seq_file学习(2)—— seq_file
作者
彭东林
pengdonglin137@163.com
平台
Linux-4.14.13
Qemu + vexpress
概述
前面介绍了single_open,下面结合一个简单的demo驱动,学习一下seq_file的用法。
下面是一张示意图:
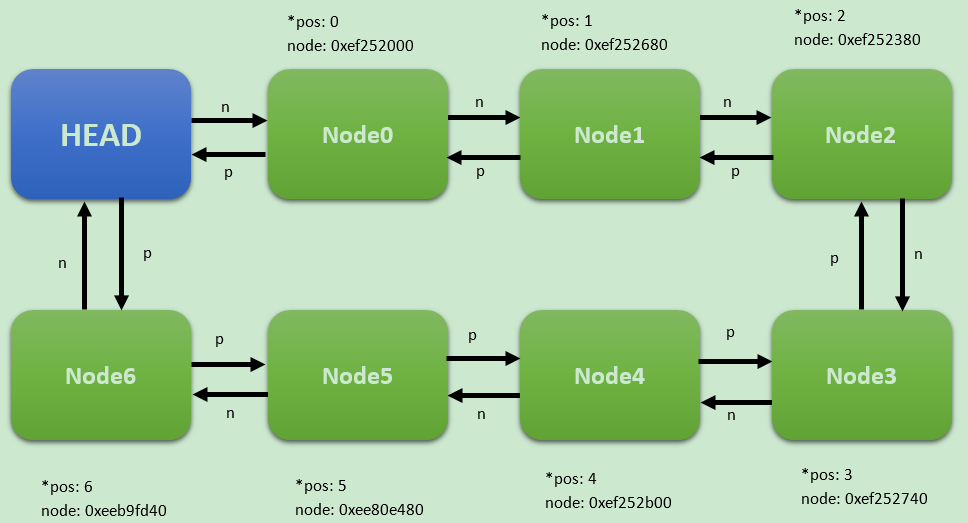
正文
seq_demo驱动里实现了一个简单的链表,在init的时候会依次创建7个节点并加入链表,然后向用户空间导出一个seq_demo的节点,读取这个节点,就会调用seq_file相关函数对链表进行遍历,输出每个节点的相关信息。
一、seq_demo驱动
1 #include <linux/init.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/seq_file.h> 4 #include <linux/debugfs.h> 5 #include <linux/fs.h> 6 #include <linux/list.h> 7 #include <linux/slab.h> 8 9 static struct dentry *seq_demo_dir; 10 static LIST_HEAD(seq_demo_list); 11 static DEFINE_MUTEX(seq_demo_lock); 12 13 struct seq_demo_node { 14 char name[10]; 15 struct list_head list; 16 }; 17 18 static void *seq_demo_start(struct seq_file *s, loff_t *pos) 19 { 20 mutex_lock(&seq_demo_lock); 21 22 return seq_list_start(&seq_demo_list, *pos); 23 } 24 25 static void *seq_demo_next(struct seq_file *s, void *v, loff_t *pos) 26 { 27 return seq_list_next(v, &seq_demo_list, pos); 28 } 29 30 static void seq_demo_stop(struct seq_file *s, void *v) 31 { 32 mutex_unlock(&seq_demo_lock); 33 } 34 35 static int seq_demo_show(struct seq_file *s, void *v) 36 { 37 struct seq_demo_node *node = list_entry(v, struct seq_demo_node, list); 38 39 seq_printf(s, "name: %s, addr: 0x%p\n", node->name, node); 40 41 return 0; 42 } 43 44 static const struct seq_operations seq_demo_ops = { 45 .start = seq_demo_start, 46 .next = seq_demo_next, 47 .stop = seq_demo_stop, 48 .show = seq_demo_show, 49 }; 50 51 static int seq_demo_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) 52 { 53 return seq_open(file, &seq_demo_ops); 54 } 55 56 static const struct file_operations seq_demo_fops = { 57 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 58 .open = seq_demo_open, 59 .read = seq_read, 60 .llseek = seq_lseek, 61 .release = seq_release, 62 }; 63 64 static int __init seq_demo_init(void) 65 { 66 int i; 67 struct seq_demo_node *node; 68 69 for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) { 70 node = kzalloc(sizeof(struct seq_demo_node), GFP_KERNEL); 71 sprintf(node->name, "node%d", i); 72 73 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&node->list); 74 list_add_tail(&node->list, &seq_demo_list); 75 } 76 77 seq_demo_dir = debugfs_create_file("seq_demo", 0444, NULL, 78 NULL, &seq_demo_fops); 79 return 0; 80 } 81 82 static void __exit seq_demo_exit(void) 83 { 84 struct seq_demo_node *node_pos, *node_n; 85 86 if (seq_demo_dir) { 87 debugfs_remove(seq_demo_dir); 88 list_for_each_entry_safe(node_pos, node_n, &seq_demo_list, list) 89 if (node_pos) { 90 printk("%s: release %s\n", __func__, node_pos->name); 91 kfree(node_pos); 92 } 93 } 94 } 95 96 module_init(seq_demo_init); 97 module_exit(seq_demo_exit); 98 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
下面是运行结果:
[root@vexpress mnt]# cat /d/seq_demo name: node0, addr: 0xef252000 name: node1, addr: 0xef252680 name: node2, addr: 0xef252380 name: node3, addr: 0xef252740 name: node4, addr: 0xef252b00 name: node5, addr: 0xee80e480 name: node6, addr: 0xeeb9fd40 name: node7, addr: 0xeeb9fd00
二、分析
在遍历链表的时候使用seq_file提供的通用接口函数,当然也可以自己实现,只需要遵循如下原则:
start:根据索引编号pos找到对应的node,并返回该node的地址,也就是show和next方法里的v
next:根据当前node的地址和索引编号计算下一个node的地址和索引编号pos,返回值就是下一个节点的地址
show:输出传入的node的信息
stop:如果在start里有加锁,那么在这里需要释放锁
结合上面的驱动分析一下:
seq_list_start:
1 struct list_head *seq_list_start(struct list_head *head, loff_t pos) 2 { 3 struct list_head *lh; 4 5 list_for_each(lh, head) 6 if (pos-- == 0) 7 return lh; 8 9 return NULL; 10 }
遍历链表,寻找索引为pos的项,找到的话,返回地址,否则返回NULL。当返回NULL的时候, stop会被调用。
seq_list_next:
1 struct list_head *seq_list_next(void *v, struct list_head *head, loff_t *ppos) 2 { 3 struct list_head *lh; 4 5 lh = ((struct list_head *)v)->next; 6 ++*ppos; 7 return lh == head ? NULL : lh; 8 }
计算下一项的地址和索引,如果遍历结束,即lh==head,返回NULL,否则返回下一项的地址。当返回NULL的时候,stop会被调用并把缓冲区中的内容吐给用户
未完待续
本文来自博客园,作者:dolinux,未经同意,禁止转载





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
2014-02-10 Android 环境搭建
2014-02-10 dl-ssl.google.com