Redux(mvc、flux、react-redux)
其他章节请看:
Redux
关于状态管理,在 Vue 中我们已经使用过 Vuex,在 spug 项目中我们使用了 mobx,接下来我们学习 Redux。
本篇以较为易懂的方式讲解mvc、flux、redux和react-redux的关系、redux 的工作流以及react-redux的原理,首先通过示例讲解 redux 的用法,接着用 react-redux 实现相同需求。
Tip:旧的项目倘若使用了 Redux,如果不会则无法干活!笔者基于 spug 项目进行,其他 react 项目也一样。
redux 简介
MVC 和 Flux
现代应用比以前做得更多也更复杂,如果缺乏一致设计会随着应用的增长而造成混乱,为了对抗混乱,开发者借助 MVC 来组织应用的功能。flux(Redux)也是如此,都是为了帮助开发者处理不断增加的复杂性。
flux 与 mvc 关注的是比应用的外观或构件应用所用到的一些特定库或技术更高层面的东西,关注应用如何组织、数据如何流转,以及职责如何分配给系统的不同部分。
flux 与 mvc 不同之处在于它提倡单向数据流,并引入了一些新概念(dispatch、action、store)以及其他方面。
稍微回顾下 MVC:
- 模型(Model) - 应用的数据,至少拥有操作关联数据的基本方法。模型是原始数据与应用代码交互的地方
- 视图(View) - 模型的表示,通常是用户界面。视图中不应有与数据表示无关的逻辑。对于前端框架,通常意味着特定视图直接与资源关联并具有与之关联的CURD(创建、读取、更新、删除)操作
- 控制器(Controller) - 将模型和视图邦在一起的粘合剂。只是粘合剂而不做更多的事情(不包含复杂的视图或数据库逻辑)
Flux 模式与 MVC 不同,没有将应用的各部分分解为模型、视图和控制器,而是定义了若干不同部分:
store- 包含应用的状态和逻辑。有点像模型action- Flux 不是直接更新状态,而是创建修改状态的 action 来修改应用状态view- 用户界面。这里指 Reactdispatch- 对 store 进行操作的一个协调器
在Flux中,用户操作界面,会创建一个 action,然后 dispatch 处理传入的 action,之后将 action 发送到 store 中更改状态,状态变化后通知视图应该使用新数据。
在 mvc 中视图和模型能彼此更新,属于双向数据流。而数据在 Flux 中更多的是单向流动。
flux 和 redux
flux 是一种范式,有许多库实现了 Flux 的核心思想,实现的方式不尽相同。
介绍一下 Flux 和 Redux 一些重要区别:
- redux 使用
单一store(即单个全局store),将所有的东西保存在一个地方。flux 可以有多个不同的 store - redux 引入
reducer,以一种更不可变的方式更改(官网:Reducer 必须是纯函数) - redux 引入
中间件,因为 action 和数据流是单向的,所以开发者可以在 Redux 中添加中间件,并在数据更新时注入自定义行为。
下图更直观的描述了 flux 与 redux 的区别:
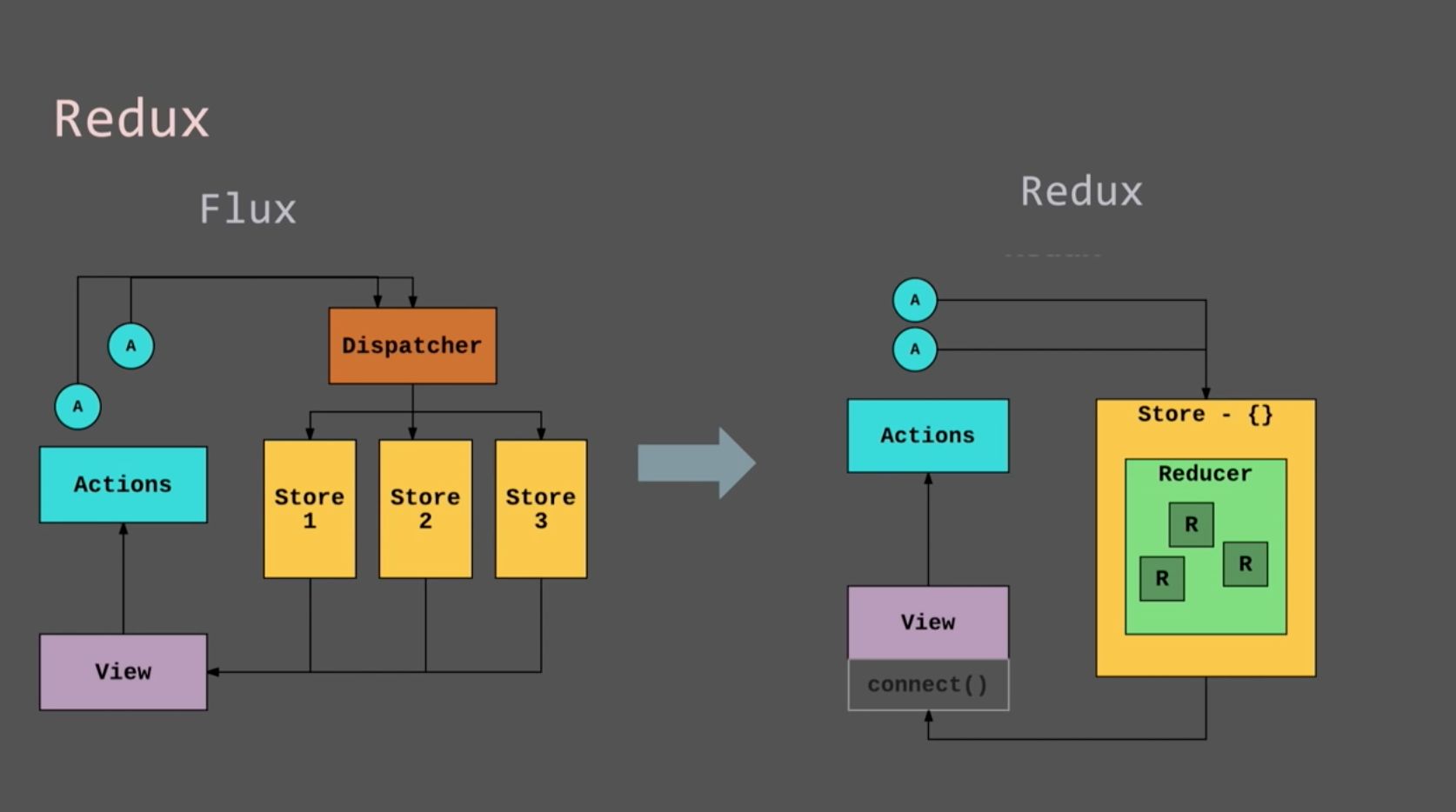
- flux 有多个 store,redux 只有一个 store
- redux 有 reducer
- redux 也是通过 dispatch 的方式通知 store 更新状态
- redux 中的 connect 用于创建容器组件,下文 react-redux 中会使用
redux 和 react-redux
redux 是状态管理的 js 库。
react 可以用在 vue、react、angular 中,不过更多的是用在 react。比如要在 vue 中使用状态管理,通常会使用 vuex。
react 项目中可以直接使用 redux,但如果在配合 react-redux 就更方便一些(下文会使用到)。
redux 工作流
下图展示了 redux 组成部分以及每个部分的职责:
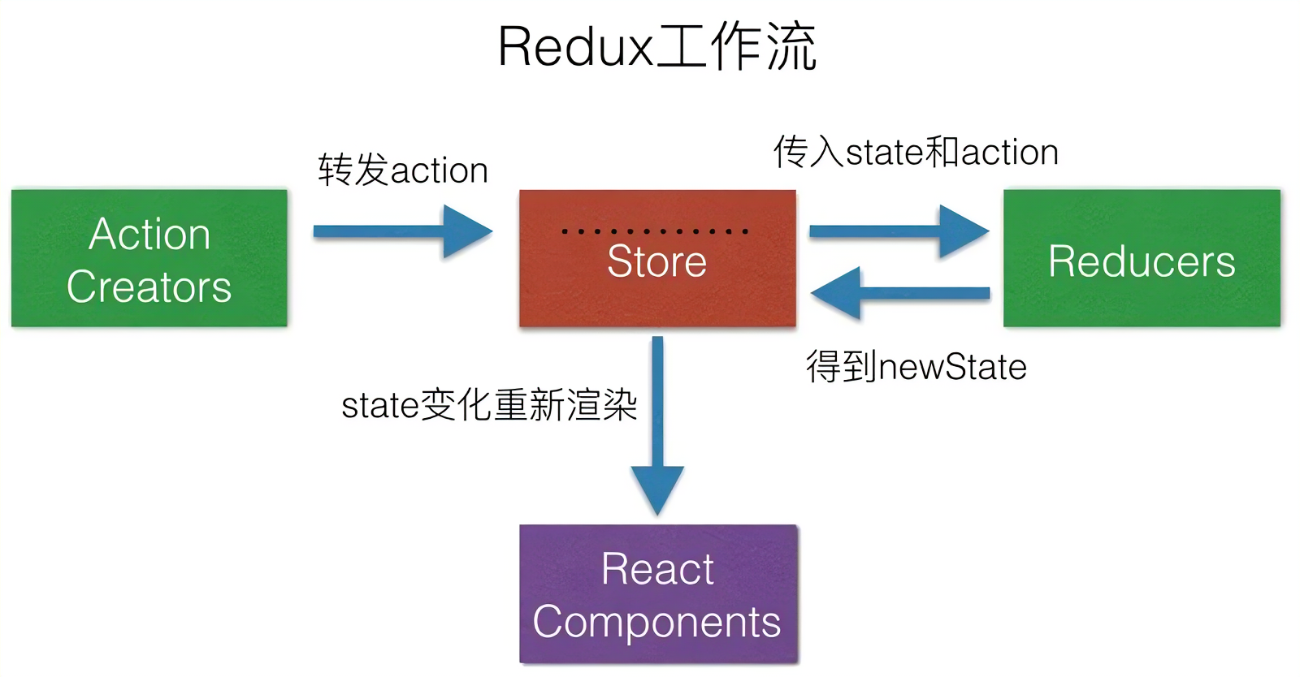
- 这里有四部分,其中 Redux 的三个核心部分是:
Action Creators、Store、Reducers 大致流程:react 组件从 store 获取状态,通过 dispatch 发送 action 给 store,store 通知 reducer 加工状态,reducer 将加工后的状态返回,然后 react 组件从 store 获取更新后的状态。- 其中 store 是单一的,而 Creators 和 Reducers 是多数。
- Reducers 负责
加工状态和初始化状态 - Action Creators 用于创建 action。而 action 只是一个普通 javascript 对象。
Tip:可以将上图理解成去饭店点餐。
- Store - 老板(一个老板)
- Reducers - 厨师(多个)
- Action Creators - 服务员(多个)
客户(react 组件)跟服务员点菜,服务员下单,老板将菜单发给厨师,厨师将食物做好,通知客户来老板这取餐。其中老板是最重要的,用于联系服务员、厨师以及客户;厨师是真正干活的人。
redux
示例
我们先用两个文件来完成一个最简单的 redux 示例,然后再实现一个完整版。
最简单的版本:只使用 Store 和 Reducer。Action 由于只是普通 js 对象,暂时就不使用 Action Creators 来创建。
Tip:关于 Reducer,如果需要把 A 组件的状态给 redux,就得给 A 构建一个 reducer,如果需要把 B 组件的状态给 redux,就得给 B 构建一个 reducer。
需求:写一个组件,里面有一个数字,点击一次按钮,数字就增加1。
// src/smallproject/MyComponent.js
import React from 'react'
export default class extends React.Component {
state = {value: 0}
// 默认加1
add = (v = 1) => {
this.setState({value: this.state.value + v})
}
render(){
return <div style={{padding: 20}}>
<p>结果值:{this.state.value}</p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.add()}>增加</button></p>
</div>
}
}
Tip:在 App.js 中引入,通过 http://localhost:3000/ 即可访问:
// src/App.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyComponent from 'smallproject/MyComponent';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<MyComponent/>
);
}
}
export default App;
接着把状态交给 redux 管理,实现效果与上面示例相同,就是把 state 提取到 redux 中。请看下面步骤:
首先安装 redux:
$ npm i redux
创建 src/redux 文件夹,用于存放 redux 的东西。
Tip:Store 用于联系 action、Reducer、State,位居 C 位,职责很重,不是我们用几句代码就能完成。需要使用 createStore。就像这样:
import { createStore } from 'redux'
新建两个文件,更新一个文件。代码如下:
// src\redux\MyComponent_reducer.js
// Reducer 的职责是初始化状态以及加工状态
// 将初始化值提前,更清晰
const initValue = 0
export default function (state = initValue, action) {
switch (action.type) {
// 加工状态
case 'INCREMENT':
return state + action.data
// 初始化
default:
return state
}
}
// src\redux\store.js
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import mycomponent from './MyComponent_reducer'
// 饭店开张前得把厨师准备好
export default createStore(mycomponent)
// src\smallproject\MyComponent.js
import React from 'react'
import store from '../redux/store'
export default class extends React.Component {
componentDidMount(){
// 监听 store 状态变化
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log(store.getState())
// 触发react渲染,否则我们看不到数字更新
this.setState({})
})
}
// 默认加1
add = (v = 1) => {
// 分发 action。这是触发 state 变化的惟一途径。
// dispatch(action)
store.dispatch({type: 'INCREMENT', data: v})
}
render(){
return <div style={{padding: 20}}>
<p>结果值:{store.getState()}</p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.add()}>增加</button></p>
</div>
}
}
稍微再分析一下这三个文件。
MyComponent_reducer 就是一个普通函数,用于初始化状态以及加工状态。比如增加一行调试语句,则可发现页面初始化时 redux 默认传递了一个很奇怪的 type,可用于初始化逻辑,后续择进入加工状态。
const initValue = 0
export default function (state = initValue, action) {
+ console.log('state', state, 'action', JSON.stringify(action))
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return state + action.data
default:
return state
}
}
// state 0 action {"type":"@@redux/INITv.e.f.o.y.8"} - 第一次
// state 0 action {"type":"INCREMENT","data":1}
store.js 通过 createStore 创建 Store,并将 reducer 放入其内。
Tip:vscode 提示 import { createStore } from 'redux' 已废弃(@deprecated We recommend using the configureStore method of the @reduxjs/toolkit package, which replaces createStore.),笔者的 redux 是 4.2.0,这里只是理解和练习 redux,所以继续这种方式。
MyComponent 中将 state 改为从 Store 中获取。
store.getState()获取 redux 的状态store.dispatch()更改 redux 的状态store.subscribe()监听 redux 状态。一旦改变,需要手动触发 react 的渲染。笔者采用this.setState({})来触发(redux 不是专门为 react 设计的),而直接调用this.render()是不会生效的。
纯函数
reducer 需要纯函数。比如 state 是一个数组,如果通过 push 这类方式是不起作用的:
export default function (state = initValue, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case INCREMENT:
// 不起作用。
state.push(action)
return state
// 正确
return [...state, action]
default:
return state
}
}
纯函数是一类特别的函数,同样的实参比得同样的输出。而且还得遵守一些规则:
- 不修改参数数据
- 不做不靠谱的事情,比如网络请求、输入设备等。网络断了...
- 不调用 Date.now() 等不纯的方法
优化 store.subscribe
现在一个的 store.subscribe 写在单个组件内,如果有10个,岂不是要写10次。我们可以将其提取到入口文件中,就像这样:
$ git diff src/index.js
...
+import store from './redux/store'
moment.locale('zh-cn');
updatePermissions();
+// 监听 store 状态变化
+store.subscribe(() => {
+ ReactDOM.render(
+ <Router history={history}>
+ <ConfigProvider locale={zhCN} getPopupContainer={() => document.fullscreenElement || document.body}>
+ <App/>
+ </ConfigProvider>
+ </Router>,
+ document.getElementById('root')
+ );
+})
ReactDOM.render(
<Router history={history}>
<ConfigProvider locale={zhCN} getPopupContainer={() => document.fullscreenElement || document.body}>
只要 redux 状态发生变化,就会重新执行 ReactDOM.render。前头我们已经了解了 react 的 Diffing 算法,知道这种方式效率也不会低到哪里去。
加入 Action Creators
首先增加两个文件,用于创建 action 的以及管理常量。
// src\redux\MyComponent_action.js
import {INCREMENT} from './const'
export const createIncrementAction = data => ({type: INCREMENT, data})
// src\redux\const.js
// 常量管理,防止单词拼错。
export const INCREMENT = 'INCREMENT'
接着修改两个文件,通过 git diff 显示如下:
$ git diff
diff --git a/src/redux/MyComponent_reducer.js b/src/redux/MyComponent_reducer.js
// src\redux\MyComponent_reducer.js
// 将初始化值提前,更清晰
+import {INCREMENT} from './const'
const initValue = 0
export default function (state = initValue, action) {
switch (action.type) {
// 加工状态
- case 'INCREMENT':
+ case INCREMENT:
return state + action.data
// 初始化
default:
diff --git a/src/smallproject/MyComponent.js b/src/smallproject/MyComponent.js
import store from '../redux/store'
+import {createIncrementAction} from '../redux/MyComponent_action'
export default class extends React.Component {
add = (v = 1) => {
// 分发 action。这是触发 state 变化的惟一途径。
// dispatch(action)
- store.dispatch({type: 'INCREMENT', data: v})
+ store.dispatch(createIncrementAction(v))
}
render(){
异步 action
现在我们创建一个异步增加的功能,每点击一次该按钮,结果就会等1秒钟在更新。
$ git diff
diff --git a/src/smallproject/MyComponent.js b/src/smallproject/MyComponent.js
@@ -16,10 +16,14 @@ export default class extends React.Component {
store.dispatch(createIncrementAction(v))
}
+ asyncAdd = () => {
+ setTimeout(this.add, 1000)
+ }
render(){
return <div style={{padding: 20}}>
<p>结果值:{store.getState()}</p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.add()}>增加</button></p>
+ <p><button onClick={() => this.asyncAdd()}>异步增加</button></p>
</div>
}
}
现在我决定不在组件中等待。于是我在 action 中增加一个 createIncrementAsyncAction,并在 MyComponent 中使用:
// src\redux\MyComponent_action.js
import {INCREMENT} from './const'
import store from './store'
export const createIncrementAction = data => ({type: INCREMENT, data})
// 创建一个异步 action。不再返回对象,而是返回函数,因为在函数中我们才能做一些异步操作
// 意思就是告诉 Store,我这里是一个函数,需要等待 1 秒后在给我改变状态
export const createIncrementAsyncAction = data => {
return () => {
setTimeout(() => {
store.dispatch((createIncrementAction(data)))
}, 1000)
}
}
// src\smallproject\MyComponent.js
...
import {createIncrementAction, createIncrementAsyncAction} from '../redux/MyComponent_action'
export default class extends React.Component {
asyncAdd = (v = 1) => {
store.dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(v))
}
render(){
return <div style={{padding: 20}}>
<p>结果值:{store.getState()}</p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.asyncAdd()}>异步增加</button></p>
</div>
}
}
再次点击异步增加,控制台报错如下:
// action 必须是对象...实际是函数...你可能需要中间件...例如 redux-thunk
redux.js:275 Uncaught Error: Actions must be plain objects. Instead, the actual type was: 'function'. You may need to add middleware to your store setup to handle dispatching other values, such as 'redux-thunk' to handle dispatching functions.
Tip: npmjs 搜索 redux-thunk 信息如下
// 它允许编写具有内部逻辑的函数,这些函数可以与Redux存储的dispatch和getState方法交互。
Thunk middleware for Redux. It allows writing functions with logic inside that can interact with a Redux store's dispatch and getState methods.
...
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import rootReducer from './reducers/index'
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
...
const INCREMENT_COUNTER = 'INCREMENT_COUNTER'
function increment() {
return {
type: INCREMENT_COUNTER
}
}
function incrementAsync() {
return dispatch => {
setTimeout(() => {
// Yay! Can invoke sync or async actions with `dispatch`
dispatch(increment())
}, 1000)
}
}
下面我们将 redux-thunk 引入进来。先安装,然后在 store.js 中引入,最后在 action 中直接使用 redux 传入的 dispatch 即可。
$ npm i redux-thunk
// src\redux\store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import mycomponent from './MyComponent_reducer'
export default createStore(mycomponent, applyMiddleware(thunk))
// src\redux\MyComponent_action.js
import {INCREMENT} from './const'
export const createIncrementAction = data => ({type: INCREMENT, data})
export const createIncrementAsyncAction = data => {
// 这些函数可以与Redux存储的dispatch和getState方法交互。所以就传进来了
return (dispatch) => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(createIncrementAction(data))
}, 1000)
}
}
redux-thunk 通过包装 store 的 dispatch 方法来工作,这样就可以处理派发普通对象以外的东西
中间件的工作方式是让开发者以一种可组合的方式介入到某个周期或流程中,意味着可以在项目中创建和使用多个相互独立的中间件函数。
中间件(官网):
- Middleware 最常见的使用场景是无需引用大量代码或依赖类似 Rx 的第三方库实现异步 actions。这种方式可以让你像 dispatch 一般的 actions 那样 dispatch 异步 actions。
- Middleware 可以让你包装 store 的 dispatch 方法来达到你想要的目的
- redux 中间件从发送 action 到 action 到达 reducer 之间的第三方扩展点,意味着 reduce 处理 action 之前,开发者有机会对该 action 进行操作和修改
总结:通常异步action会调用同步 action,而且异步action不是必须的,可以写在自己组件中。
react-redux
由于 Redux 在 react 项目中用得比较多,所以出现了 react-redux(Official React bindings for Redux),方便 redux 在 react 项目中更好的使用。
使用之前我们先看一下 react-redux 的原理图:
- 所有UI组件外都应该包裹一个容器组件。容器组件和UI组件是父子关系
- 容器组件用于和 Redux 交互
- UI 组件只能通过容器组件和 redux 交互。
- 容器组件会将 redux 的状态、操作 redux 状态的方法都通过 props 传给 Ui 组件
示例
需求:将上面 redux 的示例改成 react-redux。
实现步骤如下:
-
安装依赖包:
npm i react-redux -
将 MyComponent 组件改为 UI 组件,也就是去除与 Redux(或 Store)相关的代码即可。
// src\smallproject\MyComponent.js
import React from 'react'
import {createIncrementAction, createIncrementAsyncAction} from '../redux/MyComponent_action'
export default class extends React.Component {
// 默认加1
add = (v = 1) => {
// 分发 action。这是触发 state 变化的惟一途径。
// dispatch(action)
}
asyncAdd = (v = 1) => {
}
render(){
return <div style={{padding: 20}}>
<p>结果值:{0}</p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.add()}>增加</button></p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.asyncAdd()}>异步增加</button></p>
</div>
}
}
- 创建 MyComponent 对应的容器组件:
// src\container\MyComponent.js
// 这种引入方式也可以
import MyComponent from "smallproject/MyComponent";
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
// 创建容器组件。将 UI 组件放入第二个括号中,属于固定写法
export default connect()(MyComponent)
- App.js 则直接使用容器组件,因为容器组件包裹了UI组件。
// src\App.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyComponent from 'container/MyComponent';
import store from './redux/store'
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
// 将 store 传入容器组件。因为容器组件是通过 api 所创建,对方要求通过这种方式传递
// 若不传 store,控制台会报错:Uncaught Error: Could not find "store" in the context of "Connect(Component)".
<MyComponent store={store} />
);
}
}
export default App;
Tip: 需传入 store,否则会报错,说没有找到 "store"。
至此,组件应该就能正常显示。
- 接着我们将容器组件获取和操作 redux 的通过 props 传给UI组件
容器组件传递redux 状态以及操作状态的方法可以通过 connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) 的两个参数,就像这样:
$ git diff
diff --git a/src/container/MyComponent.js b/src/container/MyComponent.js
+// 获取状态
+const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
+ return {
+ test: 10
+ }
+}
+
+// 处理状态
+const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => {
+ return {
+ testFn: () => console.log('testFn')
+ }
+}
// 创建容器组件。将 UI 组件放入第二个括号中,属于固定写法
-export default connect()(MyComponent)
+export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent)
diff --git a/src/smallproject/MyComponent.js b/src/smallproject/MyComponent.js
export default class extends React.Component {
add = (v = 1) => {
+ this.props.testFn()
}
render(){
return <div style={{padding: 20}}>
- <p>结果值:{0}</p>
+ <p>结果值:{this.props.test}</p>
</div>
Tip:mapStateToProps 传递的是状态,所以是 key:value 的对象;mapDispatchToProps 传递的是操作状态的方法,所以是 key: valueFn;如果传递一个不正确的格式,就像这样 connect(() => {}, () => {})(MyComponent),控制台会报错如下
mapStateToProps() in Connect(Component) must return a plain object. Instead received undefined.
mapDispatchToProps() in Connect(Component) must return a plain object. Instead received undefined.
实现
上面示例我们分析了实现需求的核心步骤,最终代码如下:
- 容器组件包裹UI组件,并给UI组价提供与 Redux 交互的状态和操作状态的方法:
// src\container\MyComponent.js
// 这种引入方式也可以
import MyComponent from "smallproject/MyComponent";
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
import {createIncrementAction, createIncrementAsyncAction} from 'redux/MyComponent_action'
// 获取状态
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
value: state
}
}
// 处理状态
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => {
return {
increment: (v) => dispatch(createIncrementAction(v)),
asyncIncrement: (v) => dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(v))
}
}
// 创建容器组件。将 UI 组件放入第二个括号中,属于固定写法
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent)
Tip:mapDispatchToProps 还有一种简写方式,传对象。react-redux 会自动帮我们 dispatch。
// 简写
// 上面的写法都有 dispatch,都是将参数传给 createAction
const mapDispatchToProps = {
increment: createIncrementAction,
asyncIncrement: createIncrementAsyncAction
}
- UI 组件通过父组件(容器组件)与Redux交互:
// src\smallproject\MyComponent.js
import React from 'react'
export default class extends React.Component {
// 默认加1
add = (v = 1) => {
// 分发 action。这是触发 state 变化的惟一途径。
// dispatch(action)
this.props.increment(v)
}
asyncAdd = (v = 1) => {
this.props.asyncIncrement(v)
}
render(){
return <div style={{padding: 20}}>
<p>结果值:{this.props.value}</p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.add()}>增加</button></p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.asyncAdd()}>异步增加</button></p>
</div>
}
}
无需 store.subscribe
前面我们学习 redux 时,redux 状态更新后需要手动触发 react 渲染,于是写了下面这段代码:
// 监听 store 状态变化
store.subscribe(() => {
ReactDOM.render(
<Router history={history}>
<ConfigProvider locale={zhCN} getPopupContainer={() => document.fullscreenElement || document.body}>
<App/>
</ConfigProvider>
</Router>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
})
现在用 react-redux ,即使删除这段代码,上面示例也能正常运行。因为容器组件帮我们做了这件事。
Provider 提供 store
前面我们写了一个容器组件,并给容器组件传递了一次 store(<MyComponent store={store}/>),如果有100个容器组件,岂不是要传递100次。
react-redux 中的 Provider 只要我们写一次,它会自动帮我们把 store 传给里面的所有容器组件(容器组件是通过 connent 创建,也就能够被识别出来)。我们将其引入:
$ git diff
diff --git a/src/App.js b/src/App.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyComponent from 'container/MyComponent';
- import store from './redux/store'
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
- // 将 store 传入
- <MyComponent store={store}/>
+ <MyComponent/>
);
}
}
diff --git a/src/index.js b/src/index.js
+import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
ReactDOM.render(
<Router history={history}>
<ConfigProvider locale={zhCN} getPopupContainer={() => document.fullscreenElement || document.body}>
- <App/>
+ <Provider store={store}>
+ <App />
+ </Provider>
+
</ConfigProvider>
</Router>,
document.getElementById('root')
合并UI组件和容器组件
上面例子,我们将一个组件分成UI组件和容器组件,也就是1个变2个,如果100个组件,岂不是变成200个组件!文件数量急剧上升。
我们可以将 UI 组件放入容器组件中来解决此问题,因为对外只需要暴露容器组件。就像这样:
// src\container\MyComponent.js
import React from 'react'
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
import {createIncrementAction, createIncrementAsyncAction} from 'redux/MyComponent_action'
// UI 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
...
}
...
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent)
两个组件数据相互共享
上面示例只在一个组件中进行,实际工作至少得2个组件才有使用 redux(数据共享)的必要。
需求:为了更真实的使用 redux,这里我们再新建一个组件(Count),让两个组件相互读取对方的值。
目前 redux 文件夹下,一个组件就有一个 action 一个 reducer,在创建 Count 组件,则又得增加两个文件,而且每个文件后都写了一遍 action 或 reducer,有些繁琐。
Administrator@3L-WK-10 MINGW64 /e/lirufen/spug/src/redux
$ ll
total 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 335 Sep 1 15:45 MyComponent_action.js
-rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 362 Sep 1 14:29 MyComponent_reducer.js
-rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 102 Sep 1 14:33 const.js
-rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 224 Sep 1 15:44 store.js
我们首先优化一下目录结构。在 redux 目录中新建两个文件夹,分别用来存储 action 和 reducer。就像这样:
// 新建两个文件夹
$ mkdir actions reducers
// 移动文件到 actions,并重命名为 MyComponent.js
$ mv MyComponent_action.js ./actions/MyComponent.js
$ mv MyComponent_reducer.js ./reducers/MyComponent.js
然后复制 MyComponent 的action、reducer以及容器组件,重命名为 Count 组件即可。
现在有一个问题:创建Store时要传入 reducers,当前我们传递的只是一个组件的 reducer,现在我们有连个组件,对应两个 reducer 该如何传递?
// src\redux\store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import mycomponent from './reducers/MyComponent'
export default createStore(mycomponent, applyMiddleware(thunk))
Tip: 现在传的第一个参数就是 mycompoment,而且从 redux 中取值也是 state
// 直接取 state
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
value: state
}
}
传递多个 reducers 得使用 combineReducers 组合 reduces。最终 store.js 代码如下:
// src\redux\store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, combineReducers } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import mycomponent from './reducers/MyComponent'
import count from './reducers/Count'
// 传给combineReducers的reduxData就是存在 redux 中的数据,所以取值得换成 state.value1
const reduxData = {value1: mycomponent, value2: count}
const allReducers = combineReducers(reduxData)
export default createStore(allReducers, applyMiddleware(thunk))
最终调整一下组件双方的取值,就实现组件数据的共享了。
// MyComponent 组件取得的 Count 的值
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
value: state.value2
}
}
// Count 组件取得的 MyComponent 的值
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
value: state.value1
}
}
注:有了 react-redux 你还需要 redux。在 npmjs 的 react-redux:You'll also need to install Redux and set up a Redux store in your app.,而且你从现在代码也能发现,react-redux 主要用于创建容器组件,而创建 store 还得通过 redux 完成。
最终代码
可运行的完整代码如下:
Tip:只保留了 MyComponent 组件,因为 Count 也类似。
index.js
增加了 Provider。
// src\index.js
...
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
moment.locale('zh-cn');
updatePermissions();
ReactDOM.render(
<Router history={history}>
<ConfigProvider locale={zhCN} getPopupContainer={() => document.fullscreenElement || document.body}>
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
</ConfigProvider>
</Router>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
serviceWorker.unregister();
App.js
// src\App.js
import React, { Component, Fragment } from 'react';
import MyComponent from 'container/MyComponent';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
{/* <Count /> */}
<MyComponent />
</Fragment>
);
}
}
export default App;
store.js
// src\redux\store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, combineReducers } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import mycomponent from './reducers/MyComponent'
// 传给combineReducers的reduxData就是存在 redux 中的数据,所以取值得换成 state.value1
const reduxData = {value1: mycomponent}
const allReducers = combineReducers(reduxData)
export default createStore(allReducers, applyMiddleware(thunk))
const.js
// src\redux\const.js
// 常量管理,防止单词拼错。
export const INCREMENT = 'INCREMENT'
export const INCREMENT2 = 'INCREMENT2'
reducers\MyComponent.js
// src\redux\reducers\MyComponent.js
// 将初始化值提前,更清晰
import {INCREMENT} from 'redux/const'
const initValue = 0
export default function (state = initValue, action) {
switch (action.type) {
// 加工状态
case INCREMENT:
return state + action.data
// 初始化
default:
return state
}
}
actions\MyComponent.js
// src\redux\actions\MyComponent.js
import {INCREMENT} from 'redux/const'
export const createIncrementAction = data => ({type: INCREMENT, data})
export const createIncrementAsyncAction = data => {
return (dispatch) => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(createIncrementAction(data))
}, 1000)
}
}
container\MyComponent.js
// src\container\MyComponent.js
// 这种引入方式也可以
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
import {createIncrementAction, createIncrementAsyncAction} from 'redux/actions/MyComponent'
import React from 'react'
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// 默认加1
add = (v = 1) => {
// 分发 action。这是触发 state 变化的惟一途径。
// dispatch(action)
this.props.increment(v)
}
asyncAdd = (v = 1) => {
this.props.asyncIncrement(v)
}
render(){
return <div style={{padding: 20}}>
<p>结果值:{this.props.value}</p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.add()}>增加</button></p>
<p><button onClick={() => this.asyncAdd()}>异步增加</button></p>
</div>
}
}
// 获取状态
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
value: state.value1
}
}
// 简写
// 上面的写法都有 dispatch,都是将参数传给 createAction
const mapDispatchToProps = {
increment: createIncrementAction,
asyncIncrement: createIncrementAsyncAction
}
// 创建容器组件。将 UI 组件放入第二个括号中,属于固定写法
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent)
package.json
{
"name": "spug",
"version": "3.0.0",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
...
"react-redux": "^8.0.2",
"redux": "^4.2.0",
"redux-thunk": "^2.4.1",
},
其他章节请看:
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/pengjiali/p/16699162.html
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。


