trainData_x: # X's shape (seq_length, n_feature) X = torch.tensor(X).float() X = torch.unsqueeze(X, 0) # X's shape (1, seq_length, n_feature), 1 is batchsize output = model(X) # output's shape (1,12) output = torch.squeeze(output) predict.append(output.data.numpy())# plotplt.figure()predict = np.array(predict)predict = predict.reshape(-1, 1).squeeze()x_tick = np.arange(len(predict)) + (seq_length*n_feature)plt.plot(list(x_tick), predict, label='predict data')data_original = data.reshape(-1, 1).squeeze()plt.plot(range(len(data_original)), data_original, label='original data')plt.legend(loc='best')plt.show() |
运行结果:





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通