11.IO流
第十一章【IO流】
一、流的概念
数据以二进制的形式在程序与设备之间流动传输,就像水在管道里流动一样,所以就把这种数据传输的方式称之为输入流、输出流。
二、流的分类
根据数据的流向分为:输入流和输出流
-
输入流 :把数据从其他设备上读取到程序中的流
-
输出流 :把数据从程序中写出到其他设备上的流
根据数据的类型分为:字节流和字符流
-
字节流 :以字节为单位(byte),读写数据的流
-
字符流 :以字符为单位(char),读写数据的流
总的分类:
-
字节输入流,在程序中,以字节的方式,将设备(文件、内存、网络等)中的数据读进来
-
字节输出流,在程序中,以字节的方式,将数据写入到设备(文件、内存、网络等)中
-
字符输入流,在程序中,以字符的方式,将设备(文件、内存、网络等)中的数据读进来
-
字符输出流,在程序中,以字符的方式,将数据写入到设备(文件、内存、网络等)中
三、流的结构
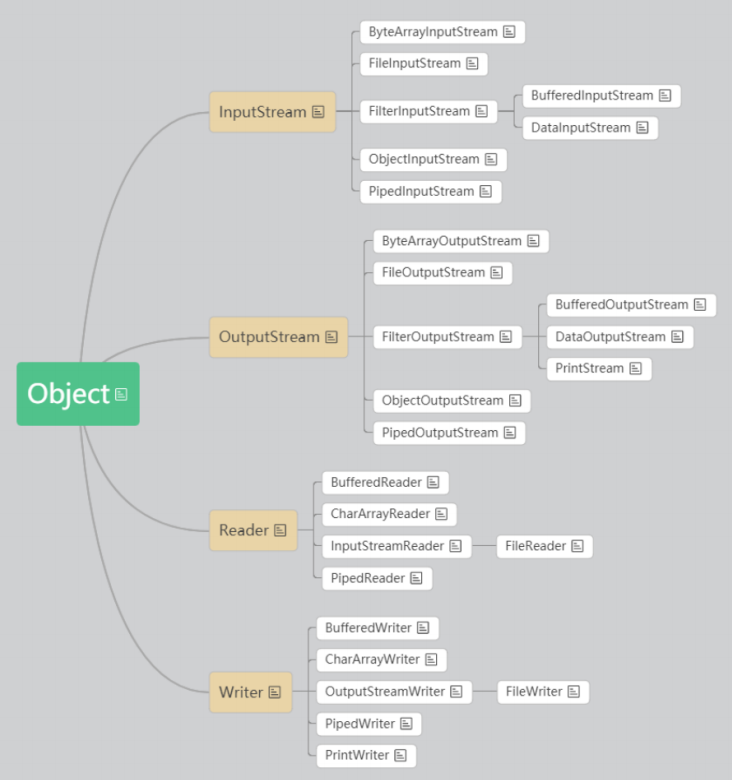
几乎所有的流,都是派生自四个抽象的父类型:
-
InputStream,代表字节输入流类型 -
OutputStream,代表字节输出流类型 -
Reader,代表字符输入流类型 -
Writer,代表字符输出流类型
基本流【节点流】:
字节输入输出流:xxxInputStream/xxxOutputStream 【xxx:设备】
字符输入输出流:xxxReader/xxxWriter
包装流:字节输入输出流,字符输入输出流
一般情况下,一个流,会具备最起码的三个特点:
- 是输入还是输出
- 是字节还是字符
- 流的目的地
四、字节流
1、概述
java.io.InputStream是所有字节输入流的抽象父类型
java.io.OutputStream是所有字节输出流的抽象父类型
在代码中,使用流操作数据的的基本步骤是:
- 声明流
- 创建流
- 使用流
- 关闭流
2、控制台
让程序一直读取和写出,那么可以加入while循环,遇到“bye”结束
public class InputAndOutputStreamTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.声明流
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
//2.创建流
in = System.in;
out = System.out;
//3.使用流
int num = -1;
byte[] by = new byte[1024];
try {
while ((num = in.read(by)) != -1) {
out.write(by, 0, num);
out.flush();
if(by[num -1] == 10 && by[num -2] == 13) {
num = num - 2;
}
String str = new String(by, 0, num);
if(str.equals("bye")) {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4.关闭流
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3、字节数组
java.io.ByteArrayInputStream负责从字节数组中读取数据
java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream负责把数据写入到字节数组中
使用字节流,从字节数组中读取数据,以及向字节数组中写数据。
public class ByteArrayStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.声明流
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
//2.创建流
byte[] arr = "hello world".getBytes();
in = new ByteArrayInputStream(arr);
out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//3.使用流
int len = -1;
byte[] by = new byte[1024];
try {
len = in.read(by);
out.write(by, 0, len);
out.flush();
//4.可视化到控制台
String str = out.toString();
System.out.println(str);
//5.调用ByteArrayOutputStream中的toByteArray方法,可以将写入到out对象中的数据返回
byte[] array = ((ByteArrayOutputStream)out).toByteArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//6.关闭流
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
4、管道
java.io.PipedInputStream负责从管道中读取数据
java.io.PipedOutputStream负责将数据写入到管道中
使用字节流,可以从管道中读取数据,以及向管道中写数据。
public class PipedStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.声明流
PipedInputStream in = null;
PipedOutputStream out = null;
//2.创建流
in = new PipedInputStream();
out = new PipedOutputStream();
//3.管道对接
try {
in.connect(out);
Thread t1 = new WriterThread(out);
Thread t2 = new ReaderThread(in);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("程序运行结束");
}
}
class WriterThread extends Thread{
private OutputStream out;
public WriterThread(OutputStream out) {
this.out = out;
}
@Override
public void run() {
byte[] arr = "hello world".getBytes();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
out.write(arr[i]);
out.flush();
Thread.sleep(100);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
class ReaderThread extends Thread{
private InputStream in;
public ReaderThread(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int len = -1;
try {
while ((len = in.read()) != -1) {
System.out.write(len);
System.out.flush();
}
System.out.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
5、文件
java.io.File类,是java中对文件和目录的抽象表示,主要用于文件和目录的创建、查找和删除等操作。
常用方法:
public String getAbsolutePath(),返回file的绝对路径
public String getPath() ,返回创建file对象时传入的路径参数(有可能是相对路径)
public String getName(),返回file的名字
public long length(),file如果表示文件,则返回文件内容的长度(字节个数)
public boolean exists(),判断此文件或目录是否真的存在
public boolean isDirectory() ,判断File表示的是否是一个目录
public boolean isFile(),判断file表示的是否是一个文件
使用字节流,可以从文件中读取数据,以及向文件中写数据。
java.io.FileInputStream,负责从文件中读取数据
java.io.FileOutputStream,负责把数据写入到文件中
public class FileStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.声明流
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
//2.创建流
try {
File f1 = new File("src/com/sxu/day19/test/a.txt");
File f2 = new File("src/com/sxu/day19/test/b.txt");
in = new FileInputStream(f1);
out = new FileOutputStream(f2);
//3.使用流
int len = -1;
byte[] by = new byte[1024];
while ((len = in.read(by)) != -1) {
out.write(by,0,len);
}
out.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
6、网络
转至 12.网络编程.md
五、字符流
1、概述
字符流,可以用字符的形式,读写数据,专门用于处理文本数据。
java.io.Reader是所有字符输入流的抽象父类型
java.io.Writer是所有字符输出流的抽象父类型
2、字符数组
使用字符流,从字符数组中读取数据,以及向字符数组中写数据。
java.io.CharArrayReader负责从字符数组中读取数据
java.io.CharArrayWriter负责把数据写入到字符数组中
public class ReaderAndWriterStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.声明流
Reader in = null;
Writer out = null;
//2.创建流
char[] arr = "hello world".toCharArray();
in = new CharArrayReader(arr);
out = new CharArrayWriter();
//3.使用流
int len = -1;
char[] ch = new char[1024];
try {
len = in.read(ch);
out.write(ch, 0, len);
out.flush();
String str = out.toString();
System.out.println(str);
//CharArrayWriter中的toCharArray方法,可以将写入到out对象中的数据返回
char[] charArray = ((CharArrayWriter)out).toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(charArray));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3、管道
使用字符流,可以从管道中读取数据,以及向管道中写数据。
java.io.PipedReader负责从管道中读取数据
java.io.PipedWriter负责将数据写入到管道中
public class PipedTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PipedReader in = null;
PipedWriter out = null;
in = new PipedReader();
out = new PipedWriter();
try {
in.connect(out);
Thread t1 = new WriterThreaed(out);
Thread t2 = new ReaderThread(in);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("程序运行结束");
}
}
class WriterThreaed extends Thread{
private Writer out;
public WriterThreaed(Writer out) {
this.out = out;
}
@Override
public void run() {
char[] arr = "hello world".toCharArray();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
out.write(arr[i]);
out.flush();
Thread.sleep(100);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
class ReaderThread extends Thread{
private Reader in;
public ReaderThread(Reader in) {
this.in = in;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int len = -1;
try {
while ((len = in.read()) != -1) {
System.out.write(len);
System.out.flush();
}
System.out.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
4、文件
使用字符流,可以从文件中读取数据,以及向文件中写数据。
java.io.FileReader ,负责从文件中读取数据
java.io.FileWriter ,负责把数据写入到文件中
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.声明流
Reader in = null;
Writer out = null;
try {
//2.创建流
File f1 = new File("src/com/sxu/day20/test/a.txt");
File f2 = new File("src/com/sxu/day20/test/b.txt");
in = new FileReader(f1);
out = new FileWriter(f2);
//3.使用流
int len = -1;
char[] ch = new char[1024];
while ((len = in.read(ch)) != -1) {
out.write(ch,0,len);
}
out.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
5、其他
其他情况,使用字符流进行读写数据时,可以借助于字节流,将字节流转换为字符流来操作。因为字符流底层也是以字节为单位来操作数据的,只不过中间会把字节按照默认或指定的字符编号,把字节转成了字符而已。
六、节点流
字节流和字符流,都属于节点流
它们的特点是,可以【直接】读取某一个地方的数据,或者【直接】把数据写入到某一个地方。
七、数据流
DataOutputStream负责把指定类型的数据,转化为字节并写出去
DataInputStream负责把读取到的若干个字节,转化为指定类型的数据
八、缓冲流
字节缓冲流
java.io.BufferedInputStream,负责给字节输入流提供缓冲功能
java.io.BufferedOutputStream,负责给字节输出流提供缓冲功能
字符缓冲流
java.io.BufferedReader,负责给字符输入流提供缓冲功能
java.io.BufferedWriter,负责给字符输出流提供缓冲功能
九、转换流
java.io.OutputStreamWriter ,可以将字节输出流转换为字符输出流,并指定编码
java.io.InputStreamReader,可以将字节输入流转换为字符输入流,并指定编码
十、对象流
在java中,并非所有对象都可以进行序列化和反序列化,而是只有实现了指定接口的对象才可以进行。java.io.Serializable接口
java.io.ObjectOutputStream,将Java对象转换为字节序列,并输出到内存、文件、网络等地方java.io.ObjectInputStream,从某一个地方读取出对象的字节序列,并生成对应的对象
java中的关键字transient,可以修饰类中的属性,它的让对象在进行序列化的时候,忽略掉这个被修饰的属性
十一、随机访问流
java.io.RandomAccessFile是JavaAPI中提供的对文件进行随机访问的流


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~