JDBC事务管理
JDBC事务管理
PreparedStatement:执行SQL的对象
1.SQL注入问题:在拼接sql时,有一些sql的特殊关键字参与字符串的拼接。会造成安全性问题
1.输入用户随便,输入密码:a' or 'a' = 'a
2.sql:select * from user where username = 'dsha' and password = 'a' or 'a' = 'a'

2.解决sql注入问题:使用PreparedStatement对象来解决
3.预编译的SQL:参数使用?作为占位符
4.步骤:
1.导入驱动jar包 mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar
2.注册驱动
3.获取数据库连接对象 Connection
4.定义sql
>注意:sql的参数使用?作为占位符。如:select * from user where username =?and password = ?;
5.获取执行sql语句的对象 PreparedStatement Connection.prepareStatement(String sql)
6.给?赋值
>方法:setXxx(参数1,参数2)
参数1:?的位置编号 从1开始
参数2:?的值
7.执行sql,接收返回结果,不需要传递sql语句
8.处理结果
9.释放资源
5.注意:以后都会使用PreparedStatement来完成增删改查的所有操作
1.可以防止SQL注入
2.效率更高
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入用户名"); String username = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("输入密码"); String password = sc.nextLine(); boolean flag = new JDBCD02().login2(username, password); if (flag){ System.out.println("登录成功!"); }else { System.out.println("用户名和密码错误!"); } } /* 登录方法 使用PreparedStatement实现 */ public boolean login2(String username,String password){ if (username==null || password==null){ return false; } //连接数据库是否登录成功 Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //获取连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //定义sql String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?"; //获取执行sql对象 pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //给?赋值 pstmt.setString(1,username); pstmt.setString(2,password); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); return rs.next(); //如果有下一行,则返回true } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtils.close(rs,pstmt,conn); } return false; }


JDBC事务管理_概述
1.事务:一个包含多个步骤的业务操作。如果这个业务操作被事务管理,则这多个步骤要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
2.操作:
1.开始事务
2.提交事务
3.回滚事务
3.使用Connection对象来管理事务
>开启事务:setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit):调用该方法设置参数为false,即开启事务
在执行sql之前开启事务
>提交事务:commit()
当所有sql都执行完提交事务
>回滚事务:rollback()
在catch中回滚事务
JDBC事务管理_实现
/* 事务操作 */ public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstmt1 = null; PreparedStatement pstmt2 = null; try { //获取连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //开启事务 conn.setAutoCommit(false); //定义SQL //张三-500 String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance - ? where id = ?"; //李四+500 String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance + ? where id = ?"; //获取SQL对象 pstmt1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1); pstmt2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2); //设置?参数 pstmt1.setDouble(1,500); pstmt1.setInt(2,1); pstmt2.setDouble(1,500); pstmt2.setInt(2,2); //执行SQL pstmt1.executeUpdate(); //手动制造异常 int i = 3/0;
pstmt2.executeUpdate(); //提交事务 conn.commit(); } catch (Exception throwables) { //事务回滚 try { if (conn!=null){ conn.rollback(); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtils.close(pstmt1,conn); JDBCUtils.close(pstmt2,null); } }

出现异常后张三的钱会减少而李四不会增加
所以使用事务来进行修改,出现报错之后回滚事务
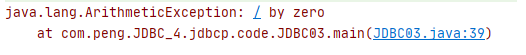
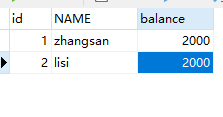 出现错误没有进行修改
出现错误没有进行修改
 正确的
正确的







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix