Linux内核链表
Linux内核链表定义在include/linux/list.h文件中
链表结构定义
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
Linux内核链表它是一个双向循环链表,里面只包含两个struct list_head结构指针。
1. 链表初始化
链表初始化有两种方式:
(1)使用LIST_HEAD宏定义个头节点并初始化
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
next和prev指针都指向自己
(2)使用函数INIT_LIST_HEAD来初始化
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
这里只是对表头做初始化,让的next和prev指针指向自己。
2. 判断链表是否为空
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
通过判断它的next指针是否指向自己来判断链表是否为空
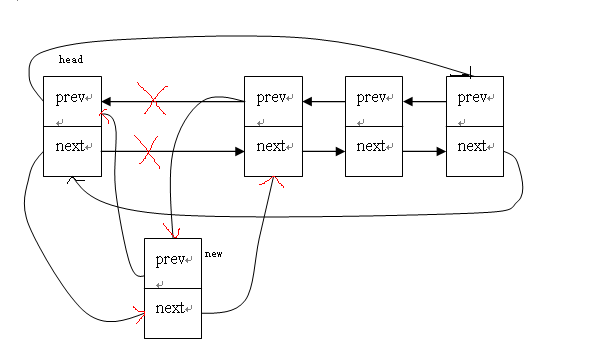
3. 插入
向一个链表插入有两种方式:一是在头节点后面插入新节点,二是在链表末尾插入新节点。
(1)在头节点后面插入新节点
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
(2)在链表末尾插入新节点
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}

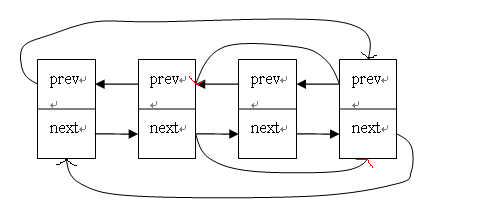
4. 删除
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
5. 遍历
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
从头节点的下一个节点开始遍历,一直末尾。


