CVE-2019-0230 s2-059 漏洞分析
0x01 问题原因
Apache Struts 框架在强制时对分配给某些标记属性的属性值执行双重计算,以便可以传递一个值,该值将在呈现标记的属性时再次计算。对于精心设计的请求,这可能会导致远程代码执行 (RCE)。
只有在 Struts 标记属性内强制使用OGNL表达式时,当表达式用于计算攻击者可以通过创建相应请求直接修改的原始未验证输入时,问题才适用。
0x02 例子
<s:url var="url" namespace="/employee" action="list"/><s:a id="%{skillName}" href="%{url}">List available Employees</s:a>
如果攻击者能够修改请求中的属性,使原始 OGNL 表达式传递到属性而无需进一步验证,则当作为请求呈现标记时,属性中包含的提供的 OGNL 表达式将计算。
0x03 影响范围
Struts 2.0.0 - Struts 2.5.20
官方建议升级到2.5.22以后。
0x04 环境
- tomcat7
- jk8
- struts2.3.7-src
0x05 源码部署
在showcase项目中,在首页showcase.jsp的head标签中加入
<head>
<title>Struts2 Showcase</title>
<%-- <s:head theme="simple"/>--%>
<s:a id="%{1+1}" href="xxx.jsp"></s:a>
</head>
在struts项目中,view里需要加入<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>才可解析jsp里的struts标签。
参考https://blog.csdn.net/sho_ko/article/details/84175306对struts的标签源码解析过程。
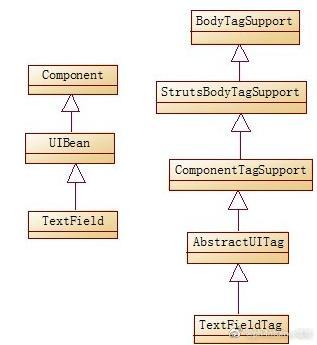
当用户发出请求时,doStartTag()开始执行,首先就调用getBean获取对应的标签组件类实例,构造函数参数值栈stack由基类StrutsBodyTagSupport的getStack()获得,request和response对象在PageContext实例中获取。然后调用populateParams();进行初始参数值的填充,populateParams()也将调用具体类中的populateParams()对自己的属性成员进行初始化。
所以我们直接debug断点在解析标签的ComponentTagSupport类的doStartTag()函数的第一行。

可以看到this的href属性就是xxx.jsp,因为文章说的在this.populateParams();里进行填充,所以我们跟进populateParams()看看,一直到抽象类的父类AbstractUITag类的populateParams操作里看到了uiBean.setId(this.id);,对id里的值进行了填充。

通过该类:
UIBean uiBean = (UIBean)this.component;
uiBean.setCssClass(this.cssClass);
uiBean.setCssStyle(this.cssStyle);
uiBean.setCssErrorClass(this.cssErrorClass);
uiBean.setCssErrorStyle(this.cssErrorStyle);
uiBean.setTitle(this.title);
uiBean.setDisabled(this.disabled);
uiBean.setLabel(this.label);
uiBean.setLabelSeparator(this.labelSeparator);
uiBean.setLabelposition(this.labelposition);
uiBean.setRequiredPosition(this.requiredPosition);
uiBean.setErrorPosition(this.errorPosition);
uiBean.setName(this.name);
uiBean.setRequiredLabel(this.requiredLabel);
uiBean.setTabindex(this.tabindex);
uiBean.setValue(this.value);
uiBean.setTemplate(this.template);
uiBean.setTheme(this.theme);
uiBean.setTemplateDir(this.templateDir);
uiBean.setOnclick(this.onclick);
uiBean.setOndblclick(this.ondblclick);
uiBean.setOnmousedown(this.onmousedown);
uiBean.setOnmouseup(this.onmouseup);
uiBean.setOnmouseover(this.onmouseover);
uiBean.setOnmousemove(this.onmousemove);
uiBean.setOnmouseout(this.onmouseout);
uiBean.setOnfocus(this.onfocus);
uiBean.setOnblur(this.onblur);
uiBean.setOnkeypress(this.onkeypress);
uiBean.setOnkeydown(this.onkeydown);
uiBean.setOnkeyup(this.onkeyup);
uiBean.setOnselect(this.onselect);
uiBean.setOnchange(this.onchange);
uiBean.setTooltip(this.tooltip);
uiBean.setTooltipConfig(this.tooltipConfig);
uiBean.setJavascriptTooltip(this.javascriptTooltip);
uiBean.setTooltipCssClass(this.tooltipCssClass);
uiBean.setTooltipDelay(this.tooltipDelay);
uiBean.setTooltipIconPath(this.tooltipIconPath);
uiBean.setAccesskey(this.accesskey);
uiBean.setKey(this.key);
uiBean.setId(this.id);
uiBean.setDynamicAttributes(this.dynamicAttributes);
进入setId操作

public void setId(String id) {
if (id != null) {
this.id = this.findString(id);
}
}
跟进findString:
protected String findString(String expr) {
return (String)this.findValue(expr, String.class);
}
在跟进findValue:
protected Object findValue(String expr, Class toType) {
if (this.altSyntax() && toType == String.class) {
return ComponentUtils.containsExpression(expr) ? TextParseUtil.translateVariables('%', expr, this.stack) : expr;
} else {
expr = this.stripExpressionIfAltSyntax(expr);
return this.getStack().findValue(expr, toType, this.throwExceptionOnELFailure);
}
}
然后可以看到TextParseUtil类了,根据if条件可知,this.altSyntax()需要ture,默认是true的。
所以默认是进入TextParseUtil.translateVariables('%', expr, this.stack)。
一直跟入,来到translateVariables

在这个while里,
while(true) {
int start = expression.indexOf(lookupChars, pos);
if (start == -1) {
++loopCount;
start = expression.indexOf(lookupChars);
}
if (loopCount > maxLoopCount) {
break;
}

在 Object o = evaluator.evaluate(var);里进行了值计算,

但是如果%{%{1+1}+1},

因为start=-1,所以执行++loopCount,
因为loopCount=2>maxLoopCount=1,所以会break这个while,导致不能执行Object o = evaluator.evaluate(var);,所以会返回值为空。
这是一个埋点。
所以我们继续追踪,来到boolean evalBody = this.component.start(this.pageContext.getOut());

我们看下这时的this.component变量,

可以看到id已经计算出来了。
进入start函数,最终来到:
public boolean start(Writer writer) {
boolean result = super.start(writer);
try {
this.evaluateParams();
this.mergeTemplate(writer, this.buildTemplateName(this.openTemplate, this.getDefaultOpenTemplate()));
} catch (Exception var4) {
LOG.error("Could not open template", var4, new String[0]);
}
进入evaluateParams,

可以看到大量熟悉的findString函数,也就是说这边是有可能再次进行ognl表达式计算的。
一路跟踪:

进入this.populateComponentHtmlId(form);
protected void populateComponentHtmlId(Form form) {
String tryId;
if (this.id != null) {
tryId = this.findStringIfAltSyntax(this.id);
} else {
String generatedId;
if (null == (generatedId = this.escape(this.name != null ? this.findString(this.name) : null))) {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Cannot determine id attribute for [#0], consider defining id, name or key attribute!", new Object[]{this});
}
tryId = null;
} else if (form != null) {
tryId = form.getParameters().get("id") + "_" + generatedId;
} else {
tryId = generatedId;
}
}

来到tryId = this.findStringIfAltSyntax(this.id);

因为altSyntax()默认true,所以来到熟悉的findString计算操作。所以this.id在第一次ognl计算成功后还会进行一次ognl计算,假如第一次ognl计算表达式的结果是%{1+2},

那么此处就存在一定的风险。但是实际情况下,不管是第一次ognl计算还是第二次ognl计算,均都没法执行复杂计算。等有进一步的poc消息。


