十七、C++字符串(二)
1、字符串的应用
需求:设计一个程序,用户输入属性id或者pass或者role可以把对应的内容显示出来,给定字符串如下:
string str{"id=user;pass=632105;role=郝英俊;"};
//设计一个程序,用户输入属性id或者pass或者role可以把对应的内容显示出来
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
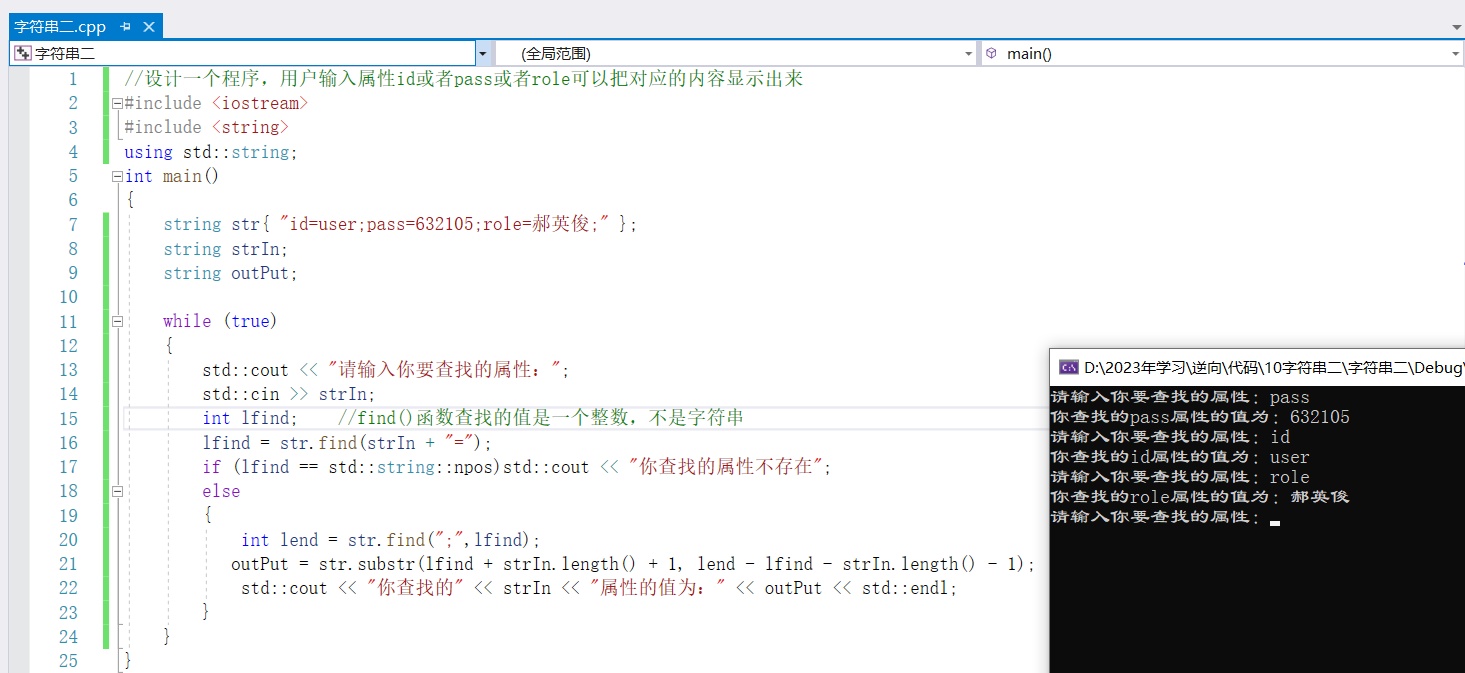
string str{ "id=user;pass=632105;role=郝英俊;" };
string strIn;
string outPut;
while (true)
{
std::cout << "请输入你要查找的属性:";
std::cin >> strIn;
int lfind; //find()函数查找的值是一个整数,不是字符串
lfind = str.find(strIn + "=");
if (lfind == std::string::npos)std::cout << "你查找的属性不存在";
else
{
int lend = str.find(";",lfind);
outPut = str.substr(lfind + strIn.length() + 1, lend - lfind - strIn.length() - 1);
std::cout << "你查找的" << strIn << "属性的值为:" << outPut << std::endl;
}
}
}
2、string函数补充
1)string插入字符串
.insert()是string类型的一个方法,可以在string字符串的指定位置插入另一个字符串,基本语法如下:
//插入字符串基本语法
.insert(要插入的位置,要插入的字符串);
string id{"id=;"}
id.insert(3,"testid"); //在第3个字符的位置插入字符串testid,最后id的值为id=testid
//插入字符串的高级用法
.insert(要插入的位置,要插入的字符个数,要插入的字符);
string id{"id=;"}
id.insert(3,6,'*'); //在第3个位置插入6个*号,最后id的值为id=******
//insert()字符串插入函数基本用法
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
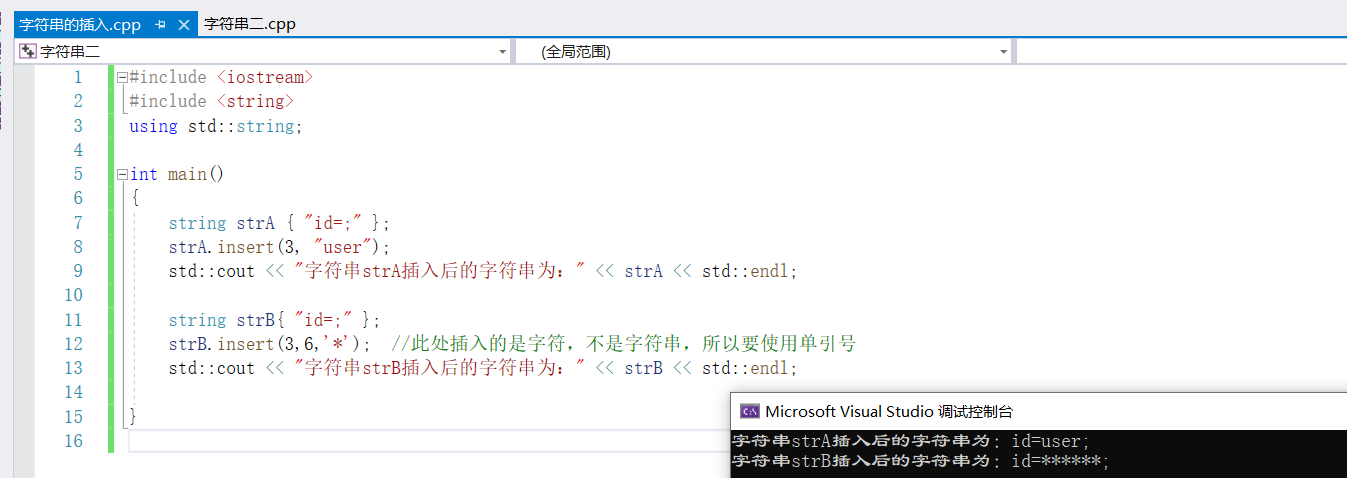
string strA { "id=;" };
strA.insert(3, "user");
std::cout << "字符串strA插入后的字符串为:" << strA << std::endl;
string strB{ "id=;" };
strB.insert(3,6,'*'); //此处插入的是字符,不是字符串,所以要使用单引号
std::cout << "字符串strB插入后的字符串为:" << strB << std::endl;
}
2)insert插入字符串的扩展用法
//insert()扩展用法语法
.insert(要插入的位置,要插入的字符串,要插入的字符串的起始位置,要插入的大小);
string id{"id=;"};
id.insert(3,"killertestid123456",6,6); //id=testis
.insert(要插入的位置,要插入的字符串,要插入的大小);
string id{"id=;"};
id.insert(3,"killertestid123456",6); //id的值为id=killer 从开始位置截取6个字符
//insert()扩展用法示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string strA{ "id=;" };
//在原字符串的第三个位置开始插入,插入的内容为此处字符串的第6个位置开始截取,截取6个
strA.insert(3, "killertestid123456", 6, 6);
std::cout << "字符串strA插入后的字符串为:" << strA << std::endl;
string strB{ "id=;" };
//在原字符串的第三个位置开始插入,插入的内容为此处字符串的第0个位置开始截取,截取6个
strB.insert(3, "killertestid123456", 6); //此处插入的是字符,不是字符串,所以要使用单引号
std::cout << "字符串strB插入后的字符串为:" << strB << std::endl;
}

3、指针数组字符串
1)string字符串不是一个单纯的指针或者数组
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string str{ "12345" };
std::cout << "字符串中第1个字符的值为:" << str[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << "字符串中第2个字符的值为:" << str[1] << std::endl;
std::cout << "字符串中第3个字符的值为:" << str[2] << std::endl;
std::cout << "字符串的地址为:" << (int)&str << std::endl;
std::cout << "str[0]的地址为:" << (int)&str[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << "str[0]的地址为:" << (int)&str[1] << std::endl;
str = str + "abcdesdajhdhjakd";
std::cout << "字符串长度增加后的地址为:" << (int)&str << std::endl;
std::cout << "字符串长度增加后str[0]的地址为:" << (int)&str[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << "字符串长度增加后str[0]的地址为:" << (int)&str[1] << std::endl;
}
/*结果显示:
如果str的地址和str[0]的地址一致,说明str相当于一个数组
但是str的地址和str[0]的地址不一样,说明str不是一个简单的数组,
从str[0]的地址开始,地址才是连续的
当字符串长度增加后,str的地址不变,但是str[0]开始,后面的每个字符的地址都会变化
*/
2)获取string字符串的指针
在内存里的布局,与C字符串(char*)不同的是,C字符串以0结尾,而string字符串由于专门记录其长度的属性,在实现的时候,并没有严格要求是否以0结尾。但是在C++11标准推出后,要求string字符串也以0结尾
通过.c_str()方法可以得到一个const char*的指针指向str储存字符数据的内存空间(返回的是一个常量指针,只能写不能读)
通过.data()方法可以得到一个const char*的指针指向str储存字符数据的内存空间
在c++17标准下,.data()方法得到的是一个char*的指针
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string str{ "12345" };
const char* baseStrA = str.c_str();
const char* baseStrB = str.data();
std::cout << "字符串的地址为:" << (int)&str << std::endl;
std::cout << "通过c_str获取的字符串地址为为:" << (int)baseStrA << std::endl;
std::cout << "通过c_str获取的字符串地址为为:" << (int)baseStrB << std::endl;
}

3)string替换字符串的内容
.replace是string类型提供的一种方法,可以替换string字符串中的内容。语法如下
//replace()字符串替换语法
.replace(要替换的内容起始位置,要替换的程度,"替换后的内容");
string str{"id=user;"};
str.replace{3,4,"zhangsan"}; //从原字符串的第三个位置开始,替换四个字符,替换内容为新的字符串
//replace()其他语法
.replace(要替换的内容起始位置,要替换的长度,替换后的字符长度,'字符');
str.replace(3,4,6,'*'); //str的内容为:id=******
//replace()字符串替换函数基本用法
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string strA{ "id=user;" };
//在原字符串的第3个位置开始替换,替换后面的4个字符
strA.replace(3, 4, "zhangsan");
std::cout << "字符串strA替换后的字符串为:" << strA << std::endl;
string strB{ "id=user;" };
//在原字符串的第3个位置开始替换,替换后面的4个字符,并替换为6个*号
strB.replace(3, 4, 6, '*'); //此处插入的是字符,不是字符串,所以要使用单引号
std::cout << "字符串strB替换后的字符串为:" << strB << std::endl;
}

4)replace()函数的扩展用法
//replace()函数的扩展语法
.replace(要替换的内容起始位置,要替换的长度,"替换后的内容",替换后内容的节选长度);
string str{"id=user;"};
str.replace(3,4,"zhangsan;pass=255;",8); //str=zhangsan
//replace()函数的扩展语法
.replace(要替换的内容起始位置,要替换的长度,"替换后的内容",替换后内容的起始位置,替换后内容的节选长度);
string str{"id=user;"};
str.replace(3,4,"zhangsan;pass=255;",5,3); //str=san;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string strA{ "id=user;" };
//在原字符串的第3个位置开始替换,替换后面的4个字符
strA.replace(3, 4, "zhangsan;pass=255;", 8);
std::cout << "字符串strA替换后的字符串为:" << strA << std::endl;
string strB{ "id=user;" };
strB.replace(3, 4, "zhangsan;pass=255;", 5, 3);
std::cout << "字符串strB替换后的字符串为:" << strB << std::endl;
}

5)字符串的删除
erase()是string类型提供的一种方法,可以删除string字符串中的内容,语法如下:
//字符串的删除erase()函数语法一
.erase(要删除的起始位置,要删除的起始长度);
string str{"id=user;"};
str.erase(3,4); //std为id=;
//从起始位置开始删除所有内容
.erase(要删除的起始位置);
string str{"id=user;"};
str.erase(3); //std为id=
.earse();删除字符串所有内容
.clear();删除字符串所有内容
4、字符串补充
1)字符的存储及读取
字符串再C/C++的学习中一直是一个比较麻烦的点,但是只要知道"计算机中万物皆数字",则所有的问题都可以迎刃而解。
字符的存储:先通过编码表转化为数子,再把数字转化为二进制进行存储(字符->编码表->二进制数字)
字符的读取:先把二进制数字读取出来,再根据编码表转化为字符(二进制数字->编码表->字符)
字符编码表:ASCII、GBK、UNICODE
2)练习
需求:设计一个程序,要求用户输入中英文混合内容,正确的计算出长度并显示出来。比如用户输入:你好,我的世界。结果输出为7。
思路:因为字符的ASCII码范围为0-127,只要超过127就表明是一个中文字符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string strIn{};
std::cout << "请输入计算长度的字符串:";
std::cin >> strIn;
int length{};
for (int i = 0; strIn[i]; i++)
{
if (strIn[i] < 0)i++;
length++;
}
std::cout << "你输入的字符串长度为:" << length << std::endl;
}

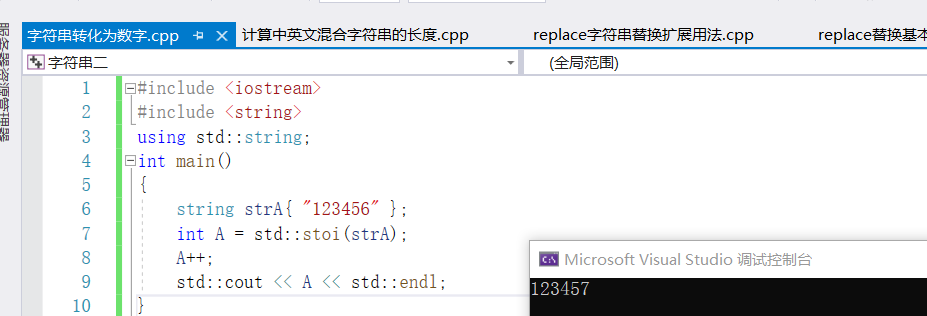
2)string字符串转化为数字
通过std::to_string(数字)可以将数字转化为字符串。通过一下函数可以将字符串转化为数字
| 作用 | 语法 | 用法 |
|---|---|---|
| 将字符串转化为int | std::stoi(字符串) | int a=stoi("123") |
| 将字符串转化为long | std::stol(字符串) | long a=stol("123") |
| 将字符串转化为long long | std::stoll(字符串) | long long a=stoll("123"); |
| 将字符串转化为unsigned long | std::stoul(字符串) | unsigned long a=stoul("123") |
| 将字符串转化为unsigned long long | std::stoull(字符串) | unsigned long long a=stoull("123") |
| 将字符串转化为float | std::stof(字符串) | float a=stof("123") |
| 将字符串转化为double | std::stod(字符串) | double a=stod("123") |
| 将字符串转化为long double | std::stold(字符串) | long double a=stold("123") |
将字符串转化为数字后,可以进行计算
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string strIn{};
std::cout << "请输入计算长度的字符串:";
std::cin >> strIn;
int length{};
for (int i = 0; strIn[i]; i++)
{
if (strIn[i] < 0)i++;
length++;
}
std::cout << "你输入的字符串长度为:" << length << std::endl;
}
3)stringstream流
std::stringstream流定义在<sstream>头文件中,std::cout组织数据的形式有时候要比string字符串要方便。std::stringstream可以像std::cout一样组织数据。std::stringstream.str()方法将会返回一个string,里面是std::stringstream的内容,即将流中的内容提取出来
//stringstream流语法
std::stringstream str;
str<<"你好"<<123;
std::string _str=str.str(); //_str的内容为"你好123"
//stringstream流简单使用
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using std::string;
int main()
{
std::stringstream strA;
strA << "你好 [" << std::hex << 500 << "] "<<std::dec<<123;
string strB = strA.str();
std::cout << strB;
}

5、游戏麟江湖排行榜设计
需求:我们通过网络获得了麟江湖游戏玩家的数据,现在我们要为我们的游戏设计一个战力(exp)排行榜系统,排序贵u则为战力由高到低,当战力相同时,根据ID的字母顺序进行排序(如A要排在B的前面)数据如下:
"id=TomyClare;exp=9523;id=Sunny;exp=9523;id=DyBaby;exp=25301;id=Simple;exp=25301;id=Bkacs11;exp=2100;id=DumpX;exp=36520;"
根据这个数据生成玩家排行榜!
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
typedef struct Role
{
string Id;
int Exp;
}*PROLE;
int main()
{
string strData{ "id=TomyClare;exp=9523;id=Sunny;exp=9523;id=DyBaby;exp=25301;id=Simple;exp=25301;id=Bkacs11;exp=2100;id=DumpX;exp=36520;" };
int istart{}, iend{}, icount{};
for (int i = 0; i < strData.length(); i++)
{
if (strData[i] == ';')
{
icount++;
i += 3;
}
}
PROLE pRole = new Role[icount / 2];
icount = 0;
do
{
istart = strData.find("id=", istart);
if (istart == std::string::npos) break;
iend = strData.find(";", istart + 3);
pRole[icount].Id = strData.substr(istart + 3, iend - istart - 3);
istart = iend + 1;
istart = strData.find("exp=", istart);
iend = strData.find(";", istart + 4);
pRole[icount++].Exp = std::stoi(strData.substr(istart + 4, iend - istart - 4));
istart = iend + 1;
} while (true);
//冒泡排序
for (int i = 1; i < icount; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < icount; j++)
{
if (pRole[j].Exp > pRole[j - 1].Exp)
{
Role tmp = pRole[j - 1];
pRole[j- 1] = pRole[j];
pRole[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < icount; i++)
{
std::cout << pRole[i].Id << " " << pRole[i].Exp << std::endl;
}
}



