注解_自定义注解_元注解和注解_解析注解
注解_自定义注解_元注解
元注解:用于描述注解的注解
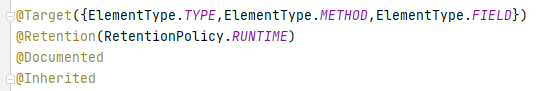
@Target:描述注解能够作用的位置
ElementType取值:
TYPE:可以作用于类上
METHOD:可以作用于方法上
FIELD:可以作用于成员变量上
@Retention:描述注解被保留的阶段
@Retention(RetentionPolicy,RUNTIME):当前被描述的注解,会保留到class字节码文件中,并被JVM读取到
@Documented:描述注解是否被抽取到api文档中
@Inherited:描述注解是否被子类继承
注解_解析注解
在程序使用(解析)注解:获取注解中定义的属性值
1.获取注解定义的位置的对象 (Class,Method,Field)
2.获取指定的注解
getAnnotation(Class)
//其实就是在内存中生成了一个该注解接口的子类实现对象
public class ProImpl implements Pro{ public String className() { return "com.peng.title3.HelloWorld1.junit.reflect.Demo1"; } public String methodName() { return "show"; } }
3.调用注解中的抽象方法获取配置的属性值
使用注解修改:实现配置文件案例运行方法的案例
/* 描述需要执行的类名,和方法名 */ @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Pro { String className(); String methodName(); }
public class Demo2 { public void show(){ System.out.println("Demo2..show"); } }
public class Demo1 { public void show(){ System.out.println("Demo1..show"); } }
@Pro(className = "com.peng.title3.HelloWorld1.junit.reflect.Demo1",methodName = "show") public class ReflectTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1.解析注解 //获取该类的字节码文件对象 Class<ReflectTest2> reflect = ReflectTest2.class; //2.获取上边的注解对象 //其实就是在内存中生成了一个该注解接口的子类实现对象 /* 好比就是 public class ProImpl implements Pro{ public String className() { return "com.peng.title3.HelloWorld1.junit.reflect.Demo1"; } public String methodName() { return "show"; } } */ Pro an = reflect.getAnnotation(Pro.class); //3.调用注解对象中定义的抽象方法,获取返回值 String className = an.className(); String methodName = an.methodName(); //3.加载该类进内存 Class cls = Class.forName(className); //4.创建对象 Object obj = cls.newInstance(); //5.获取方法对象 Method method = cls.getMethod(methodName); //6.执行方法 method.invoke(obj); } }
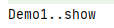







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix