HashMap存储自定义类型键值和LinkedHashMap集合
HashMap存储自定义类型键值
Map集合保证key是唯一的:
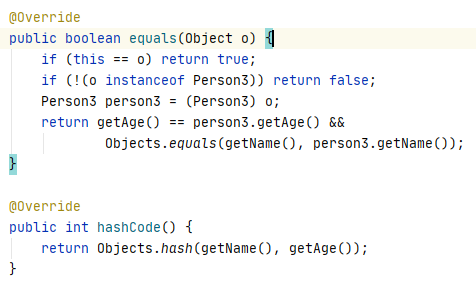
作为key的元素,必须重写hashCode方法和equals方法,保证key唯一.
HashMap<String, Person3> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("北京",new Person3("张三",18)); map.put("上海",new Person3("李四",19)); map.put("广州",new Person3("王五",20)); map.put("北京",new Person3("赵六",18)); Set<String> set = map.keySet(); for (String key : set){ Person3 value = map.get(key); System.out.println(key+"-->"+value); }

key:Person类型
Person类就必须重写hashCode方法和equals方法,以保证key唯一
value:String类型(可以重复)
没有重写hashCode和equals还有重复的
HashMap<Person3, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(new Person3("张三",18),"北京"); map.put(new Person3("李四",19),"上海"); map.put(new Person3("王五",20),"广州"); map.put(new Person3("张三",18),"Q北京Q"); Set<Map.Entry<Person3, String>> set = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Person3,String> entry : set){ Person3 key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"-->"+value); }


LinkedHashMap集合
LinkedHashMap<K,V> entends HashMap<K,V>
Map 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。
底层原理:
哈希表+链表(记录元素的顺序)
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("a","a"); map.put("c","c"); map.put("b","b"); map.put("a","d"); System.out.println(map);//key不允许重复,无序 LinkedHashMap<String, String> linked = new LinkedHashMap<>(); linked.put("a","a"); linked.put("c","c"); linked.put("b","b"); linked.put("a","d"); System.out.println(linked);//key不允许重复,有序
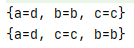







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix