linux系统库函数之memcpy
551 #ifndef __HAVE_ARCH_MEMCPY
552 /**
553 * memcpy - Copy one area of memory to another
554 * @dest: Where to copy to
555 * @src: Where to copy from
556 * @count: The size of the area.
557 *
558 * You should not use this function to access IO space, use memcpy_toio()
559 * or memcpy_fromio() instead.
560 */
561 void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t count)
562 {
563 char *tmp = dest;
564 const char *s = src;
565
566 while (count--)
567 *tmp++ = *s++;
568 return dest;
569 }
570 EXPORT_SYMBOL(memcpy);
552 /**
553 * memcpy - Copy one area of memory to another
554 * @dest: Where to copy to
555 * @src: Where to copy from
556 * @count: The size of the area.
557 *
558 * You should not use this function to access IO space, use memcpy_toio()
559 * or memcpy_fromio() instead.
560 */
561 void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t count)
562 {
563 char *tmp = dest;
564 const char *s = src;
565
566 while (count--)
567 *tmp++ = *s++;
568 return dest;
569 }
570 EXPORT_SYMBOL(memcpy);
571 #endif
memcpy函数是内存拷贝函数,用于将一段内存空间数据拷贝到另一段内存空间中,但是它和memmove函数不同的是,它对内存空间有要求的,dest和src所指向的内存空间不能重叠,否则的数据是错误的。
例如:
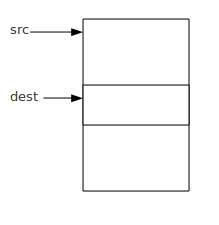
src所指向的内存空间后面部分数据被新拷贝的数据给覆盖了,所以拷贝到最后,数据肯定不是原来的数据。
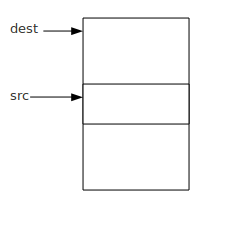
如果内存空间像上图所示,就不会导致数据拷贝错误这种情况,也就说你在使用这个函数之前,还需要做一个判断,如果dest < src你才能使用这个函数,不过完全没有必要,你直接使用另外一个函数memmove函数就可以了。


