NLP(六) 分块、句法分析、依存分析
原文链接:http://www.one2know.cn/nlp6/
- 内置分块器
分块:从文本中抽取短语
import nltk
text = 'Lalbagh Botanical Garden is a well known botanical garden in Bengaluru, India.'
# 文本切割成多个句子
sentences = nltk.sent_tokenize(text)
for sentence in sentences:
words = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)
tags = nltk.pos_tag(words)
chunks = nltk.ne_chunk(tags) # 实现分块,返回树结构
print(chunks)
输出:
(S
(PERSON Lalbagh/NNP)
(PERSON Botanical/NNP Garden/NNP)
is/VBZ
a/DT
well/RB
known/VBN
botanical/JJ
garden/NN
in/IN
(GPE Bengaluru/NNP)
,/,
(GPE India/NNP)
./.)
- 编写简单的RE分块器
import nltk
text = 'Ravi is the CEO of a company. He is very powerful public speaker also.'
# 词性语法规则
grammar = '\n'.join([
'NP: {<DT>*<NNP>}', # 一个或多个DT后紧跟一个NNP
'NP: {<JJ>*<NN>}', # 一个或多个JJ后紧跟一个NN
'NP: {<NNP>+}', # 一个或多个NNP组成
])
sentences = nltk.sent_tokenize(text)
for sentence in sentences:
words = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)
tags = nltk.pos_tag(words)
# 将语法规则放到RegexpParser对象中
chunkparser = nltk.RegexpParser(grammar)
result = chunkparser.parse(tags)
print(result)
输出:
(S
(NP Ravi/NNP)
is/VBZ
(NP the/DT CEO/NNP)
of/IN
a/DT
(NP company/NN)
./.)
(S
He/PRP
is/VBZ
very/RB
(NP powerful/JJ public/JJ speaker/NN)
also/RB
./.)
- 训练分块器
IOB标注格式:
| 列 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| IOB第一列 | 输入句子中的单词 |
| IOB第二列 | 单词对应的词性 |
| IOB第三列 | I(内部词),O(外部词),B(开始词);加上词种类的后缀 |
| 例子: | |
| Rockwell NNP B-NP | |
| International NNP I-NP | |
| Corp. NNP I-NP | |
| 's POS B-NP | |
| Tulsa NNP I-NP | |
| unit NN I-NP | |
| said VBD B-VP | |
| it PRP B-NP | |
| 代码: |
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import conll2000,treebank_chunk # 两个数据集
# 简单的分块器,抽取NNP(专有名词)
def mySimpleChunker():
grammar = 'NP: {<NNP>+}'
return nltk.RegexpParser(grammar)
# 不抽取任何东西,只用于检验算法能否正常运行
def test_nothing(data):
cp = nltk.RegexpParser("")
print(cp.evaluate(data))
# 测试mySimpleChunker()函数
def test_mysimplechunker(data):
schunker = mySimpleChunker()
print(schunker.evaluate(data))
datasets = [
conll2000.chunked_sents('test.txt',chunk_types=['NP']),
treebank_chunk.chunked_sents(),
]
# 前50个IOB标注语句 计算分块器的准确率
for dataset in datasets:
test_nothing(dataset[:50])
print('---------------------')
test_mysimplechunker(dataset[:50])
print()
输出:
ChunkParse score:
IOB Accuracy: 38.6%%
Precision: 0.0%%
Recall: 0.0%%
F-Measure: 0.0%%
---------------------
ChunkParse score:
IOB Accuracy: 48.2%%
Precision: 71.1%%
Recall: 17.2%%
F-Measure: 27.7%%
ChunkParse score:
IOB Accuracy: 45.0%%
Precision: 0.0%%
Recall: 0.0%%
F-Measure: 0.0%%
---------------------
ChunkParse score:
IOB Accuracy: 50.7%%
Precision: 51.9%%
Recall: 8.8%%
F-Measure: 15.1%%
- 递归下降句法分析
递归先序遍历句法分析树
NLTK的RD分析器
import nltk
def RDParserExample(grammar,textlist):
# RecursiveDescentParser递归下降分析器
parser = nltk.parse.RecursiveDescentParser(grammar)
for text in textlist:
sentence = nltk.word_tokenize(text)
for tree in parser.parse(sentence):
print(tree)
tree.draw()
# 利用grammar创建CFG对象
grammar = nltk.CFG.fromstring("""
S -> NP VP
NP -> NNP VBZ
VP -> IN NNP | DT NN IN NNP
NNP -> 'Tajmahal' | 'Agra' | 'Bangalore' | 'Karnataka'
VBZ -> 'is'
IN -> 'in' | 'of'
DT -> 'the'
NN -> 'capital'
""")
# 测试
text = [
"Tajmahal is in Agra",
"Bangalore is the capital of Karnataka",
]
RDParserExample(grammar,text)
输出:
(S (NP (NNP Tajmahal) (VBZ is)) (VP (IN in) (NNP Agra)))
(S
(NP (NNP Bangalore) (VBZ is))
(VP (DT the) (NN capital) (IN of) (NNP Karnataka)))


- shift-reduce句法分析
shift-reduce句法分析器:从左到右单线程,也可以从上到下多线程
import nltk
def SRParserExample(grammer,textlist):
parser = nltk.parse.ShiftReduceParser(grammer)
for text in textlist:
sentence = nltk.word_tokenize(text)
for tree in parser.parse(sentence):
print(tree)
tree.draw()
grammar = nltk.CFG.fromstring("""
S -> NP VP
NP -> NNP VBZ
VP -> IN NNP | DT NN IN NNP
NNP -> 'Tajmahal' | 'Agra' | 'Bangalore' | 'Karnataka'
VBZ -> 'is'
IN -> 'in' | 'of'
DT -> 'the'
NN -> 'capital'
""")
text = [
"Tajmahal is in Agra",
"Bangalore is the capital of Karnataka",
]
SRParserExample(grammar,text)
输出:
(S (NP (NNP Tajmahal) (VBZ is)) (VP (IN in) (NNP Agra)))

- 依存句法分析和主观依存分析
import nltk
# 依存相关规则
grammar = nltk.grammar.DependencyGrammar.fromstring("""
'savings' -> 'small'
'yield' -> 'savings'
'gains' -> 'large'
'yield' -> 'gains'
""")
sentence = 'small savings yield large gains'
dp = nltk.parse.ProjectiveDependencyParser(grammar)
print(sorted(dp.parse(sentence.split())))
for t in sorted(dp.parse(sentence.split())):
print(t)
t.draw()
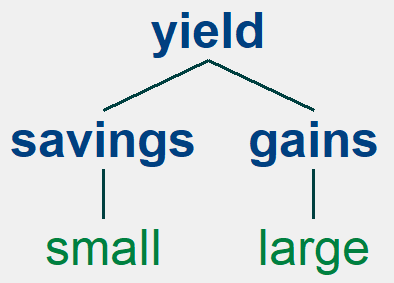
输出:
[Tree('yield', [Tree('savings', ['small']), Tree('gains', ['large'])])]
(yield (savings small) (gains large))
- 线图句法分析
from nltk.grammar import CFG
from nltk.parse.chart import ChartParser,BU_LC_STRATEGY
# BNF格式文法 开始符号:S 终结符号:单词
grammar = CFG.fromstring("""
S -> T1 T4
T1 -> NNP VBZ
T2 -> DT NN
T3 ->IN NNP
T4 -> T3 | T2 T3
NNP -> 'Tajmahal' | 'Agra' | 'Bangalore' | 'Karnataka'
VBZ -> 'is'
IN -> 'in' | 'of'
DT -> 'the'
NN -> 'capital'
""")
cp = ChartParser(grammar,BU_LC_STRATEGY,trace=True)
# trace=True可以看见分析过程
# strategy=BU_LC_STRATEGY是默认的,不写好像也行
sentence = 'Bangalore is the capital of Karnataka'
tokens = sentence.split()
chart = cp.chart_parse(tokens) # 对单词列表分析,并存到chart对象
parses = list(chart.parses(grammar.start())) # 将chart取到的所有分析树赋给parses
print('Total Edges :',len(chart.edges())) # 输出chart对象所有边的数量
for tree in parses: # 打印所有分析树
print(tree)
tree.draw()
输出:
|.Bangal. is . the .capita. of .Karnat.|
|[------] . . . . .| [0:1] 'Bangalore'
|. [------] . . . .| [1:2] 'is'
|. . [------] . . .| [2:3] 'the'
|. . . [------] . .| [3:4] 'capital'
|. . . . [------] .| [4:5] 'of'
|. . . . . [------]| [5:6] 'Karnataka'
|[------] . . . . .| [0:1] NNP -> 'Bangalore' *
|[------> . . . . .| [0:1] T1 -> NNP * VBZ
|. [------] . . . .| [1:2] VBZ -> 'is' *
|[-------------] . . . .| [0:2] T1 -> NNP VBZ *
|[-------------> . . . .| [0:2] S -> T1 * T4
|. . [------] . . .| [2:3] DT -> 'the' *
|. . [------> . . .| [2:3] T2 -> DT * NN
|. . . [------] . .| [3:4] NN -> 'capital' *
|. . [-------------] . .| [2:4] T2 -> DT NN *
|. . [-------------> . .| [2:4] T4 -> T2 * T3
|. . . . [------] .| [4:5] IN -> 'of' *
|. . . . [------> .| [4:5] T3 -> IN * NNP
|. . . . . [------]| [5:6] NNP -> 'Karnataka' *
|. . . . . [------>| [5:6] T1 -> NNP * VBZ
|. . . . [-------------]| [4:6] T3 -> IN NNP *
|. . . . [-------------]| [4:6] T4 -> T3 *
|. . [---------------------------]| [2:6] T4 -> T2 T3 *
|[=========================================]| [0:6] S -> T1 T4 *
Total Edges : 24
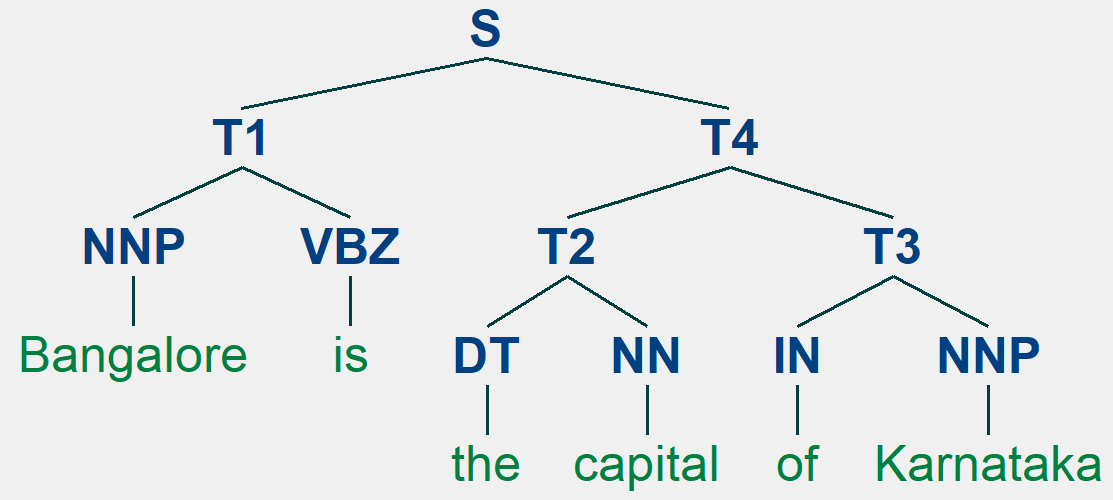
(S
(T1 (NNP Bangalore) (VBZ is))
(T4 (T2 (DT the) (NN capital)) (T3 (IN of) (NNP Karnataka))))




【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET 原生驾驭 AI 新基建实战系列:向量数据库的应用与畅想
· 从问题排查到源码分析:ActiveMQ消费端频繁日志刷屏的秘密
· 一次Java后端服务间歇性响应慢的问题排查记录
· dotnet 源代码生成器分析器入门
· ASP.NET Core 模型验证消息的本地化新姿势
· ThreeJs-16智慧城市项目(重磅以及未来发展ai)
· .NET 原生驾驭 AI 新基建实战系列(一):向量数据库的应用与畅想
· Ai满嘴顺口溜,想考研?浪费我几个小时
· Browser-use 详细介绍&使用文档
· 软件产品开发中常见的10个问题及处理方法