AtCoder Beginner Contest 265(Java)
A题
题意:
让你去买苹果,你有2种购买方式
买1个苹果花费x元
买3个苹果花费y元。
问最少用多少钱可以买到 n个苹果
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in); 6 int x=sc.nextInt();int y=sc.nextInt();int n=sc.nextInt(); 7 int t=(n/3)*y+(n%3)*x; 8 System.out.println(Math.min(t,x*n)); 9 10 } 11 }
B题
简单模拟
数组版本
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 6 int n=sc.nextInt(); 7 int m=sc.nextInt(); 8 long t=sc.nextInt(); 9 int arr[]=new int[n+1]; 10 long vis[]=new long[n+1]; 11 for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ 12 arr[i]=sc.nextInt(); 13 vis[i]=0; 14 } 15 // for(int i=1;i<n;i++) System.out.println(arr[i]+" "+vis[i]); 16 // System.out.println("fuck11"); 17 for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ 18 int x=sc.nextInt(); 19 long y=sc.nextInt(); 20 // System.out.println(x+" "+y); 21 vis[x]=y; 22 } 23 // System.out.println("fuck22"); 24 boolean flag=true; 25 for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ 26 t=t+vis[i]; 27 t=t-arr[i]; 28 if(t<=0){ 29 flag=false; 30 break; 31 } 32 33 } 34 if(flag==true){ 35 System.out.println("Yes"); 36 }else{ 37 System.out.println("No"); 38 } 39 } 40 }
map版本(学习java中用map进行数据映射)
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 5 int n=sc.nextInt(); 6 int m=sc.nextInt(); 7 long t=sc.nextInt(); 8 int arr[]=new int[n+1]; 9 for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ 10 arr[i]=sc.nextInt(); 11 } 12 Map<Integer,Long> vis = new HashMap<>(); 13 14 for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ 15 Integer x=sc.nextInt(); 16 Long y=sc.nextLong(); 17 vis.put(x,y); // put添加元素(键和值) 18 // vis[x]=y; 19 } 20 // System.out.println("fuck22"); 21 boolean flag=true; 22 for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ 23 if(vis.containsKey(i)){ //判断map种是否存在值i 24 t=t+vis.get(i); //get根据键获取值 25 } 26 27 t=t-arr[i]; 28 if(t<=0){ 29 flag=false; 30 break; 31 } 32 33 } 34 if(flag==true){ 35 System.out.println("Yes"); 36 }else{ 37 System.out.println("No"); 38 } 39 } 40 }
C题
简单模拟
学习字符串数组输入
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 5 int n=sc.nextInt(); 6 int m=sc.nextInt(); 7 char[][] mp=new char[n+100][m+100]; 8 int[][] vis=new int[n+100][m+100]; 9 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) 10 for(int j=0;j<=m;j++) 11 vis[i][j]=0; 12 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 13 mp[i]=sc.next().toCharArray(); 14 } 15 // for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 16 // for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ 17 // System.out.print(mp[i][j]); 18 // } 19 // System.out.println(); 20 // } 21 int ansx=0,ansy=0,flag=0; 22 int curx=0,cury=0; 23 vis[0][0]=1; 24 while(curx>=0&&cury>=0&&curx<n&&cury<m){ 25 if(mp[curx][cury]=='R'){ 26 cury=cury+1; 27 }else if(mp[curx][cury]=='L'){ 28 cury=cury-1; 29 }else if(mp[curx][cury]=='U'){ 30 curx=curx-1; 31 }else if(mp[curx][cury]=='D'){ 32 curx=curx+1; 33 } 34 35 if((curx>=0&&cury>=0&&curx<n&&cury<m)){ 36 if(vis[curx][cury]>1){ 37 flag=1; 38 break; 39 }else{ 40 vis[curx][cury]+=1; 41 } 42 ansx=curx; 43 ansy=cury; 44 } 45 46 } 47 if(flag==1){ 48 System.out.println("-1"); 49 }else{ 50 System.out.println((ansx+1)+" "+(ansy+1)); 51 } 52 } 53 }
D题
由于X,Y,Z,W不相交且具有前后顺序,因此可以使用单调队列进行模拟取数求和判断
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 5 int n=sc.nextInt(); 6 long P=sc.nextLong(); 7 long Q=sc.nextLong(); 8 long R=sc.nextLong(); 9 long[] arr=new long[n+100]; 10 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 11 arr[i]=sc.nextLong(); 12 } 13 ArrayDeque<Long> arrayDeque = new ArrayDeque(); 14 // arrayDeque.addFirst(1); 15 // System.out.println(arrayDeque.getFirst()); 16 long temp=P; 17 int st=1,ok=0; 18 long sum=0; 19 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 20 arrayDeque.addLast(arr[i]); 21 sum+=arr[i]; 22 // System.out.println(arrayDeque+","+sum); 23 if(sum==temp){ 24 arrayDeque.clear(); 25 sum=0; 26 if(st==1){ 27 st=2; 28 temp=Q; 29 }else if(st==2){ 30 st=3; 31 temp=R; 32 }else if(st==3){ 33 ok=1; 34 break; 35 } 36 37 }else if(sum>temp){ 38 while((sum>temp)&&(!arrayDeque.isEmpty())){ 39 long cur= (long) arrayDeque.getFirst(); 40 arrayDeque.removeFirst(); 41 sum-=cur; 42 } 43 if(sum==temp){ 44 arrayDeque.clear(); 45 sum=0; 46 if(st==1){ 47 st=2; 48 temp=Q; 49 }else if(st==2){ 50 st=3; 51 temp=R; 52 }else if(st==3){ 53 ok=1; 54 break; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 if(ok==1){ 60 System.out.println("Yes"); 61 }else{ 62 System.out.println("No"); 63 } 64 } 65 }
E题
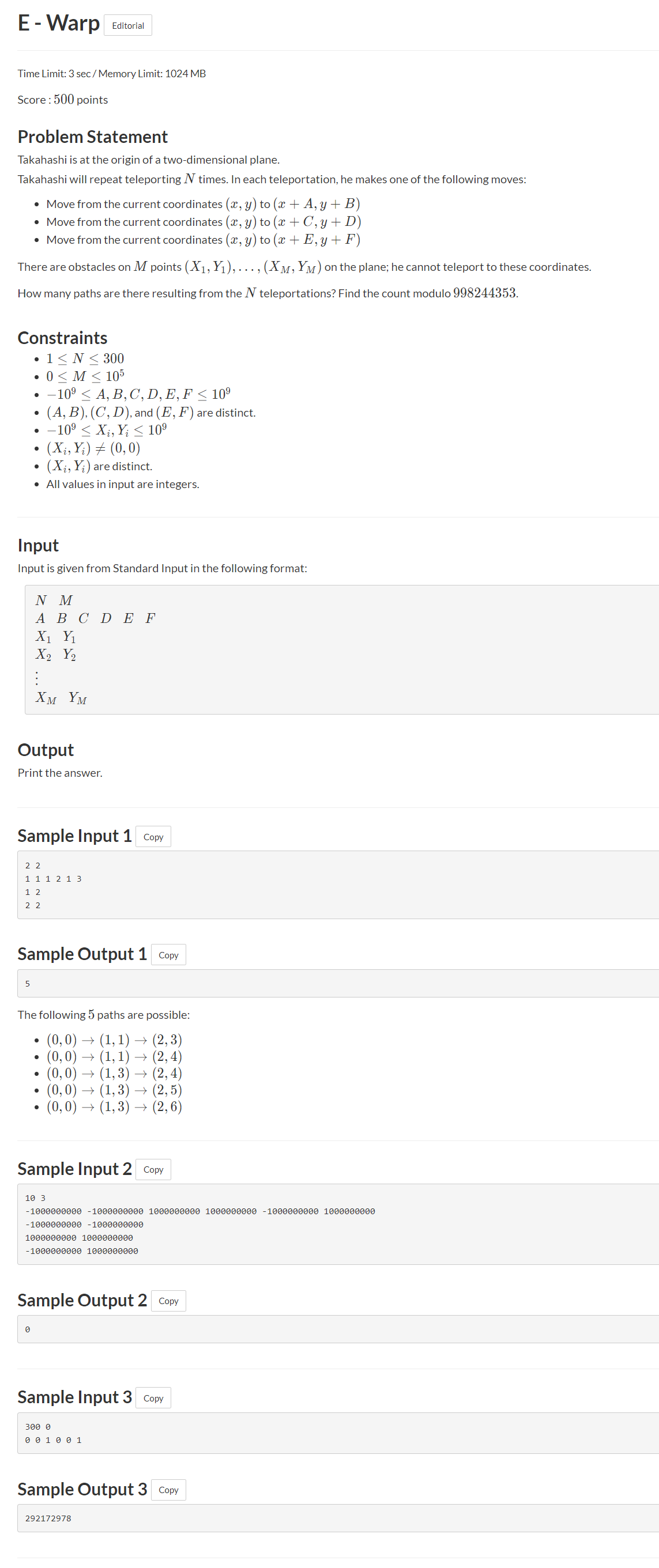
这题很明显需要用DP进行转移。从之前经验看,用二维数组存下整张图,但是发现图的数据范围用数组存不下。因此重新看了一下题意,发现我们只需要知道3种传输方式各位多少就行。那么这样的话,我们就可以列出状态转移方程。
dp[i,j,k]:表示传输方式1用了i次,传输方式2用了j次,传输方式3用了k次。
1 import javafx.util.Pair; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 public class Main { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 long mod=998244353; 8 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 9 int n=sc.nextInt(); 10 int m=sc.nextInt(); 11 int[] f=new int[10]; 12 for(int i=1;i<=6;i++){ 13 f[i]=sc.nextInt(); 14 } 15 // HashMap<Pair<Long,Long>,Long> hashMap=new HashMap<>(); 16 HashSet hashSet = new HashSet<String>(); 17 for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ 18 long x=sc.nextLong(); 19 long y=sc.nextLong(); 20 // hashMap.put(new Pair<>(x,y),1L); 21 hashSet.add(x+","+y); 22 } 23 long[][][] dp=new long[305][305][305]; 24 dp[0][0][0]=1L; 25 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){ 26 for(int j=0;j<=n-i;j++){ 27 for(int k=0;k<=n-i-j;k++){ 28 long curx=f[1]*i+f[3]*j+f[5]*k; 29 long cury=f[2]*i+f[4]*j+f[6]*k; 30 // if(hashMap.containsKey(new Pair<>(curx,cury))){ 31 // continue; 32 // } 33 if(hashSet.contains(curx+","+cury)) continue; 34 35 if(i-1>=0) 36 dp[i][j][k]=(dp[i-1][j][k]+dp[i][j][k])%mod; 37 if(j-1>=0) 38 dp[i][j][k]=(dp[i][j-1][k]+dp[i][j][k])%mod; 39 if(k-1>=0) 40 dp[i][j][k]=(dp[i][j][k-1]+dp[i][j][k])%mod; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 long ans=0; 45 for(int i=0;i<=301;i++){ 46 for(int j=0;j<=301;j++){ 47 for(int k=0;k<=301;k++){ 48 if(i+j+k==n){ 49 ans=(ans+dp[i][j][k])%mod; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 System.out.println(ans); 55 } 56 } 57 /* 58 * dp[i,j,k]:表示当前在(i,j)位置上,且传递k次了 59 * 60 * */





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· Apache Tomcat RCE漏洞复现(CVE-2025-24813)