C# 通过P/Invoke调用C/C++函数
公共语言运行库 (CLR) 的 interop 功能(称为平台调用 (P/Invoke)),可以使用 P/Invoke 来调用 Windows API 函数。P/Invoke简介
官网:Marshaling Data with Platform Invoke 包含平台调用类型转换
动态链接库,windows环境的格式是.dll,linux环境的是.so。 不能引用静态库.lib 或 .a
引用的时候,[DllImport("Test.dll", EntryPoint = "sum")]
可以简写为Test,
[DllImport("Test", EntryPoint = "sum")]
windows环境下自动取寻找Test.dll,Linux环境下自动寻找 libTest.so
一、VS 用 C++ 创建动态链接库
- 创建Win32 Console Application。本例中我们创建一个叫做“Test”的Solution。
- 将Application Type设定为DLL。在接下来的 Win32 Application Wizard 的 Application Settings 中,将 Application type 从 Console application 改为 DLL:
- 将方法暴露给DLL接口。现在在这个Solution中,目录和文件结构是这样的:
编辑 Test.cpp 如下:
#include "stdafx.h" extern "C" { _declspec(dllexport) int sum(int a, int b) { return a + b; } }
Step 4:编译
直接编译即可。
二、在C#中通过P/Invoke调用Test.dll中的sum()方法
P/Invoke很简单。请看下面这段简单的C#代码:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; namespace CSharpusedll { class Program { [DllImport("Test.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)] private static extern int sum(int a, int b); //加属性CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl,否则发生错误“托管的PInvoke签名与非托管的目标签名不匹配” static void Main(string[] args) { int result = sum(2, 3); Console.WriteLine("DLL func execute result: {0}", result); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
编译并执行这段C#程序,执行时别忘了把Test.dll拷贝到执行目录(Debug)中。
注:函数的参数名可以与C++中定义的不一样,类型和参数个数一致即可。
也可加EntryPoint属性,这样提供一个入口,以便C#里面可以用不同于dll中的函数名Sum。。
[DllImport("Test.dll", EntryPoint = "sum")] private static extern int Sum(int a, int b);
参考:[科普小短文]在C#中调用C语言函数(静态调用Native DLL,Windows & Microsoft.Net平台
三、Win32类型对应.Net类型

BOOL=System.Int32
BOOLEAN=System.Int32
BYTE=System.UInt16
CHAR=System.Int16
COLORREF=System.UInt32
DWORD=System.UInt32
DWORD32=System.UInt32
DWORD64=System.UInt64
FLOAT=System.Float
HACCEL=System.IntPtr
HANDLE=System.IntPtr
HBITMAP=System.IntPtr
HBRUSH=System.IntPtr
HCONV=System.IntPtr
HCONVLIST=System.IntPtr
HCURSOR=System.IntPtr
HDC=System.IntPtr
HDDEDATA=System.IntPtr
HDESK=System.IntPtr
HDROP=System.IntPtr
HDWP=System.IntPtr
HENHMETAFILE=System.IntPtr
HFILE=System.IntPtr
HFONT=System.IntPtr
HGDIOBJ=System.IntPtr
HGLOBAL=System.IntPtr
HHOOK=System.IntPtr
HICON=System.IntPtr
HIMAGELIST=System.IntPtr
HIMC=System.IntPtr
HINSTANCE=System.IntPtr
HKEY=System.IntPtr
HLOCAL=System.IntPtr
HMENU=System.IntPtr
HMETAFILE=System.IntPtr
HMODULE=System.IntPtr
HMONITOR=System.IntPtr
HPALETTE=System.IntPtr
HPEN=System.IntPtr
HRGN=System.IntPtr
HRSRC=System.IntPtr
HSZ=System.IntPtr
HWINSTA=System.IntPtr
HWND=System.IntPtr
INT=System.Int32
INT32=System.Int32
INT64=System.Int64
LONG=System.Int32
LONG32=System.Int32
LONG64=System.Int64
LONGLONG=System.Int64
LPARAM=System.IntPtr
LPBOOL=System.Int16[]
LPBYTE=System.UInt16[]
LPCOLORREF=System.UInt32[]
LPCSTR=System.String
LPCTSTR=System.String
LPCVOID=System.UInt32
LPCWSTR=System.String
LPDWORD=System.UInt32[]
LPHANDLE=System.UInt32
LPINT=System.Int32[]
LPLONG=System.Int32[]
LPSTR=System.String
LPTSTR=System.String
LPVOID=System.UInt32
LPWORD=System.Int32[]
LPWSTR=System.String
LRESULT=System.IntPtr
PBOOL=System.Int16[]
PBOOLEAN=System.Int16[]
PBYTE=System.UInt16[]
PCHAR=System.Char[]
PCSTR=System.String
PCTSTR=System.String
PCWCH=System.UInt32
PCWSTR=System.UInt32
PDWORD=System.Int32[]
PFLOAT=System.Float[]
PHANDLE=System.UInt32
PHKEY=System.UInt32
PINT=System.Int32[]
PLCID=System.UInt32
PLONG=System.Int32[]
PLUID=System.UInt32
PSHORT=System.Int16[]
PSTR=System.String
PTBYTE=System.Char[]
PTCHAR=System.Char[]
PTSTR=System.String
PUCHAR=System.Char[]
PUINT=System.UInt32[]
PULONG=System.UInt32[]
PUSHORT=System.UInt16[]
PVOID=System.UInt32
PWCHAR=System.Char[]
PWORD=System.Int16[]
PWSTR=System.String
REGSAM=System.UInt32
SC_HANDLE=System.IntPtr
SC_LOCK=System.IntPtr
SHORT=System.Int16
SIZE_T=System.UInt32
SSIZE_=System.UInt32
TBYTE=System.Char
TCHAR=System.Char
UCHAR=System.Byte
UINT=System.UInt32
UINT32=System.UInt32
UINT64=System.UInt64
ULONG=System.UInt32
ULONG32=System.UInt32
ULONG64=System.UInt64
ULONGLONG=System.UInt64
USHORT=System.UInt16
WORD=System.UInt16
WPARAM=System.IntPtr
参考: C# 与 C++ 数据类型对照
另外,在做一个密码卡项目时,C语言数据类型 转换.NET类型,主要如下
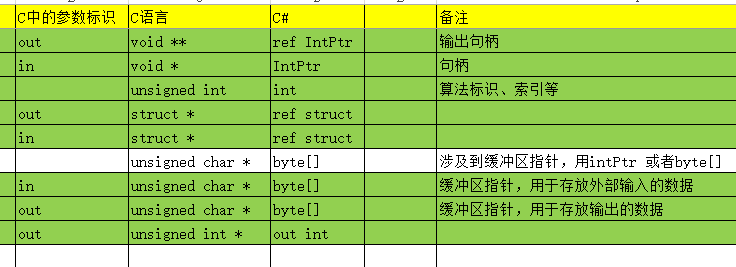
四、C语言常见方法解析
1、memset() 的作用:在一段内存块中填充某个给定的值,通常用于数组初始化与数组清零。
它是直接操作内存空间,mem即“内存”(memory)的意思。该函数的原型为:
# include <string.h> void *memset(void *s, int c, unsigned long n);
函数的功能:将指针变量 s 所指向的前 n 字节的内存单元用一个“整数” c 替换,注意 c 是 int 型。s 是 void* 型的指针变量,所以它可以为任何类型的数据进行初始化。
eg:
unsigned char ucTmpData[512];
memset(ucTmpData, 0, sizeof(ucTmpData));
对应C# : byte[] ucTmpData= new byte[512];
2、memcpy
memcpy是memory copy的缩写,意为内存复制,在写C语言程序的时候,我们常常会用到它。它的函原型如下:
void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t n);
它的功能是从src的开始位置拷贝n个字节的数据到dest。如果dest存在数据,将会被覆盖。memcpy函数的返回值是dest的指针。memcpy函数定义在string.h头文件里。
五、如何在Windows和Linux上进行跨平台P/Invoke
time:2020年
参考:https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/370237900211533404.html
在做一个加密卡(PCI设备)项目时,用到.net core调用C函数,提供接口用在Linux上时,为了兼容windows和Linux,在外部函数引入(DllImport)的问题上,参考了上面这个回答。其中:
在.NET的代码中,透过DllImport引入外部函数时,指定的链接库模块不要加扩展名。比如native.dll,只要写native就好。windows中,会自动寻找native.dll,Linux下对应的是libnative.so。
六、常见问题
1、Attempted to read or write protected memory. This is often an indication that other memory is corrupt
尝试读取或写入受保护的内存。这通常表示其他内存已损坏
可以看下,结构体大小的问题。
最近在做国密SM2的时候遇到的一个问题:
在某厂商加密卡【1】中定义的 ECC结构体【ECCrefPrivateKey】中ECCref_MAX_BITS =256;
在另一个加密机厂商【2】的接口中,定义的ECC结构体【ECCrefPrivateKey】中ECCref_MAX_BITS =512;
此时用【1】的定义的结构体 去请求【2】的接口时,就会报出上面的问题。
所以要看清定义中结构体的大小问题。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号