crash命令 —— list
参考:
说明
头节点是A_head: struct A_head { // -h: 内嵌了list_head的结构体的地址 ... // -O: list_head在头节点中的偏移量,只能跟-h搭配 struct list_head list; // -H: list_head的地址 int b; // -s: 想要查看的结构体的成员的偏移量 }; 普通节点是A: struct A { // -h: 内嵌了list_head的结构体的地址 ... // -o: list_head普通中的偏移量 struct list_head list; // -H: list_head的地址 char pid; // -s: 想要查看的结构体的成员的偏移量 }; 假设将来A通过A.list挂到A_head. -H: list_head的地址 -h: 内嵌了list_head的结构体A_head或者A的地址 -o: 在普通节点中list_head在A中的偏移,格式A.list -O: 在头结点中list_head在A中的偏移,格式A_head.list。当头节点跟普通节点不同的时候需要这个参数,在输出的内容里不会输出头节点的内容。 -s: 要查看的结构体的成员
示例
- 遍历线程组thread_group
当创建线程的时候,当前进程下的所有线程的task_struct都通过thread_node挂在了task_struct->signal->thread_head下面。
list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_group, &p->group_leader->thread_group); list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_node, &p->signal->thread_head);
线程组中的task的signal是相同的,所以先获取signal的地址,然后遍历thread_head链表即可。
以task 714为例:
crash> task -R signal 714 PID: 714 TASK: ffff889e1449c000 CPU: 14 COMMAND: "kvm" signal = 0xffff889ecdaab600,
然后查看thread_head的地址:
crash> signal_struct.nr_threads,thread_head 0xffff889ecdaab600 nr_threads = 17 thread_head = { next = 0xffff889ecd9789b8, prev = 0xffff88a031cf89b8 }
当前线程组有17个线程,开始遍历:
crash> list -o task_struct.thread_node -s task_struct.pid,tgid -H ffff889ecdaab610 ffff889ecd978000 pid = 451 tgid = 451 ffff889ed1c44000 pid = 452 tgid = 451 ffff8899f8bb2000 pid = 456 tgid = 451 ffff8897bc884000 pid = 480 tgid = 451 ffff8897bc880000 pid = 487 tgid = 451 ffff8897bc882000 pid = 488 tgid = 451 ffff8897bc886000 ...
-
遍历cgroup_root
-
以下面的数据结构关系为例:
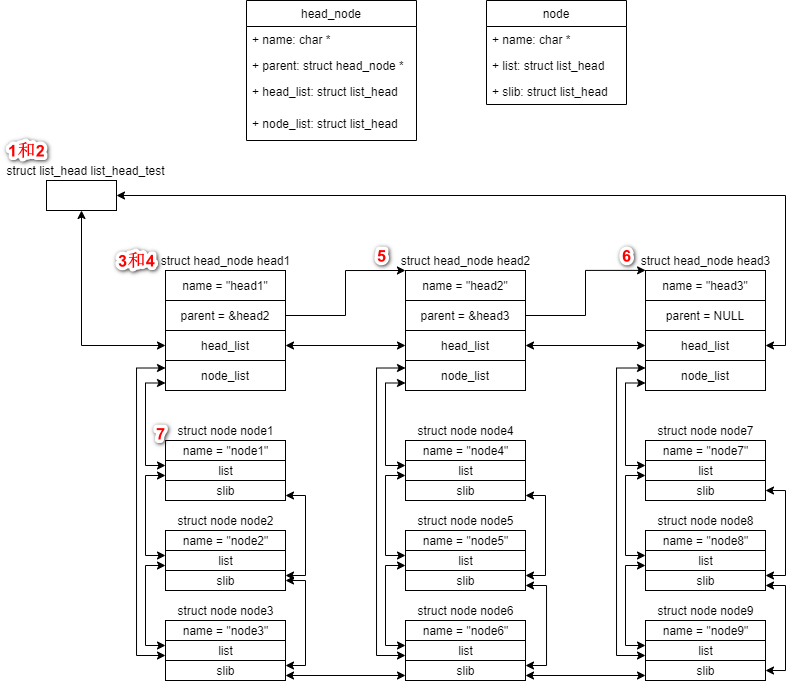
说明:
- head_node使用head_list连接到list_head_test中
- head_node之间有父子关系
- head_node的node通过node.list连到head_node.node_list下面
- 所有的node通过node.slib连接在一起
- 上面的标号表示的是下面的对应的示例程序使用的起始地址
- 查看
list_head_test地址
crash> sym list_head_test ffffffffad245b30 (d) list_head_test
- 查看
list_head_test链表下挂的head_node
crash> list -o head_node.head_list -s head_node.name -H ffffffffad245b30 ffff93b2850c3b40 // struct head_node的地址 name = 0xfffffffface7a68f "head1", ffff93b2850c3b80 // struct head_node的地址 name = 0xfffffffface7a695 "head2", ffff93b2850c3bc0 // struct head_node的地址 name = 0xfffffffface7a69b "head3",
- 查看
head1的parent
crash> list -o head_node.parent -s head_node.name ffff93b2850c3b40 ffff93b2850c3b40 name = 0xfffffffface7a68f "head1", ffff93b2850c3b80 name = 0xfffffffface7a695 "head2", ffff93b2850c3bc0 name = 0xfffffffface7a69b "head3",
在结构体中,parent没有采用list_head链表,所以不能用-h或者-H
- 查看
head_node1下的node成员
crash> list -o node.list -s node.name -O head_node.node_list -h ffff93b2850c3b40 ffff93b2850c3c00 name = 0xfffffffface7a6a1 "node1", ffff93b2850c3c40 name = 0xfffffffface7a6a7 "node2", ffff93b2850c3c80 name = 0xfffffffface7a6ad "node3",
- 查看
head_node2下的node成员
crash> list -o node.list -s node.name -O head_node.node_list -h ffff93b2850c3b80 ffff93b2850c3cc0 name = 0xfffffffface7a6b3 "node4", ffff93b2850c3d00 name = 0xfffffffface7a6b9 "node5", ffff93b2850c3d40 name = 0xfffffffface7a6bf "node6",
- 查看
head_node3下的node成员
crash> list -o node.list -s node.name -O head_node.node_list -h ffff93b2850c3bc0 ffff93b2850c3d80 name = 0xfffffffface7a6c5 "node7", ffff93b2850c3dc0 name = 0xfffffffface7a6cb "node8", ffff93b2850c3e00 name = 0xfffffffface7a6d1 "node9",
- 查看
node.slib链表中的成员
使用node1的起始地址
crash> list -o node.slib -s node.name -h ffff93b2850c3c00 ffff93b2850c3c00 name = 0xfffffffface7a6a1 "node1", ffff93b2850c3c40 name = 0xfffffffface7a6a7 "node2", ffff93b2850c3c80 name = 0xfffffffface7a6ad "node3", ffff93b2850c3cc0 name = 0xfffffffface7a6b3 "node4", ffff93b2850c3d00 name = 0xfffffffface7a6b9 "node5", ffff93b2850c3d40 name = 0xfffffffface7a6bf "node6", ffff93b2850c3d80 name = 0xfffffffface7a6c5 "node7", ffff93b2850c3dc0 name = 0xfffffffface7a6cb "node8", ffff93b2850c3e00 name = 0xfffffffface7a6d1 "node9",
如果使用-O参数,那么会把传入地址当作头节点,输出的内容不包含头节点的内容:
crash> list -o node.slib -s node.name -O node.slib -h ffff93b2850c3c00 ffff93b2850c3c40 name = 0xfffffffface7a6a7 "node2", ffff93b2850c3c80 name = 0xfffffffface7a6ad "node3", ffff93b2850c3cc0 name = 0xfffffffface7a6b3 "node4", ffff93b2850c3d00 name = 0xfffffffface7a6b9 "node5", ffff93b2850c3d40 name = 0xfffffffface7a6bf "node6", ffff93b2850c3d80 name = 0xfffffffface7a6c5 "node7", ffff93b2850c3dc0 name = 0xfffffffface7a6cb "node8", ffff93b2850c3e00 name = 0xfffffffface7a6d1 "node9",
其他
-o
那么list只能查看list_head串起来的链表吗?
当然不是,上面的输出parent链表也说明了这一点。在list的帮助文档里说:
[-o] offset The offset within the structure to the "next" pointer (default is 0). If non-zero, the offset may be entered in either of two manners: 1. In "structure.member" format; the "-o" is not necessary. 2. A number of bytes; the "-o" is only necessary on processors where the offset value could be misconstrued as a kernel
- 场景1
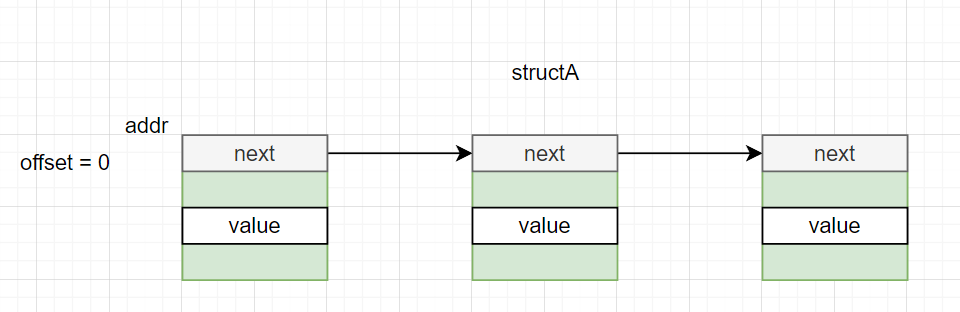
list -s structA.value addr
or
list -o 0 -s structA.value addr
- 场景2
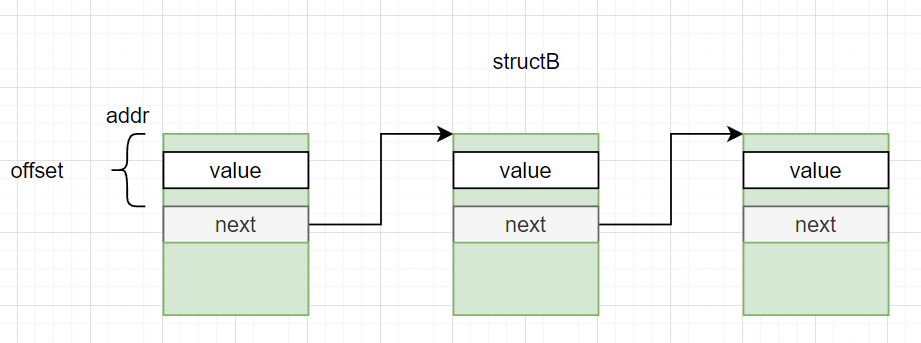
list -o structB.next -s structB.value addr
or
list -o offset -s structB.value addr
-l
-l参数的帮助:
-l offset Only used in conjunction with -s, if the start address argument is a pointer to an embedded list head (or any other similar list linkage structure whose first member points to the next linkage structure), the offset to the embedded member may be entered in either of the following manners: 1. in "structure.member" format. 2. a number of bytes.
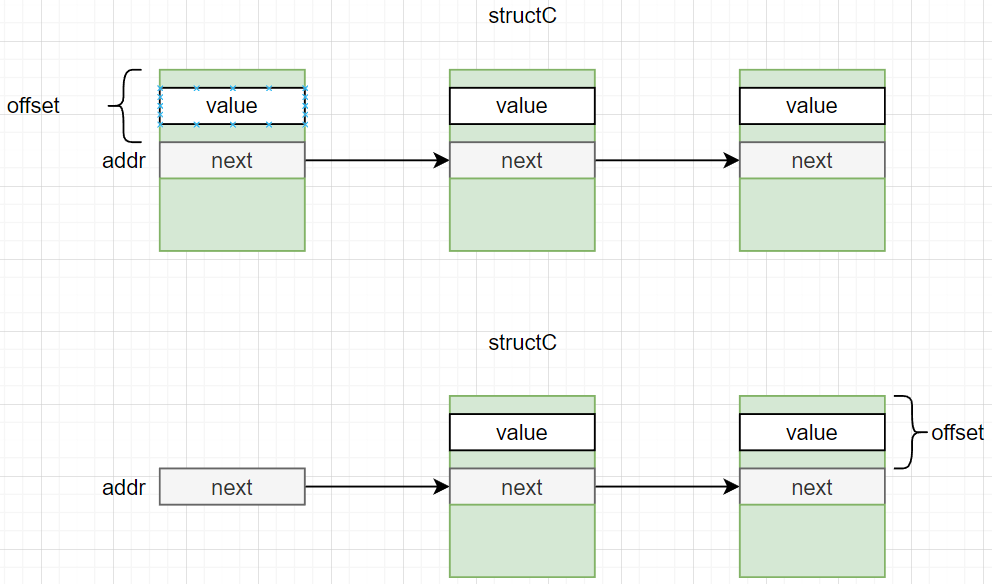
list -l structC.next -s structC.value addr
or
list -l offset -s structC.value addr
示例:
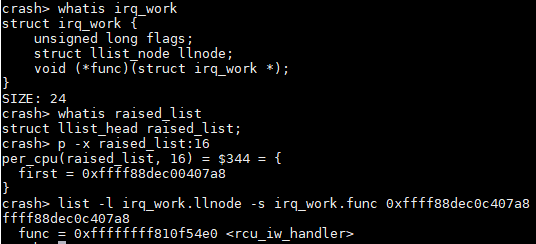
可以想象,如果next位置移到了结构体开头,那么下面几种做法都可以:
list -o structD.next -s strcutD.value addr
or
list -l structD.next -s structD.value vaddr
or
list -s structD.value addr
示例:
本文来自博客园,作者:dolinux,未经同意,禁止转载
合集:
crash工具使用方法




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
2017-03-23 用C扩展Python3
2017-03-23 交叉编译Python-3.6.0到aarch64/aarch32 —— 支持sqlite3