Centos6.8 下 从零开始 部署 Java Web 应用
一、硬件信息
CPU:
[root@localhost ~]# grep 'physical id' /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l 2 [root@localhost ~]# grep 'core id' /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l 4 [root@localhost ~]# grep 'processor' /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l 16 [root@localhost ~]# dmidecode -s processor-version Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU L5520 @ 2.27GHz Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU L5520 @ 2.27GHz
系统:
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/issue CentOS release 6.8 (Final) Kernel \r on an \m
内存:
[root@localhost ~]# free -h
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 15G 12G 3.1G 4K 185M 2.6G
-/+ buffers/cache: 9.7G 5.9G
Swap: 7.9G 51M 7.8G
硬盘:
[root@localhost ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root
50G 8.7G 38G 19% /
tmpfs 7.8G 0 7.8G 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 477M 39M 414M 9% /boot
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_home
860G 3.8G 812G 1% /home
software:
[root@localhost tomcat8.35]# sh bin/version.sh Using CATALINA_BASE: /home/server/tomcat8.35/ Using CATALINA_HOME: /home/server/tomcat8.35/ Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /home/server/tomcat8.35/temp Using JRE_HOME: /usr Using CLASSPATH: /home/server/tomcat8.35/bin/bootstrap.jar:/home/server/tomcat8.35/bin/tomcat-juli.jar Server version: Apache Tomcat/8.5.35 Server built: Nov 3 2018 17:39:20 UTC Server number: 8.5.35.0 OS Name: Linux OS Version: 2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64 Architecture: amd64 JVM Version: 1.8.0_191-b12 JVM Vendor: Oracle Corporation
[root@localhost ~]# java -version java version "1.8.0_191" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_191-b12) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.191-b12, mixed mode)
CPU:2核4核心16线程
系统:Centos6.8
内存:16G
硬盘:50G + 860G + 477M
软件:Tomcat8.35 \ JDK1.8.0_191-b12
二、调整Linux设置
2.1、调整DNS
1)编辑DNS
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/resolv.conf [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf #阿里云 DNS nameserver 223.5.5.5 nameserver 223.6.6.6 #Google DNS nameserver 8.8.8.8
2)重启网络服务
[root@localhost ~]# service network restart
正在关闭接口 em2: [确定]
关闭环回接口: [确定]
弹出环回接口: [确定]
弹出界面 em2: Determining if ip address 221.235.184.199 is already in use for device em2...
[确定]
2.2、调整软件源
[root@localhost ~]# mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
[root@localhost ~]# wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-6.repo
[root@localhost ~]# yum makecache
如果无wget命令,则手动编辑。
2.3、安装ntp ,用于同步系统时间
1)安装并启动
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install ntp
2)同步时间
[root@localhost ~]# ntpdate time.nuri.net 23 Dec 21:13:45 ntpdate[30444]: adjust time server 211.115.194.21 offset -0.020057 sec
3)增加时间服务器, time.nuri.net
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/ntp.conf [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/ntp.conf # For more information about this file, see the man pages # ntp.conf(5), ntp_acc(5), ntp_auth(5), ntp_clock(5), ntp_misc(5), ntp_mon(5). driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift # Permit time synchronization with our time source, but do not # permit the source to query or modify the service on this system. restrict default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery restrict -6 default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery # Permit all access over the loopback interface. This could # be tightened as well, but to do so would effect some of # the administrative functions. restrict 127.0.0.1 restrict -6 ::1 # Hosts on local network are less restricted. #restrict 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap # Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project. # Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html). server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst server time.nuri.net iburst #broadcast 192.168.1.255 autokey # broadcast server #broadcastclient # broadcast client #broadcast 224.0.1.1 autokey # multicast server #multicastclient 224.0.1.1 # multicast client #manycastserver 239.255.254.254 # manycast server #manycastclient 239.255.254.254 autokey # manycast client # Enable public key cryptography. #crypto includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw # Key file containing the keys and key identifiers used when operating # with symmetric key cryptography. keys /etc/ntp/keys # Specify the key identifiers which are trusted. #trustedkey 4 8 42 # Specify the key identifier to use with the ntpdc utility. #requestkey 8 # Specify the key identifier to use with the ntpq utility. #controlkey 8 # Enable writing of statistics records. #statistics clockstats cryptostats loopstats peerstats
4)设置当前时区为上海
[root@localhost ~]# rm -rf /etc/localtime [root@localhost ~]# ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
5)启动ntpd服务
ntpd 已停 [root@localhost ~]# service ntpd start 正在启动 ntpd: [确定] [root@localhost ~]# service ntpd status ntpd (pid 30317) 正在运行...
[root@loahlhost ~]# chkconfig --level 2345 ntpd on
https://www.cnblogs.com/kerrycode/archive/2015/08/20/4744804.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/flytogalaxy/p/8471675.html
2.4、关闭selinux
1)临时关闭:
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce Enforcing [root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0 [root@localhost ~]# getenforce Permissive
2)永久关闭:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
SELINUX=enforcing 改为 SELINUX=disabled
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/selinux # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted
2.5、调整ulimit
1)查看当前限制
[root@localhost ~]# ulimit -a core file size (blocks, -c) 0 data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited scheduling priority (-e) 0 file size (blocks, -f) unlimited pending signals (-i) 63653 max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64 max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited open files (-n) 1024 pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8 POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200 real-time priority (-r) 0 stack size (kbytes, -s) 10240 cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited max user processes (-u) 63653 virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited file locks (-x) unlimited
2)临时增加系统对当前用户每个进程可以同时打开的最大文件数,可以运行的最大并发进程数( ulimit设置参考 )
[root@localhost ~]# ulimit -n 65535 [root@localhost ~]# ulimit -u 65535
3)永久修改
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/security/limits.conf
在文件末尾添加以下内容:
* soft noproc 65535
* hard noproc 65535 * soft nofile 65535 * hard nofile 65535
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/security/limits.conf # /etc/security/limits.conf # #Each line describes a limit for a user in the form: # #<domain> <type> <item> <value> # #Where: #<domain> can be: # - a user name # - a group name, with @group syntax # - the wildcard *, for default entry # - the wildcard %, can be also used with %group syntax, # for maxlogin limit # #<type> can have the two values: # - "soft" for enforcing the soft limits # - "hard" for enforcing hard limits # #<item> can be one of the following: # - core - limits the core file size (KB) # - data - max data size (KB) # - fsize - maximum filesize (KB) # - memlock - max locked-in-memory address space (KB) # - nofile - max number of open file descriptors # - rss - max resident set size (KB) # - stack - max stack size (KB) # - cpu - max CPU time (MIN) # - nproc - max number of processes # - as - address space limit (KB) # - maxlogins - max number of logins for this user # - maxsyslogins - max number of logins on the system # - priority - the priority to run user process with # - locks - max number of file locks the user can hold # - sigpending - max number of pending signals # - msgqueue - max memory used by POSIX message queues (bytes) # - nice - max nice priority allowed to raise to values: [-20, 19] # - rtprio - max realtime priority # #<domain> <type> <item> <value> # #* soft core 0 #* hard rss 10000 #@student hard nproc 20 #@faculty soft nproc 20 #@faculty hard nproc 50 #ftp hard nproc 0 #@student - maxlogins 4
* soft noproc 65535
* hard noproc 65535 * soft nofile 65535 * hard nofile 65535 # End of file
4)再次查看当前限制信息
core file size (blocks, -c) 0 data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited scheduling priority (-e) 0 file size (blocks, -f) unlimited pending signals (-i) 63653 max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64 max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited open files (-n) 65535 pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8 POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200 real-time priority (-r) 0 stack size (kbytes, -s) 10240 cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited max user processes (-u) 63653 virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited file locks (-x) unlimited
https://blog.csdn.net/noizz/article/details/2486339
2.6、调整SSH,保持长连接
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
ClientAliveInterval 60 #server每隔60秒发送一次请求给client,然后client响应,从而保持连接
ClientAliveCountMax 3 #server发出请求后,客户端没有响应得次数达到3,就自动断开连接,正常情况下,client不会不响应
[root@localhost ~]# service sshd restart 停止 sshd: [确定] 正在启动 sshd: [确定]
2.7、 安装crontab
[root@localhost ~]# yum install vixie-cron crontab
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --level 2345 crond on
2.8、安装辅助命令
[root@localhost ~]# yum install wget zip unzip lrzsz telnet
三、安装执行环境
3.1、下载JAVA JDK
[root@localhost ~]# wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: gpw_e24=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "https://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u191-b12/2787e4a523244c269598db4e85c51e0c/jdk-8u191-linux-x64.rpm"
#安装JAVA JDK
[root@localhost ~]# yum install jdk-8u191-linux-x64.rpm
3.2、安装MySQL
1)下载MySQL
[root@localhost ~]# wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.7/mysql-5.7.24-1.el6.x86_64.rpm-bundle.tar [root@localhost ~]# tar xvf mysql-5.7.24-1.el6.x86_64.rpm-bundle.tar [root@localhost ~]# yum install mysql-*.rpm [root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/my.cnf
2)编辑mysql配置,在[mysqld]下面添加配置
max_connections=1000
wait_timeout=50
sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION"
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/my.cnf
# For advice on how to change settings please see # http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/server-configuration-defaults.html [mysqld] # # Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data # cache in MySQL. Start at 70% of total RAM for dedicated server, else 10%. # innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M # # Remove leading # to turn on a very important data integrity option: logging # changes to the binary log between backups. # log_bin # # Remove leading # to set options mainly useful for reporting servers. # The server defaults are faster for transactions and fast SELECTs. # Adjust sizes as needed, experiment to find the optimal values. # join_buffer_size = 128M # sort_buffer_size = 2M # read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M datadir=/var/lib/mysql socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
#最大链接数
max_connections=1000
wait_timeout=50
sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION" #MySQL在完成某些join(连接)需求的时候,为了减少参与join的“被驱动表”的读取次数以提高性能, #需要使用到join buffer来协助完成join操作,当join buffer 太小, #MySQL不会将该buffer存入磁盘文件而是先将join buffer中的结果与需求join的表进行操作, #然后清空join buffer中的数据,继续将剩余的结果集写入次buffer中 join_buffer_size = 512M tmp_table_size = 128M tmpdir = /tmp #该值设置过小将导致单个记录超过限制后写入数据库失败,且后续记录写入也将失败 max_allowed_packet = 100M innodb_buffer_pool_size=4096M innodb_log_file_size = 512M #MySQL读入缓冲区的大小 read_buffer_size = 64M #MySQL的随机读缓冲区大小 read_rnd_buffer_size = 16M #MySQL的顺序读缓冲区大小 sort_buffer_size = 16M #查询缓存 query_cache_size=100M key_buffer_size=64m thread_cache_size=64 #开启慢查询日志 slow_query_log = 1 #超出次设定值的SQL即被记录到慢查询日志 long_query_time = 6 slow_query_log_file = /var/log/mysql/slow.log #表示记录下没有使用索引的查询 log_queries_not_using_indexes = 1 # Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks symbolic-links=0 log-error=/var/log/mysql/mysqld.log pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
3)启动msyql
[root@localhost ~]# service mysqld start
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --level 2345 mysqld on
4)查看msyql root密码
[root@localhost ~]# grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
5)登录mysql
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -p密码
6)修改密码
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '新密码';
7)编辑防火墙,开放端口3306
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
添加一条命令:
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 3306 -j ACCEPT
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/iptables # Firewall configuration written by system-config-firewall # Manual customization of this file is not recommended. *filter :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 3306 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited -A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited COMMI
8)重启防火墙
[root@localhost ~]# service iptables restart
3.3、安装redis
[root@localhost ~]# yum install epel-release #添加epel源 [root@localhost ~]# yum install redis [root@localhost ~]# service redis start
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --level 2345 redis on
3.4、下载Tomcat ( 官网下载地址 )
[root@localhost ~]# wget -P /home/server/tomcat8 http://mirrors.hust.edu.cn/apache/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.35/bin/apache-tomcat-8.5.35.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# cd /home/server/tomcat8
[root@localohst ~]# tar zxvf apache-tomcat-8.5.35.tar.gz
3.5、上传Web应用代码
上传至 /home/server/tomcat8.35/webapps/
➜ ~ rsync webApllication.war root@www.xxx.com:/home/server/tomcat8.35/webapps/
[root@localohst ~]# jar xvf webApllication.war
3.6、jvisualvm远程监控tomcat
1)添加如下配置:
[root@localohst ~]# vi /home/server/tomcat8/venus_server/bin/startup.sh
SERVER_ROOT_DIR=`pwd`
export CATALINA_OPTS="$CATALINA_OPTS
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote
-Djava.rmi.server.hostname=服务器外网ip
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=端口
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=true
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.password.file=SERVERROOTDIR/conf/jmxremote.password−Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.access.file=SERVERROOTDIR/conf/jmxremote.password−Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.access.file=SERVER_ROOT_DIR/conf/jmxremote.access"
[root@localohst ~]# cat /home/server/tomcat8/venus_server/bin/startup.sh
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Start Script for the CATALINA Server
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Better OS/400 detection: see Bugzilla 31132
os400=false
case "`uname`" in
OS400*) os400=true;;
esac
# resolve links - $0 may be a softlink
PRG="$0"
while [ -h "$PRG" ] ; do
ls=`ls -ld "$PRG"`
link=`expr "$ls" : '.*-> \(.*\)$'`
if expr "$link" : '/.*' > /dev/null; then
PRG="$link"
else
PRG=`dirname "$PRG"`/"$link"
fi
done
PRGDIR=`dirname "$PRG"`
EXECUTABLE=catalina.sh
# Check that target executable exists
if $os400; then
# -x will Only work on the os400 if the files are:
# 1. owned by the user
# 2. owned by the PRIMARY group of the user
# this will not work if the user belongs in secondary groups
eval
else
if [ ! -x "$PRGDIR"/"$EXECUTABLE" ]; then
echo "Cannot find $PRGDIR/$EXECUTABLE"
echo "The file is absent or does not have execute permission"
echo "This file is needed to run this program"
exit 1
fi
fi
# jvisualvm settings
SERVER_ROOT_DIR=`pwd`
export CATALINA_OPTS="$CATALINA_OPTS
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote
-Djava.rmi.server.hostname=0.0.0.0
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=1100
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=true
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.password.file=$SERVER_ROOT_DIR/conf/jmxremote.password
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.access.file=$SERVER_ROOT_DIR/conf/jmxremote.access"
# enf of jvisualvm
#设置启动内存
export JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -server -Xms6144m -Xmx6144m -XX:NewSize=1024m -XX:MaxNewSize=2048m -XX:SurvivorRatio=2 -XX:+UseParallelGC"
exec "$PRGDIR"/"$EXECUTABLE" start "$@"
2)设置远程监控账号:
[root@localhost conf]# vi /home/server/tomcat8.35/conf/jmxremote.access
内容如下:
用户名 权限类型(readonly:只读,readwrite:读写)
[root@localhost conf]# cat jmxremote.access guest readonly root readwrite
设置远程监控密码:
用户名 密码
[root@localhost conf]# vi /home/server/tomcat8.35/conf/jmxremote.password
[root@localhost conf]# cat /home/server/tomcat8.35/conf/jmxremote.password
guest xxxxxx
root xxxxxx
3)设置文件权限
[root@localhost conf]# chmod 600 /home/server/tomcat8.35/conf/jmxremote*
4)启动web应用
[root@localhost conf]# sh /home/server/tomcat8.35/bin/startup.sh
3.7、辅助shell
1.内存监控,并回收脚本
#!/bin/bash LIMIT=512 LOG_FILE="/var/log/timing_dropcaches.log" #定时清理系统内存 #https://blog.csdn.net/gaojinshan/article/details/40710369 used=`free -m | awk 'NR==2' | awk '{print $3}'` free=`free -m | awk 'NR==2' | awk '{print $4}'` echo "===========================" >> $LOG_FILE date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M.%S" >> $LOG_FILE echo "Memory usage | [Use:${used}MB][Free:${free}MB] | [${LIMIT}]MB" >> $LOG_FILE # drop caches when the free memory less than 2G if [ $free -le $LIMIT ] ; then #sync && echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches #sync && echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches sync && echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo "OK" >> $LOG_FILE else echo "Not required" >> $LOG_FILE fi
2.日志清理脚本
[root@localhost ~]# crontab -e
#删除2天前的日志 /usr/bin/find /home/server/tomcat8.35 -name *.log -mtime +2 | grep `date +%Y` | xargs rm -Rf {} > /dev/null 2>&1
四、压力测试
4.1、安装Webbench
wget http://home.tiscali.cz/~cz210552/distfiles/webbench-1.5.tar.gz tar -zxvf ./webbench-1.5.tar.gz yum install -y gcc ctags cd ./webbench-1.5 make &make install make clean
参考:webbench安装
4.2、使用说明
t是benchmark持续多久。
c是指time时间内请求多少次。
比如我们测试百度, 启动100个客户端同时请求百度首页,持续60S:
webbench -t 60 -c 100 http://www.baidu.com/
4.3、运行结果
五、jvisualvm远程监控
5.1、启动jvisualvm
➜ ~ jvisualvm
5.2、添加远程主机

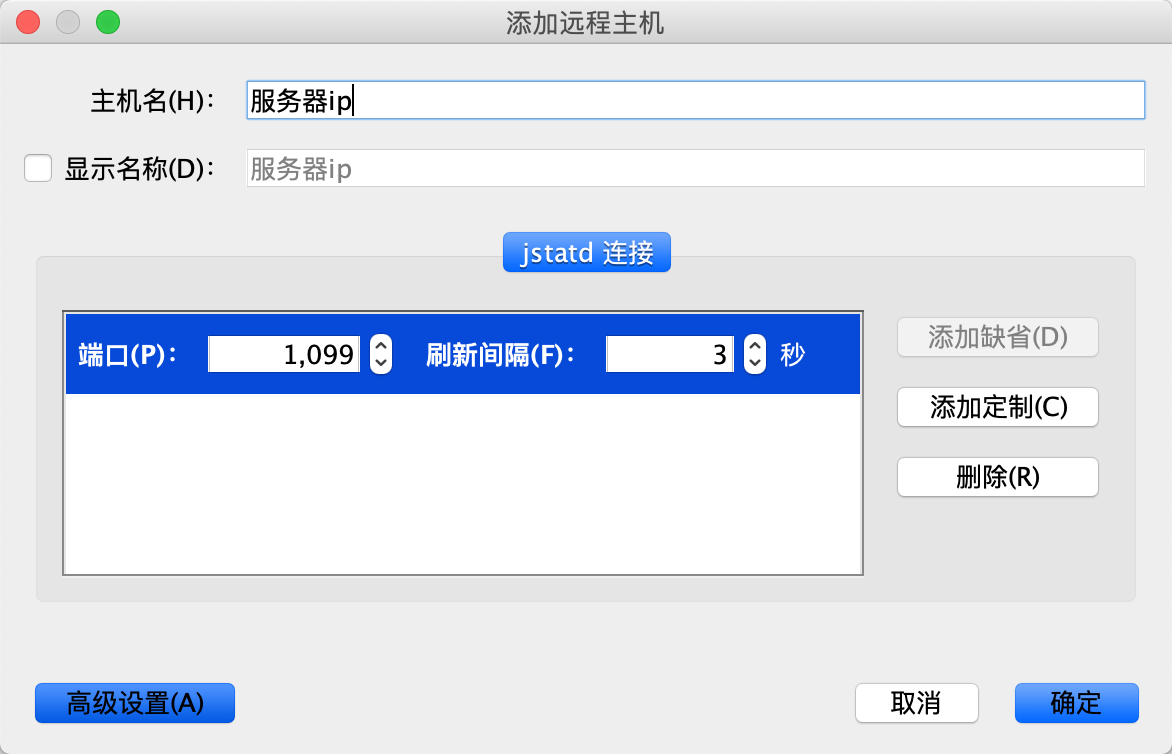
5.3、输入服务IP、默认端口1099,点击确认。
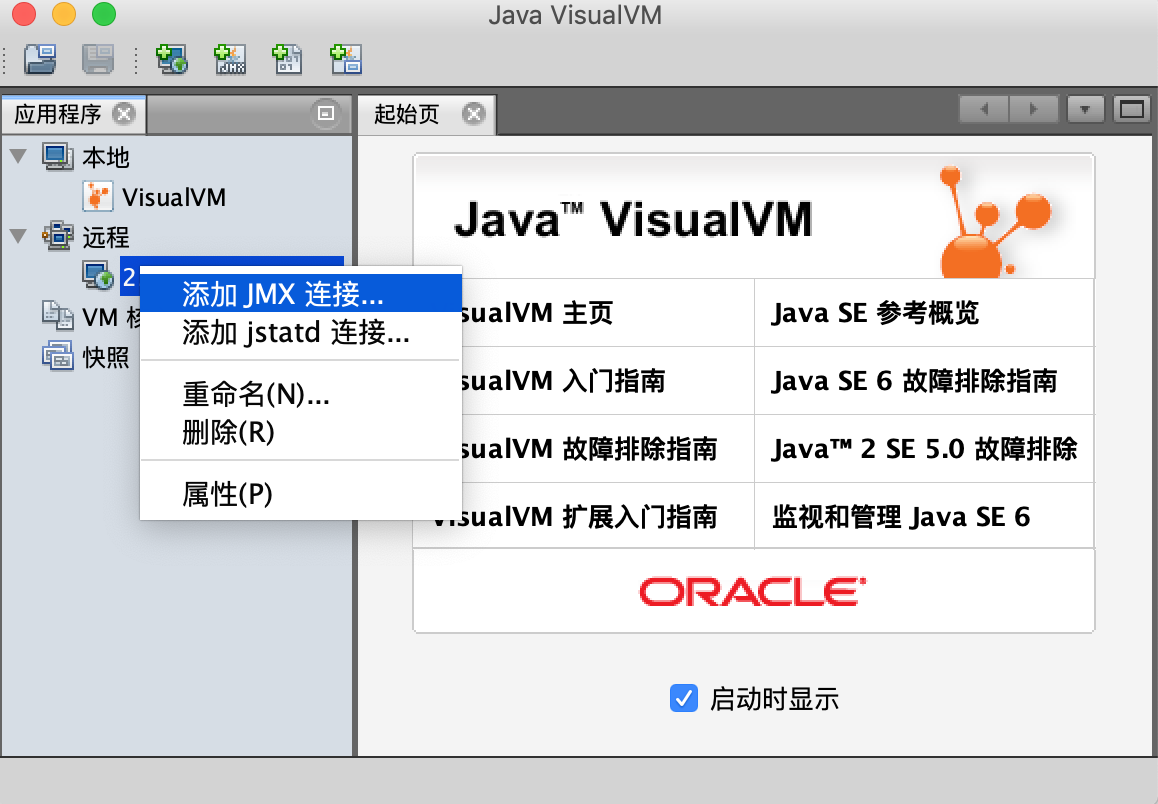
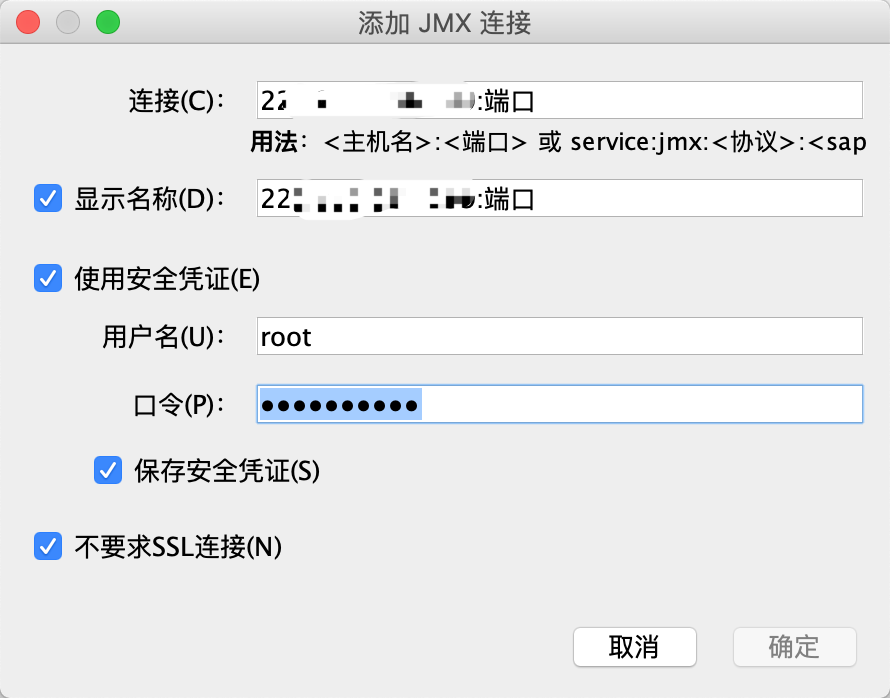
5.4、添加JMX连接,输入端口(本文1100)、用户名、密码,勾选不要求SSL。
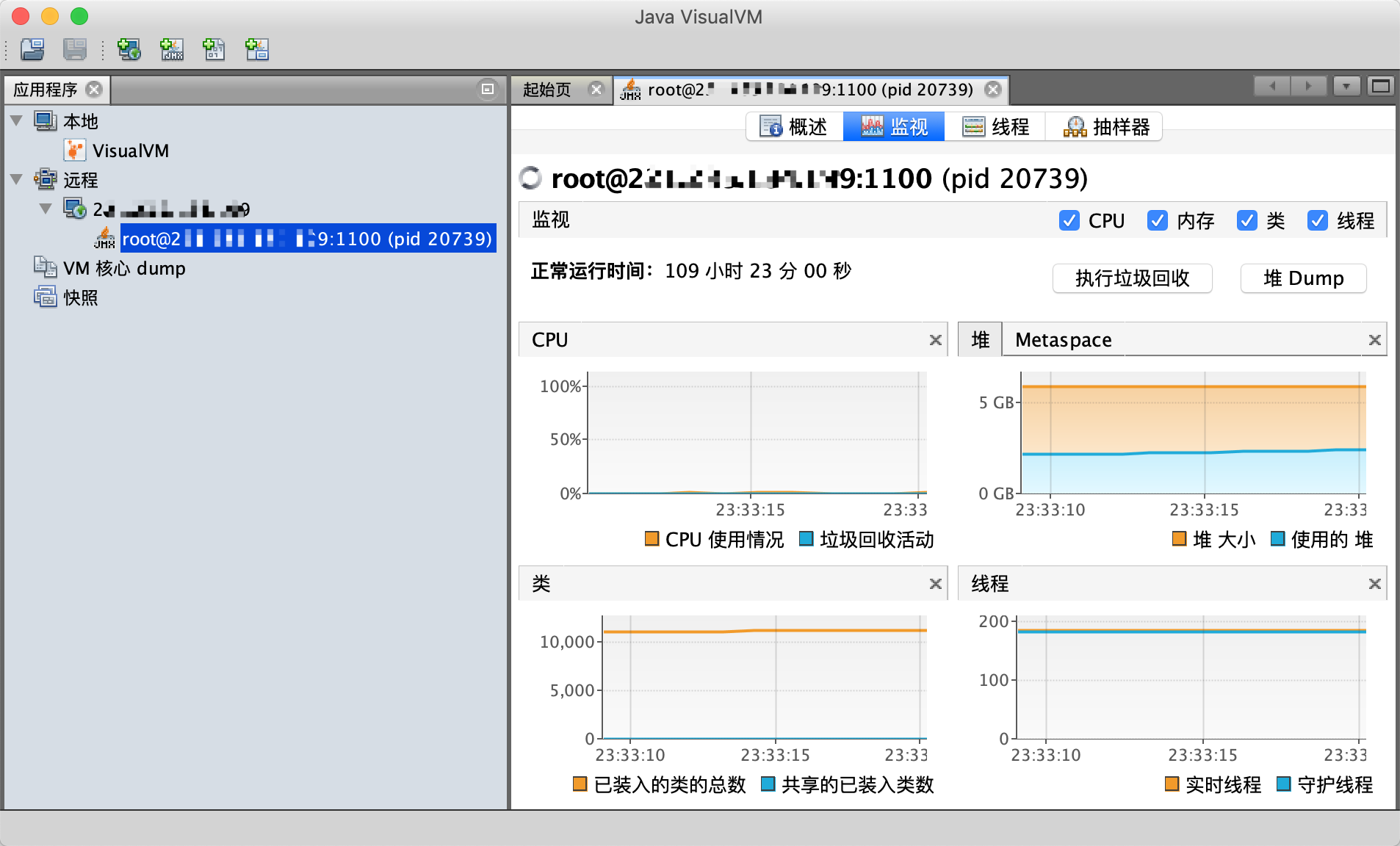
5.5、打开连接,查看监控信息。
六、JProfiler远程监控
6.1、下载JProfiler并安装
[root@localhost ~]# wget https://download-keycdn.ej-technologies.com/jprofiler/jprofiler_linux_9_1_1.rpm [root@localhsot ~]# yum -y install jprofiler_linux_9_1_1.rpm
6.2、下载并安装JProfile客户端,输入注册码
下载地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1o8kAHIi
https://download-keycdn.ej-technologies.com/jprofiler/jprofiler_windows-x64_9_1_1.exe https://download-keycdn.ej-technologies.com/jprofiler/jprofiler_windows-x64_9_1_1.zip
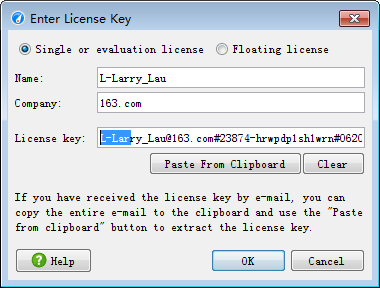
注册码:

L-Larry_Lau@163.com#23874-hrwpdp1sh1wrn#0620 L-Larry_Lau@163.com#36573-fdkscp15axjj6#25257 L-Larry_Lau@163.com#5481-ucjn4a16rvd98#6038 L-Larry_Lau@163.com#99016-hli5ay1ylizjj#27215 L-Larry_Lau@163.com#40775-3wle0g1uin5c1#0674 -------------------------------------------------------------- L-Larry_Lau@163.com#7009-14frku31ynzpfr#20176 L-Larry_Lau@163.com#49604-1jfe58we9gyb6#5814 L-Larry_Lau@163.com#25531-1qcev4yintqkj#23927 L-Larry_Lau@163.com#96496-1qsu1lb1jz7g8w#23479 L-Larry_Lau@163.com#20948-11amlvg181cw0p#171159
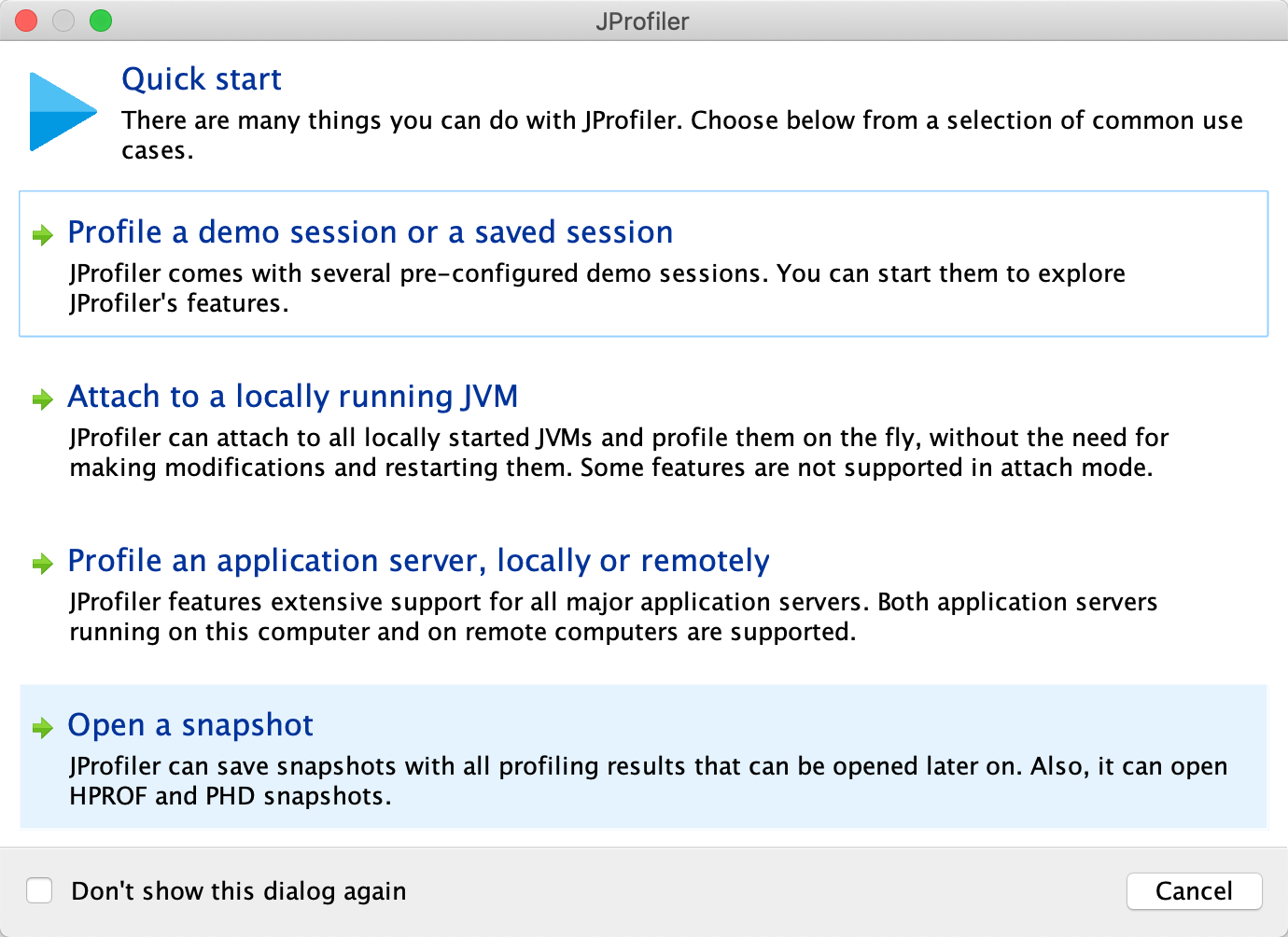
打开软件,选择 Pfofile an application server,locally or remotely
选择对应的Tomcat版本

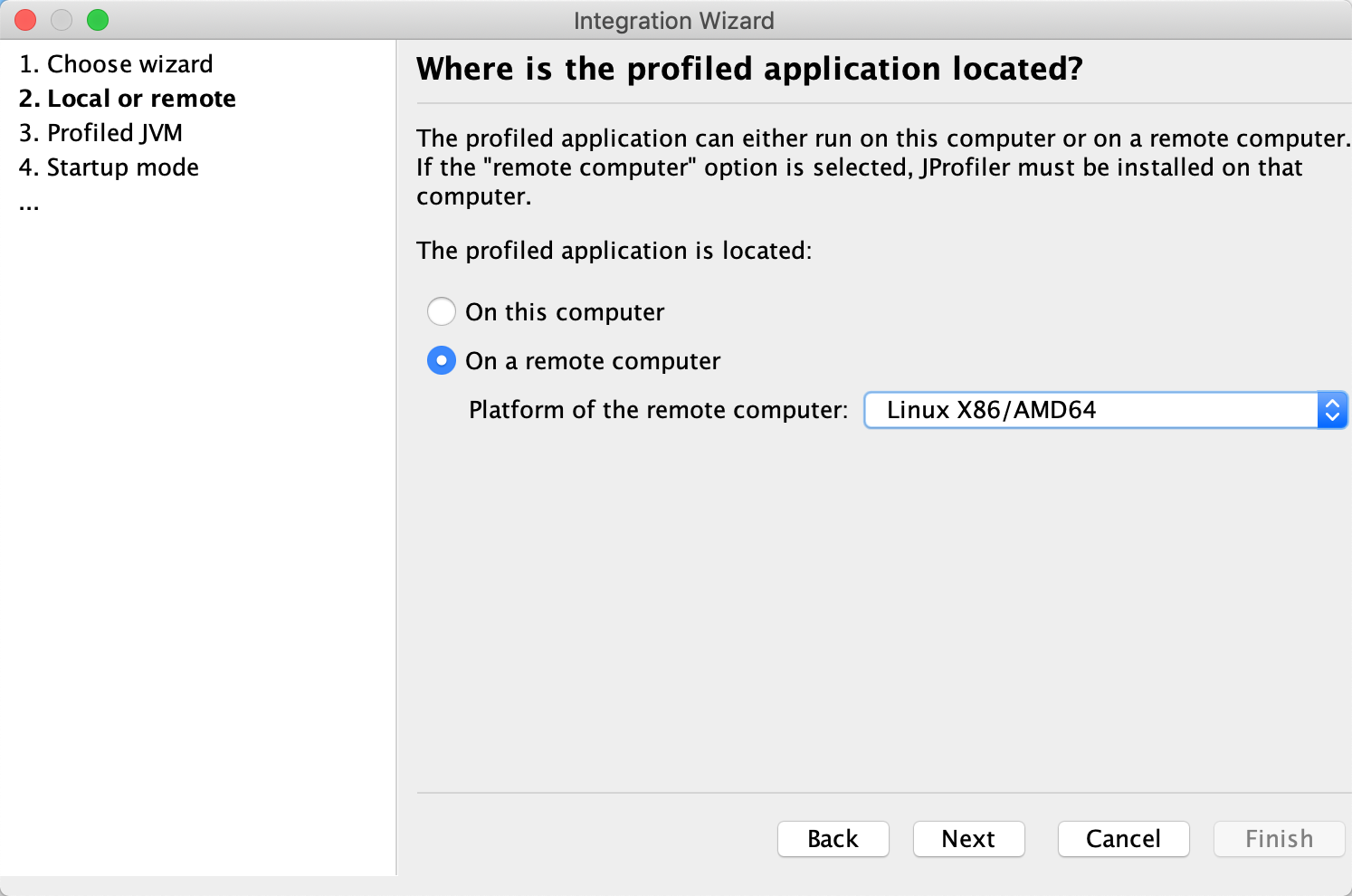
选择 On a remote computer, 服务器的系统版本
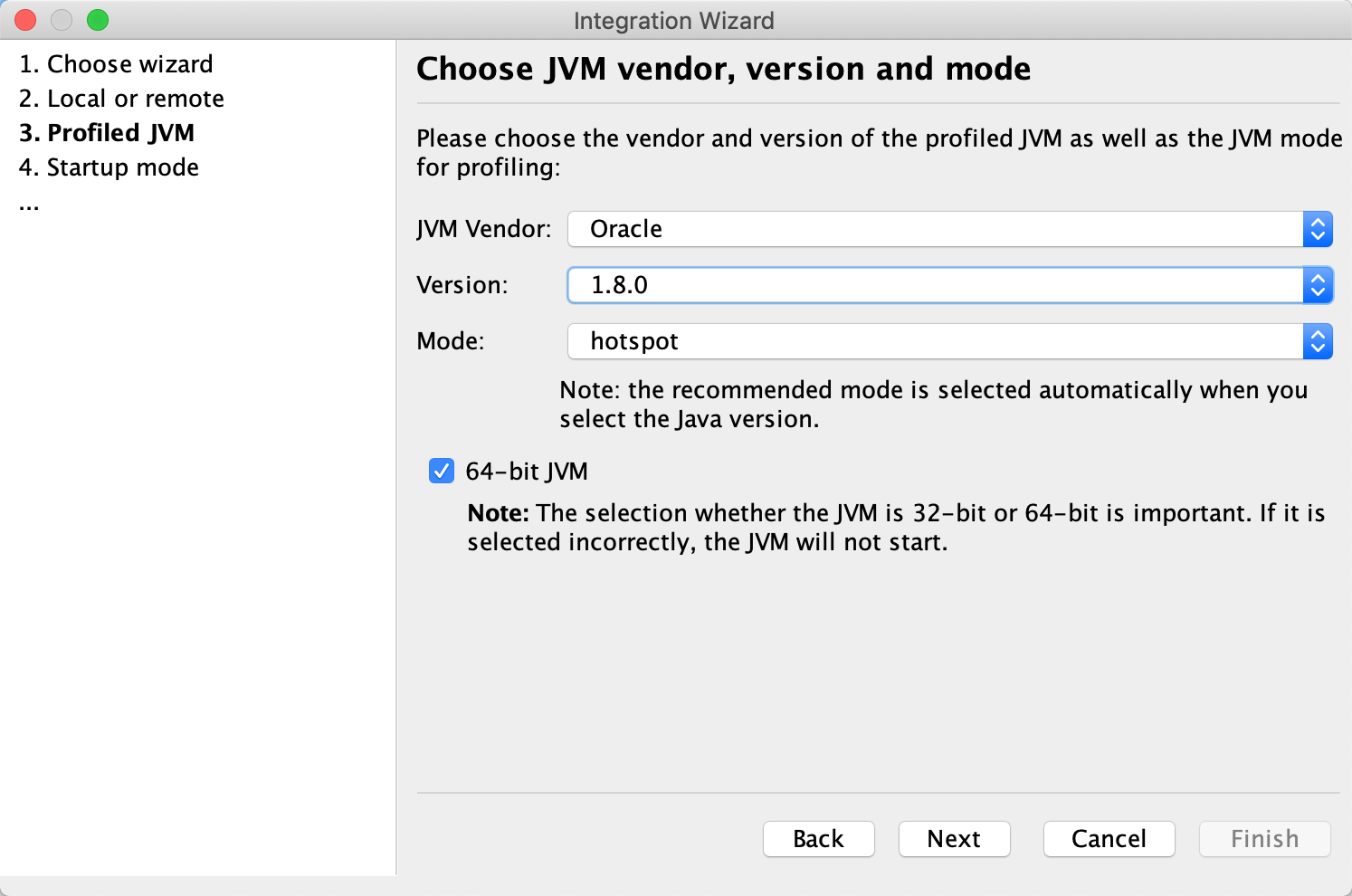
选择JAVA虚拟机的版本
选择稍后远程连接服务器

输入服务器域名或IP

输入服务器端JProfiler安装目录 /opt/jprofiler9

上传服务器Tomcat的startup.sh启动脚本
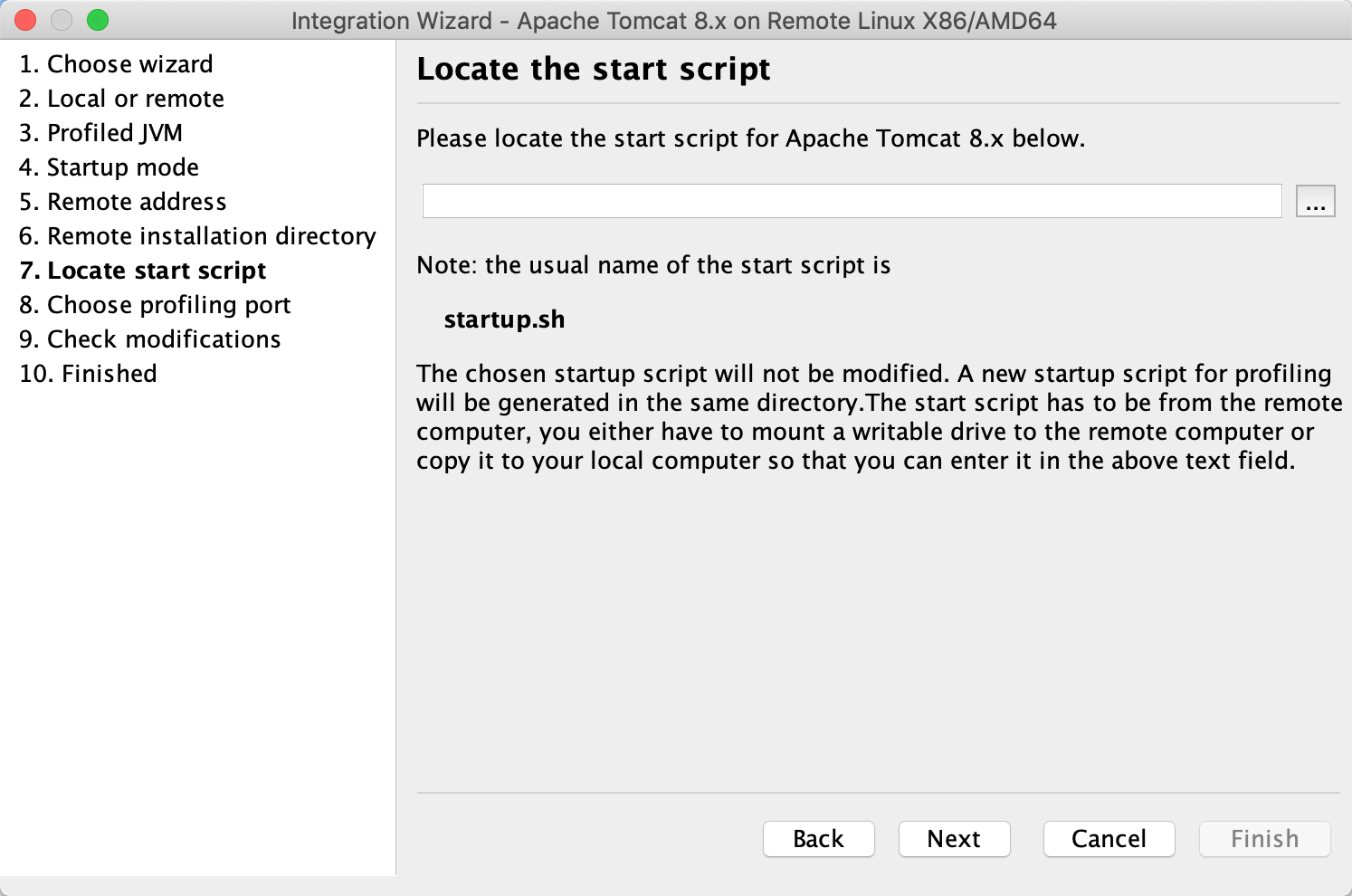
输入监控连接端口,默认即可
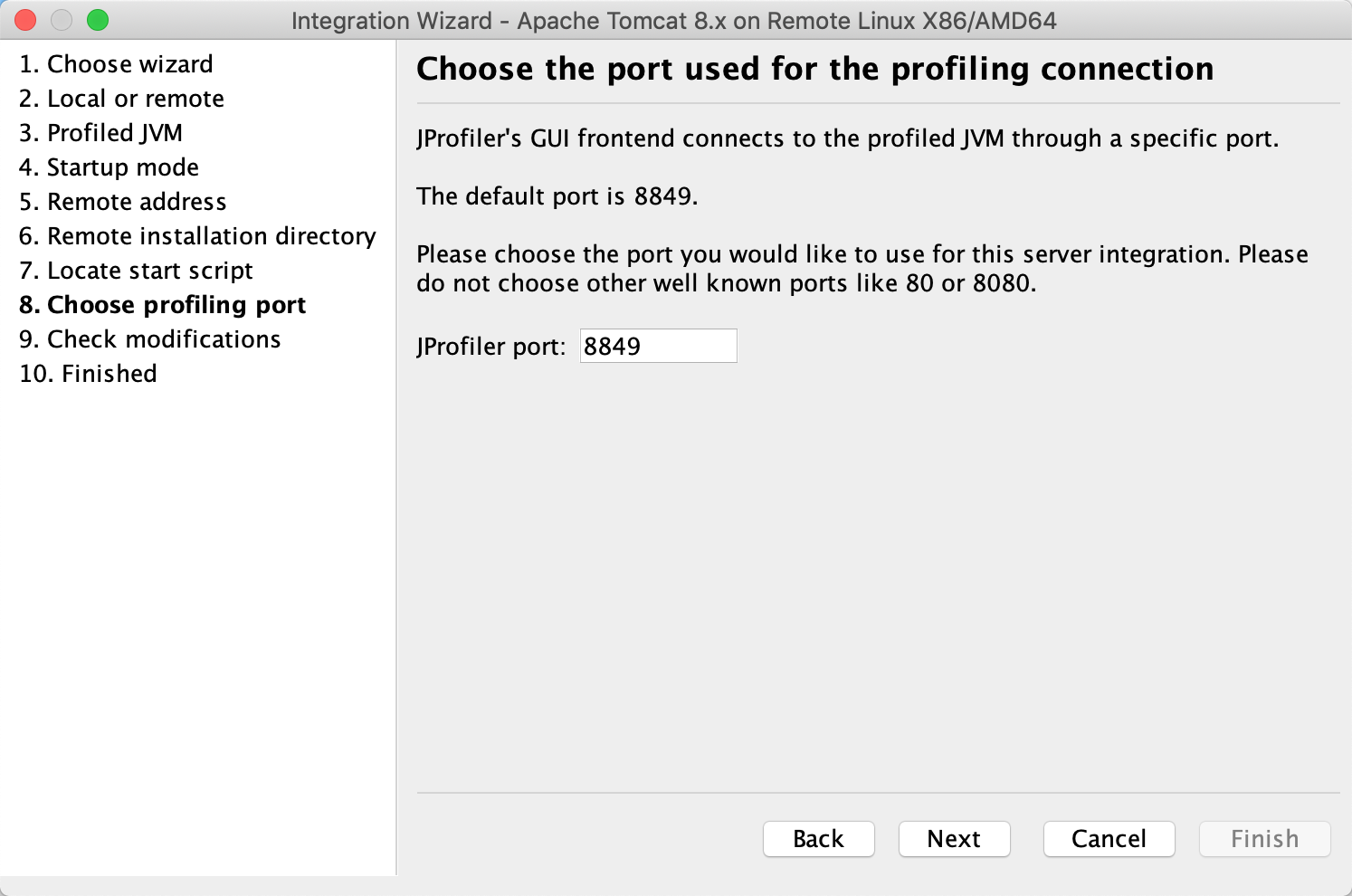
此时会在之前上传的startup.sh文件的同目录下生成一个startup_jprofiler.sh文件,把该文件上传至服务器的Tomcat的bin目录下,使用startup_jprofiler.sh启动Tomcat。
再打开软件JProfiler,选择刚刚设置的连接配置,进行远程监控操作。
查看线程情况, 选择左菜单Threads,选择颜色为红色的线程,右键菜单选择 Show Call Tree For Selected Thread。
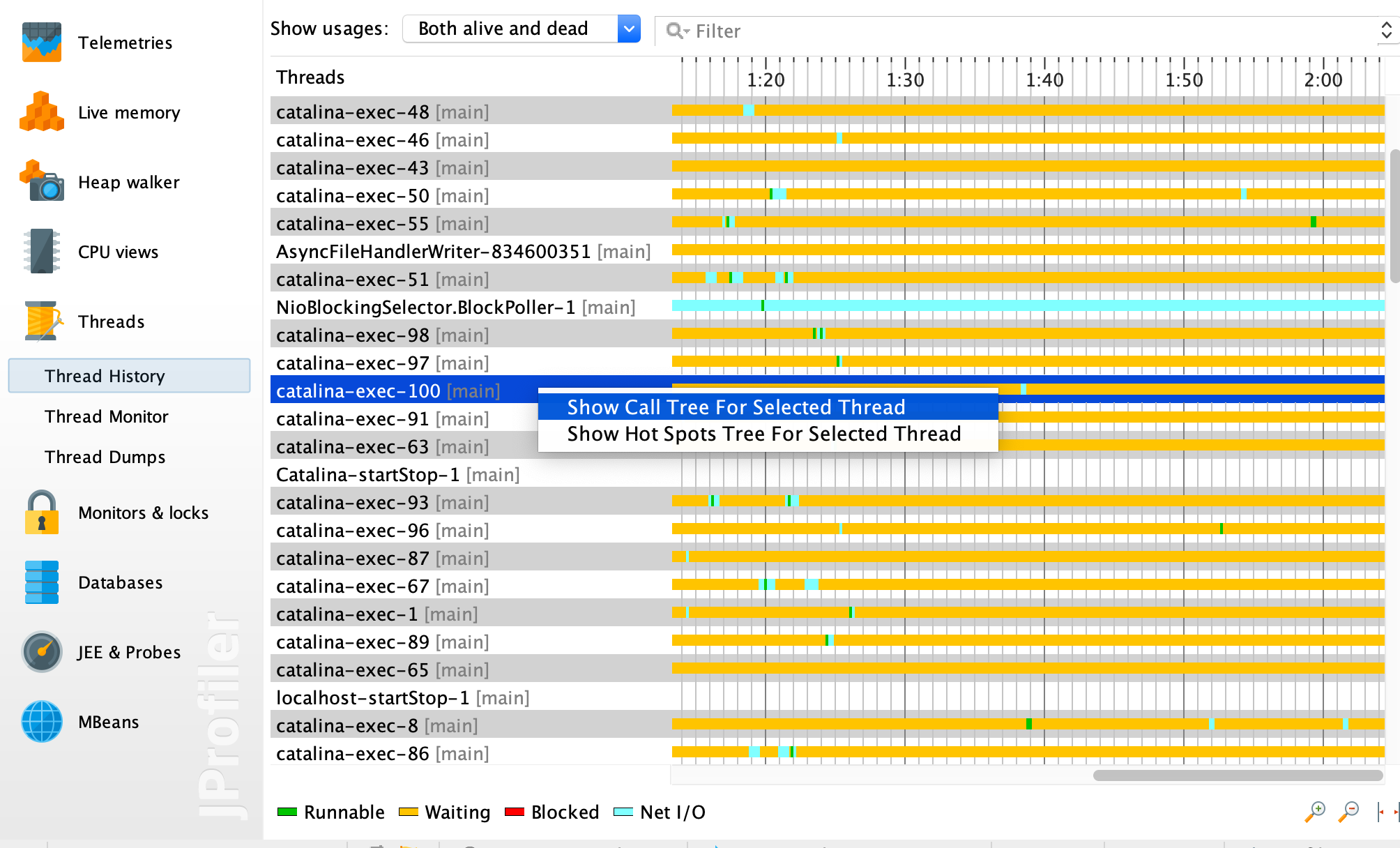
查看线程最耗时的操作是在哪个调用栈上,比对对应的源码,找到导致线程阻塞的原因。
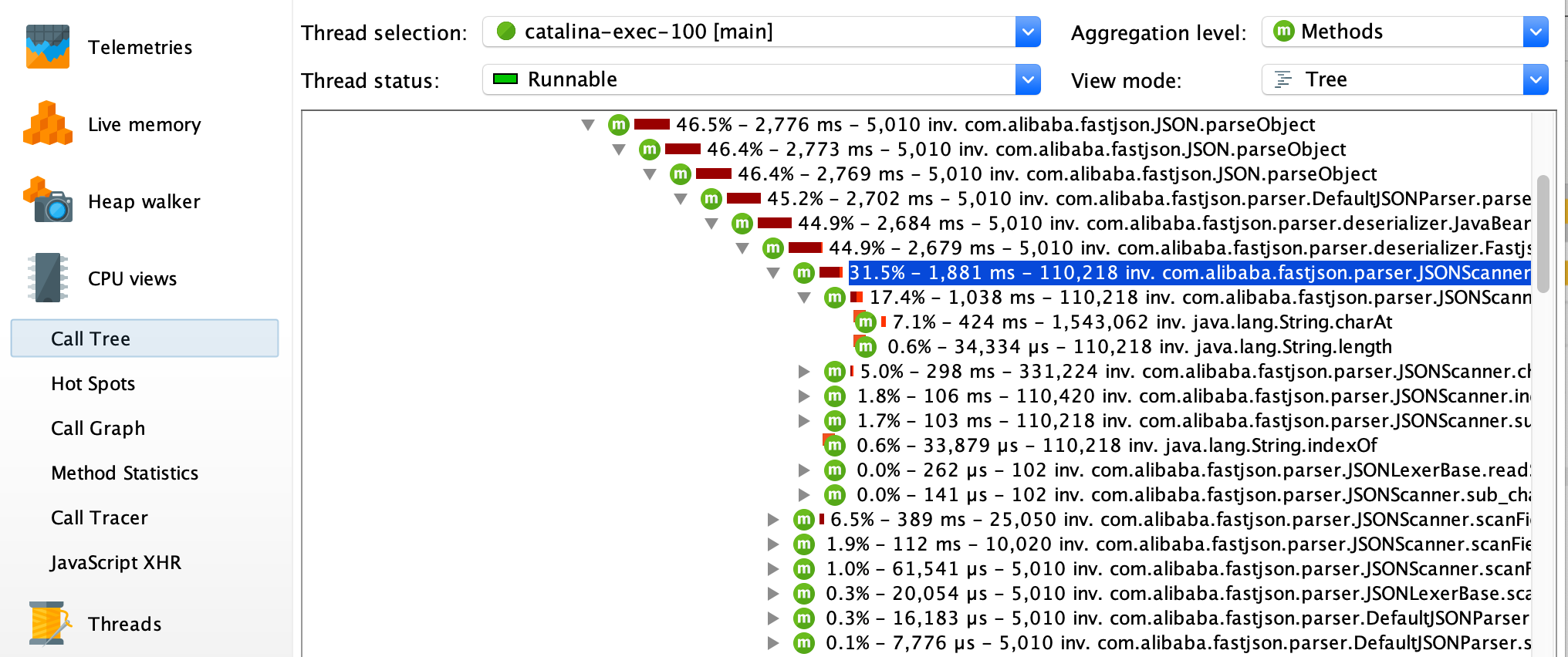
或者结合查看内存的使用情况,定位到是哪个类对象使用内存开销过大。

参考:Java性能分析神器-JProfiler详解 使用JProfiler进行内存分析
最后一步,使用webbench进行压力测试,使用监控工具分析应用的性能瓶颈或排查其他比如内存泄漏等程序问题。
PS:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/d59b3b971aa3
https://www.cnblogs.com/wuweidong/p/5815348.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号