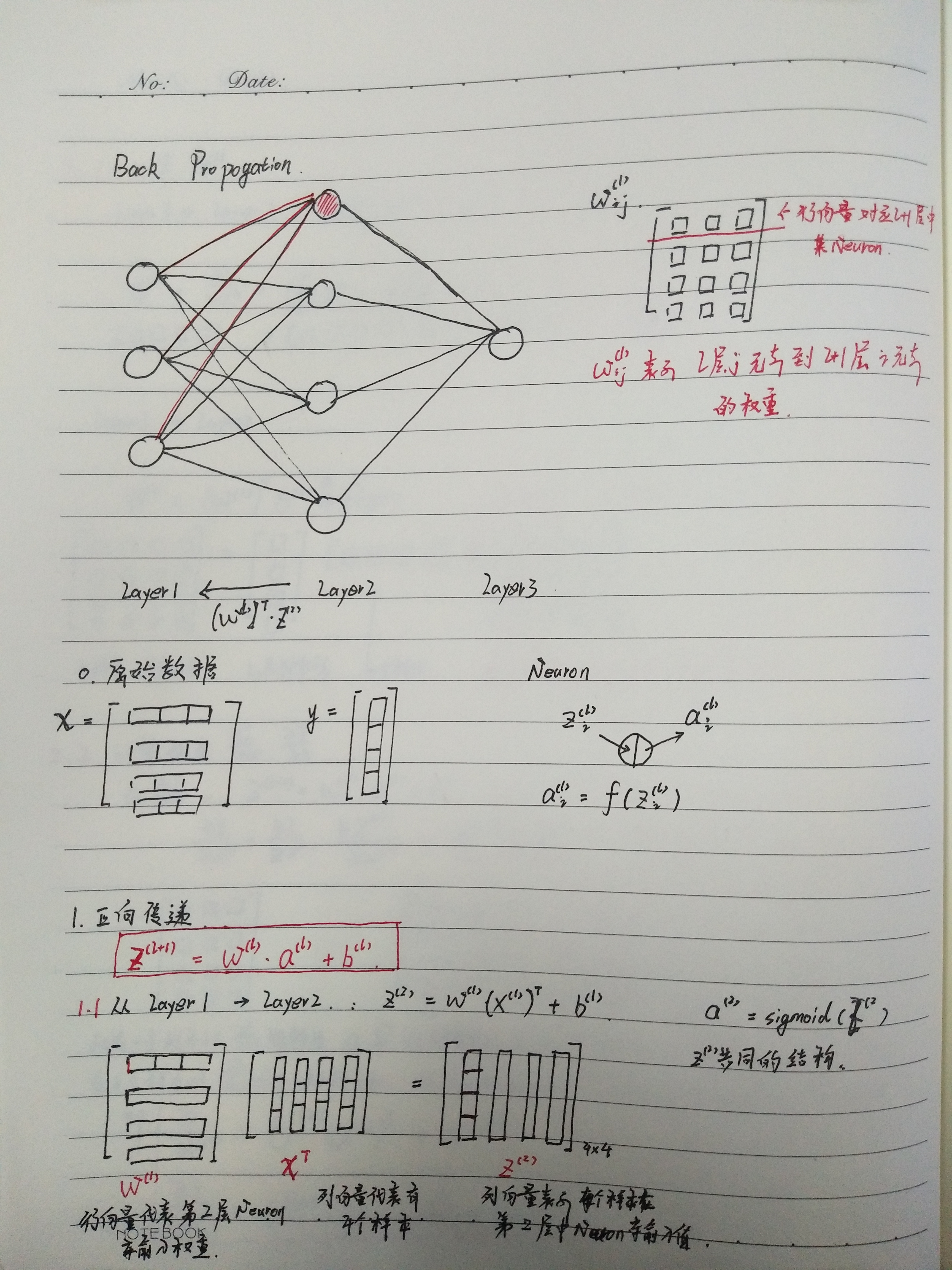
back propogation 的线代描述
参考资料:
算法部分:
standfor, ufldl : http://ufldl.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/UFLDL_Tutorial
一文弄懂BP:https://www.cnblogs.com/charlotte77/p/5629865.html
代码部分:
siraj raval ,4分钟搭建神经网络: http://192.168.73.134/www.sohu.com/a/162305418_697750
这是我个人学习笔记,希望其他阅读者已经学习过 ufldl关于 neural network 和 back propogation的内容。
最重要的就是 求解梯度更新公式的矩阵形式(笔记中红框中部分):


python 代码,numpy 实现:
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
r'''
build a neural network by plain numpy
loss (latex)
J(w,b) = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i}^{m}\frac{1}{2}\left \| h_{wb}(x^{(i)}) - y^{(i)} \right \|^2 +\sum \sum \sum W^{(l)}_{(ij)}
'''
def getData():
x = np.array([[0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 1], [1, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1]])
y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0])[:, np.newaxis]
return x, y
def sigmoid(x, deriv=False):
if deriv is True:
fx = sigmoid(x)
return fx * (1.0 - fx)
else:
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x))
x, y = getData()
fy = sigmoid(y)
# print(fy)
# np.random.seed(30)
w1 = np.random.random([4, 3])
b1 = np.random.random([4, 1])
w2 = np.random.random([1, 4])
b2 = np.random.random([1, 1])
max_iter = 100000
nita = 0.0 # regular
step_size = 0.1
for i in range(0, max_iter):
# forward
z2 = np.dot(w1, x.T) + b1 # 4×4+4×1 (broadcasting)
a2 = sigmoid(z2)
z3 = np.dot(w2, a2) + b2[0, 0]
y_hat = sigmoid(z3)
# mse
mse = (1.0 / y.shape[0]) * np.dot((y.T - y_hat).T, y.T - y_hat)[0, 0]
if i % 500 == 0 or mse < 0.0001:
print('when i=' + str(i) + '; mse:' + str(mse))
if mse < 0.0001:
break
# backward
# partial
delta_3 = (y_hat - y.T) * sigmoid(z3, deriv=True)
delta_2 = np.dot(w2.T, delta_3) * sigmoid(z2, deriv=True)
partial_w2 = np.dot(delta_3, a2.T) + nita * w2
partial_b2 = np.dot(delta_3, np.ones([4, 1]))
partial_w1 = np.dot(delta_2, x) + nita * w1
partial_b1 = np.dot(delta_2, np.ones([4, 1]))
# update parameter
w2 -= step_size * partial_w2
b2 -= step_size * partial_b2
w1 -= step_size * partial_w1
b1 -= step_size * partial_b1
print(y_hat)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号