CSS备忘录
一、层定位
普通流、浮动和绝对定位
position : static | absolute | fixed | relative
position:satic 就是普通流(普通流中的元素的位置由元素在 HTML 中的位置决定。)
position:relative就是相对定位(相对定位的元素框会偏移某个距离。元素仍然保持其未定位前的形状,它原本所占的空间仍保留)
比如:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <meta name="generator" content="editplus" /> <meta name="author" content="guanqing" /> <meta name="keywords" content="" /> <meta name="description" content="" /> </head> <style type="text/css"> <!--
#a { width:200px; height:500px; background:red; left:10px; top:20px; position:relative; }
#b { width:20px; height:50px; background:green; }
--> </style> <body>
<div id="b"></div> <div id="a"> </div> </body> <html>
效果:a层相对于b层,相对于上面的距离是20px;相对于B的左边10px;
position:absolute 表示绝对定位,将对象从文档流中拖出,也就是浮在其他的层之上。如果父的层有属性position:relative,该层浮在该父层之上,left,top的值也是相对于父层,没有则依据 body 对象。
代码:
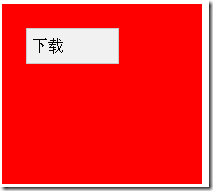
<meta name="description" content="" /> </head> <style type="text/css"> <!-- #downloadDiv{ padding:5px; margin:2px; width:160px; border:1px solid #ccc; background:#f1f1f1; } #downloadDiv{ width:81px; line-height: 24px; left:30px; top:30px; position:absolute; } #a { width:200px; height:180px; background:red; /* position:relative;*/ } --> </style> <body> <div id="a"> <div id="downloadDiv">下载</div> </div> </body> <html>
相对boday的效果: :
相对a层的效果: