OVS内核流表查询过程
概括
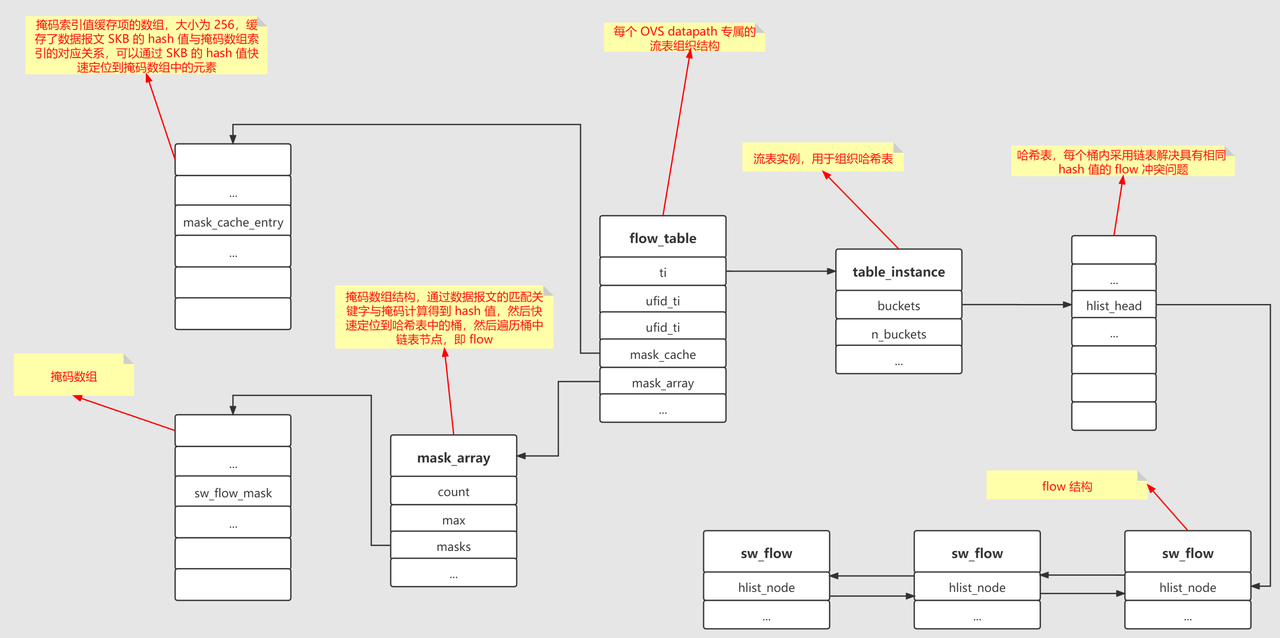
现在的OVS使用microflow+megaflow缓存查询流表,ovs整体流程是从ovs_vport_receive(datapath/vport.c)开始,然后进入ovs_dp_process_packet(datapath/datapath.c),这个时候调用ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats(datapath/flow_table.c)开始查,查microflow获得mask_array里的索引索找到mask,通过mask去找megaflow里的掩码元素,再去定位哈希桶,如果没找到就upcall去用户态:
- 查找 microflow 缓存:根据数据报文 SKB 的 hash 值,定位到 mask_cache_entry 数组中的某个元素,并得到该元素缓存的掩码数组索引值;
- 查找 megaflow 缓存:根据步骤 1 中查找到的掩码数组索引值,定位到掩码数组中的某个元素,并得到该元素的掩码,然后根据掩码定位到具体的哈希桶,并遍历该哈希桶中的所有节点,直到找到匹配的 flow。
说的是流表过程,所以就从ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats开始。
正文
查找 microflow 缓存
OVS 内核态流表查找的入口函数是定义在 datapath/flow_table.c 文件中的,在ovs_dp_process_packet里调用: flow = ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats(&dp->table, key, skb_get_hash(skb), &n_mask_hit);
struct sw_flow *ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats(struct flow_table *tbl,
const struct sw_flow_key *key,
u32 skb_hash,
u32 *n_mask_hit)
{
struct mask_array *ma = rcu_dereference(tbl->mask_array);
struct table_instance *ti = rcu_dereference(tbl->ti);
struct mask_cache_entry *entries, *ce;
struct sw_flow *flow;
u32 hash;
int seg;
*n_mask_hit = 0;
if (unlikely(!skb_hash)) {
u32 mask_index = 0;
return flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit, &mask_index);
}
/* Pre and post recirulation flows usually have the same skb_hash
* value. To avoid hash collisions, rehash the 'skb_hash' with
* 'recirc_id'. */
if (key->recirc_id)
skb_hash = jhash_1word(skb_hash, key->recirc_id);
ce = NULL;
hash = skb_hash;
entries = this_cpu_ptr(tbl->mask_cache);
/* Find the cache entry 'ce' to operate on. */
for (seg = 0; seg < MC_HASH_SEGS; seg++) {
int index = hash & (MC_HASH_ENTRIES - 1);
struct mask_cache_entry *e;
e = &entries[index];
if (e->skb_hash == skb_hash) {
flow = flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit,
&e->mask_index);
if (!flow)
e->skb_hash = 0;
return flow;
}
if (!ce || e->skb_hash < ce->skb_hash)
ce = e; /* A better replacement cache candidate. */
hash >>= MC_HASH_SHIFT;
}
/* Cache miss, do full lookup. */
flow = flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit, &ce->mask_index);
if (flow)
ce->skb_hash = skb_hash;
return flow;
}ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats() 的函数参数如下:
- tbl:类型为 struct flow_table,表示专属于每个 datapath 的流表组织结构;
- key:类型为 struct sw_flow_key,表示从数据报文提取出来的匹配关键字;
- skb_hash:表示数据报文 SKB 的 hash 值;
- n_mask_hit:输出参数,表示尝试匹配掩码的次数。
1.当skb_hash为0的时候,完全查找mask_array表,不更新cache
// 如果 skb_hash 为 0,则 full lookup
if (unlikely(!skb_hash)) {
u32 mask_index = 0;
return flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit, &mask_index);
}
// 当数据报文需要在 OVS 中重新进入流水线
if (key->recirc_id)
skb_hash = jhash_1word(skb_hash, key->recirc_id);这里说的不更新的:因为skb_hash默认就是0,如果找到了,更不更新都是0,没找到就更不影响了
2.找到mask_cache_entry存在mask_index
ce = NULL;
hash = skb_hash;
// mask_cache_entry 数组,大小为 256,即 microflow cache
// 获取当前cpu的mash_cache
entries = this_cpu_ptr(tbl->mask_cache);
/* Find the cache entry 'ce' to operate on. */
// 将 hash 分为 4 个字节,从低到高的顺序,进行查找,这样一个hash可以用4个桶,效率高
//MC_HASH_SEGS = 4
for (seg = 0; seg < MC_HASH_SEGS; seg++) {
//MC_HASH_ENTRIES = 256
int index = hash & (MC_HASH_ENTRIES - 1); // 255是8位1,这样就是获得最后8位(1字节)
struct mask_cache_entry *e;
e = &entries[index];
if (e->skb_hash == skb_hash) {
flow = flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit,
&e->mask_index);
if (!flow)
e->skb_hash = 0;
return flow;
}
// 选出 4 个字节中 skb hash 值最小的那个,作为没找到缓存时的最佳候选
if (!ce || e->skb_hash < ce->skb_hash)
ce = e; /* A better replacement cache candidate. */
// MC_HASH_SHIFT = 8
hash >>= MC_HASH_SHIFT;
}主要说一下hash:
32位的hash值,变成4个8位,正好是mask_cache_entry[256]大小,相当于一个hash值对应4个桶的位置,有一个匹配就行,这种好处就是减小hash冲突的覆盖,如果4个桶都没有匹配,就找一个的最小的mask_cache_entry->skb_hash,更新这个mask_cache_entry。
3.没找到mask_cache_entry就遍历找mask_array表,并且更新
flow = flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit, &ce->mask_index);
if (flow)
ce->skb_hash = skb_hash;
flow_lookup里:
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit);
if (flow) { /* Found */
*index = i;
return flow;
}首先是更新mask_index,传的就是地址,在flow_lookup里会更新。如果找到了flow,把skb_hash更新一下就行了。这整个过程就是相当于一级缓存。
查找 megaflow 缓存
查找 megaflow 缓存的入口函数是定义在 datapath/flow_table.c 文件中的 flow_lookup 函数:
static struct sw_flow *flow_lookup(struct flow_table *tbl,
struct table_instance *ti,
const struct mask_array *ma,
const struct sw_flow_key *key,
u32 *n_mask_hit,
u32 *index)
{
struct sw_flow_mask *mask;
struct sw_flow *flow;
int i;
if (*index < ma->max) {
mask = rcu_dereference_ovsl(ma->masks[*index]);
if (mask) {
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit);
if (flow)
return flow;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < ma->max; i++) {
if (i == *index)
continue;
mask = rcu_dereference_ovsl(ma->masks[i]);
if (!mask)
continue;
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit);
if (flow) { /* Found */
*index = i;
return flow;
}
}
return NULL;
}1.传进来的mask_array索引值index有效
// 根据传入的 index 获取到掩码数组的掩码,根据该掩码进行查找
if (*index < ma->max) {
// 从掩码数组里获取掩码
mask = rcu_dereference_ovsl(ma->masks[*index]);
if (mask) {
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit);
if (flow)
return flow;
}
}index在掩码数组的范围内,先通过rcu_dereference_ovsl获取mask,然后看能否找到flow,找到了就可以返回了。真正进行megaflow查询的是masked_flow_lookup函数,下边讲。
2.索引值index无效,就遍历每个mask_array
for (i = 0; i < ma->max; i++) {
if (i == *index) // 刚才已经查找过
continue;
mask = rcu_dereference_ovsl(ma->masks[i]); // 从掩码数组里获取掩码
if (!mask)
continue;
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit);
if (flow) { /* Found */
*index = i; // 找到了就更新mask_cache_entry
return flow;
}
}真正查找megaflow的函数:masked_flow_lookup()
static struct sw_flow *masked_flow_lookup(struct table_instance *ti,
const struct sw_flow_key *unmasked,
const struct sw_flow_mask *mask,
u32 *n_mask_hit)
{
struct sw_flow *flow;
struct hlist_head *head;
u32 hash;
struct sw_flow_key masked_key;
// 根据mask,计算masked后的key,用以支持通配符
ovs_flow_mask_key(&masked_key, unmasked, false, mask);
// 根据masked key和mask.range 计算hash值
hash = flow_hash(&masked_key, &mask->range);
// 根据hash值,找到sw_flow的链表头
head = find_bucket(ti, hash);
// mask命中次数+1
(*n_mask_hit)++;
// 遍历链表,解决hash冲突用的拉链法,所以是一条链
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(flow, head, flow_table.node[ti->node_ver]) {
// mask相同、hash相同并且key相同,则匹配到流表
if (flow->mask == mask && flow->flow_table.hash == hash &&
flow_cmp_masked_key(flow, &masked_key, &mask->range))
return flow;
}
return NULL;
}find_bucket 函数
static struct hlist_head *find_bucket(struct table_instance *ti, u32 hash)
{
hash = jhash_1word(hash, ti->hash_seed);
return &ti->buckets[hash & (ti->n_buckets - 1)]; // hash的低N位作为index
}这样就找到了flow
缓存没有命中
直接看datapath.c

未命中就会执行upcall了



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 2025年我用 Compose 写了一个 Todo App
· 张高兴的大模型开发实战:(一)使用 Selenium 进行网页爬虫