java线程池工具
ExecutorServiceFactory
package com.nblh.office.threadpool;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* 线程池服务工厂
* @author Administrator
*/
public class ExecutorServiceFactory {
private static ExecutorServiceFactory executorFactory = new ExecutorServiceFactory();
private int corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1;
private int maximumPoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2 + 1;
private long keepAliveTime = 5;
private TimeUnit unit = TimeUnit.MINUTES;
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>( 20 * 10000 );
private ExecutorServiceFactory() {
}
public static ExecutorServiceFactory getInstance() {
return executorFactory;
}
/**
* 创建一个可根据需要创建新线程的线程池,但是在以前构造的线程可用时将重用它们。对于执行很多短期异步任务的程序而言,这些线程池通常可提高程序性能。调用
* execute 将重用以前构造的线程(如果线程可用)。如果现有线程没有可用的,则创建一个新线程并添加到池中。终止并从缓存中移除那些已有 60
* 秒钟未被使用的线程。因此,长时间保持空闲的线程池不会使用任何资源。注意,可以使用 ThreadPoolExecutor
* 构造方法创建具有类似属性但细节不同(例如超时参数)的线程池。
*
* @return
*/
public ExecutorService createCachedThreadPool() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(getThreadFactory("cache"));
return executorService;
}
/**
* 创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池,以共享的无界队列方式来运行这些线程。在任意点,在大多数 nThreads
* 线程会处于处理任务的活动状态。如果在所有线程处于活动状态时提交附加任务
* ,则在有可用线程之前,附加任务将在队列中等待。如果在关闭前的执行期间由于失败而导致任何线程终止
* ,那么一个新线程将代替它执行后续的任务(如果需要)。在某个线程被显式地关闭之前,池中的线程将一直存在。
*
* @return
*/
public ExecutorService createFixedThreadPool(int count) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(count, getThreadFactory("fixed"));
return executorService;
}
/**
* 自定义线程池
* @param count
* @return
*/
public ExecutorService createCustomThreadPool() {
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize,
maximumPoolSize,
keepAliveTime,
unit,
workQueue, getThreadFactory("custom"));
return executorService;
}
/**
* 获取线程池工厂
* @return
*/
private ThreadFactory getThreadFactory(final String type) {
return new ThreadFactory() {
AtomicInteger sn = new AtomicInteger();
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
ThreadGroup group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() : Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
Thread t = new Thread(group, r);
t.setName(type+ "_Thread-No_" + sn.incrementAndGet());
return t;
}
};
}
}
ExecutorProcessPool
package com.nblh.office.threadpool;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* 线程处理类
* 创建 createFixedThreadPool 和 createCachedThreadPool 线程池
* ExecutorProcessPool.getInstance().executeByFixedThread( new Runnable(){ ... });
* ExecutorProcessPool.getInstance().executeByCacheThread( new Runnable(){ ... });
*
* 由于 Executors工具类自定义的队列大小为Integer.MAX_VALUE, 当任务队列过多时,可能会出现OOM
* ExecutorProcessPool.getInstance().executeByCustomThread( new Runnable(){ ... });
*/
public class ExecutorProcessPool {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExecutorProcessPool.class);
private static ExecutorProcessPool pool = new ExecutorProcessPool();
private ExecutorService cacheExcecutor;
private ExecutorService fixedExcecutor;
private ExecutorService customExcecutor;
/**
* 创建可缓存的线程池
*/
private ExecutorProcessPool(){
cacheExcecutor = ExecutorServiceFactory.getInstance().createCachedThreadPool();
fixedExcecutor = ExecutorServiceFactory.getInstance().createFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2);
customExcecutor = ExecutorServiceFactory.getInstance().createCustomThreadPool();
return;
}
/**
* 返回线程池工具类实例
* @return
*/
public static ExecutorProcessPool getInstance() {
return pool;
}
/**
* 1.线程缓存空闲60后销毁
* 3.线程数0~Integer.maxvalue
* 2.队列SynchronousQueue 大小1
* @param task
*/
public void executeByCacheThread(Runnable task) {
cacheExcecutor.execute(task);
log("cache " , (ThreadPoolExecutor) cacheExcecutor);
}
/**
* 1. 线程池大小 Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2
* 2. 无界队列 Integer.maxvalue
* @param task
*/
public void executeByFixedThread(Runnable task) {
fixedExcecutor.execute(task);
log("fixed" , (ThreadPoolExecutor) fixedExcecutor);
}
/**
* 1. 线程池核心数 Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1
* 2. 最大线程数 Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()*2 + 1
* 3. 超过核心线程数小的线程 空闲5分钟销毁
* 4. 有界队列,超过20*10000 , 中止接收任务
* @param task
*/
public void executeByCustomThread(Runnable task) {
customExcecutor.execute(task);
log("custom", (ThreadPoolExecutor) customExcecutor);
}
/**
* 日志记录
*/
public void log(String name, ThreadPoolExecutor tpe) {
String status = "[Thread] "+ name +" activeCount: " + tpe.getActiveCount() + " ; CompletedTaskCount: " + tpe.getCompletedTaskCount() + " ; Queue Size: "+ tpe.getQueue().size() + "; taskCount: " + tpe.getTaskCount();
logger.warn(status );
}
/**
* 停止所有任务进程
*/
public static void shutdownAll() {
pool.cacheExcecutor.shutdown();
pool.fixedExcecutor.shutdown();
pool.customExcecutor.shutdown();
}
}
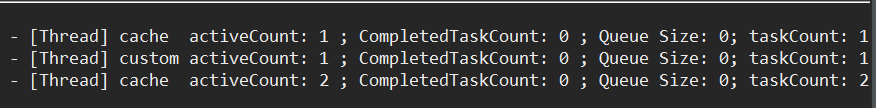
结果
public static void main(String[]args) {
public static void main(String[]args) {
Runnable run = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
for(int i=0; i<4;i++) {
if( i %3 ==0) {
ExecutorProcessPool.getInstance().executeByCacheThread(run);
continue;
}
if( i % 2 ==0) {
ExecutorProcessPool.getInstance().executeByCustomThread(run);
continue;
}
}
}
如果觉得文章对您有用,请点下推荐。您的支持将鼓励我继续创作!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号