Springboot+swagger2.7集成开发
Springboot+swagger2.7集成开发
Springboot+swagger2.7集成开发
本篇文章是介绍最新的springboot和swagger2.7集成开发和2.0稍微有一些出入:
- Springboot集成环境配置
- Swagger2.7集成
- 集成测试
Springboot集成环境配置
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。 —— [ INFO深入学习]
代码块
开发Spring Boot应用,例如:
@RestController class App { @RequestMapping("/") String home() { "hello" } }
引入SpringBoot的JAR文件.
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.2.7.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency>
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @EnableAutoConfiguration public class Example { @RequestMapping("/") String index() { return "Hello World!"; } @RequestMapping("/index/{sayHello}") String index(@PathVariable String sayHello) { return "Hello "+sayHello+"!!!"; } }
application.hellowmsg=Hello World server.port=8081 #端口 logging.level.=INFO
编制Application.java
@EnableScheduling @EnableTransactionManagement @SpringBootApplication public class App extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(App.class); app.setWebEnvironment(true); app.setShowBanner(false); Set<Object> set = new HashSet<Object>(); // set.add("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); app.setSources(set); app.run(args); }
运行Application.java
看到
2017-11-15 16:14:08.391 INFO 12524 --- [ main] s.d.s.w.s.ApiListingReferenceScanner : Scanning for api listing references
2017-11-15 16:14:08.607 INFO 12524 --- [ main] s.b.c.e.t.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8081 (http)
并没有出错,表示成功,直接访问http://localhost:8081/,输出Hello World!
Swagger2.7集成
加入maven的仓库文件
<!--swagger2 integration -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
创建SwaggerConfig的配置文件
import static com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import com.fasterxml.classmate.TypeResolver; import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder; import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors; import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors; import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo; import springfox.documentation.service.ApiKey; import springfox.documentation.service.AuthorizationScope; import springfox.documentation.service.SecurityReference; import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType; import springfox.documentation.spi.service.contexts.SecurityContext; import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket; import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2; @Configuration @EnableSwagger2 @ConfigurationProperties public class SwaggerConfig { @Value("${swagger.version}") private String version; @Autowired private TypeResolver typeResolver; @Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.hp.ctrl")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()).build().apiInfo(apiInfo()); } private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder().title("构建RESTful APIs").description("更多请关注:http://my.csdn.net/elvishehai") .license("The Apache License, Version 2.0") .licenseUrl("http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html").termsOfServiceUrl("http://my.csdn.net/elvishehai") .version(version).build(); } }
下一步写REST的COTR
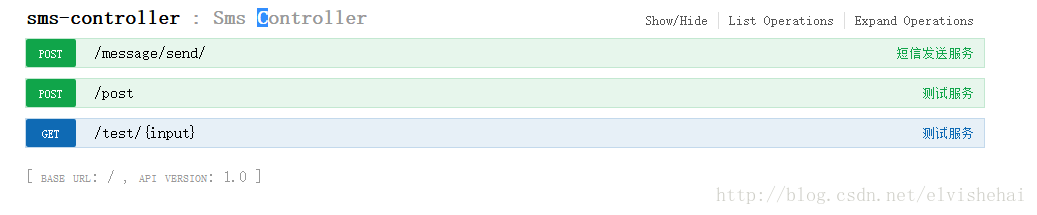
@Api(value = "API - SMSController")
@RestController
public class SmsController {
@ApiOperation(value = "测试服务", notes = "测试服务")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "smsRequestBean", value = "用户详细实体SmsRequestBean", required = true, dataType = "SmsRequestBean")
@RequestMapping(value = "/post", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String post(@RequestBody SmsRequestBean smsRequestBean) {
return "服务测试成功,你输入的参数为:" + smsRequestBean.getApplicationId();
}
@ApiOperation(value = "测试服务", notes = "测试服务", consumes = "application/json", produces = "application/json")
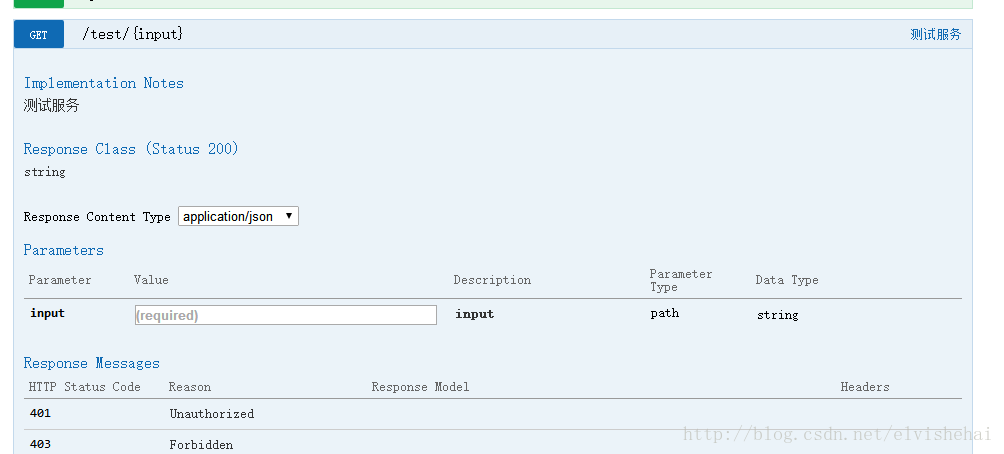
@RequestMapping(value = "/test/{input}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getUser(@PathVariable("input") String input) {
return "服务测试成功,你输入的参数为:" + input;
}
}
- swagger通过注解表明该接口会生成文档,包括接口名、请求方法、参数、返回信息的等等。
- @Api:修饰整个类,描述Controller的作用
- @ApiOperation:描述一个类的一个方法,或者说一个接口
- @ApiParam:单个参数描述
- @ApiModel:用对象来接收参数
- @ApiProperty:用对象接收参数时,描述对象的一个字段
- @ApiResponse:HTTP响应其中1个描述
- @ApiResponses:HTTP响应整体描述
- @ApiIgnore:使用该注解忽略这个API
- @ApiError :发生错误返回的信息
- @ApiParamImplicitL:一个请求参数
- @ApiParamsImplicit 多个请求参数
运行application.java
在浏览器上输入http://localhost:8081/swagger-ui.html
可以看到上面,测试就成功。
在上图请求的页面中,我们看到user的Value是个输入框?是的,Swagger除了查看接口功能外,还提供了调试测试功能,我们可以点击上图中右侧的Model Schema(黄色区域:它指明了User的数据结构),此时Value中就有了user对象的模板,我们只需要稍适修改,点击下方“Try it out!”按钮,即可完成了一次请求调用!
此时,你也可以通过几个GET请求来验证之前的POST请求是否正确。
相比为这些接口编写文档的工作,我们增加的配置内容是非常少而且精简的,对于原有代码的侵入也在忍受范围之内。因此,在构建RESTful API的同时,加入swagger来对API文档进行管理,是个不错的选择。
+参考信息
http://swagger.io/ Swagger官方网站



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号