LeetCode 链表
基础部分
160. 相交链表
简单
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
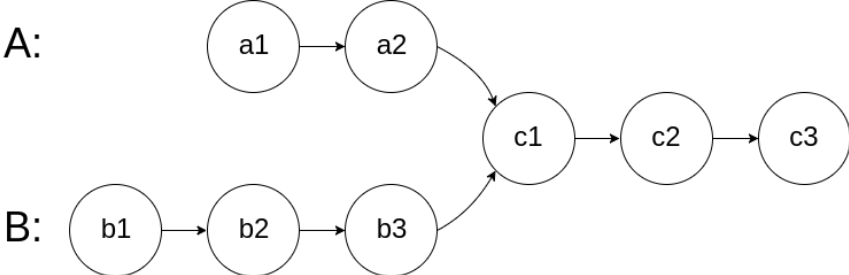
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:

输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
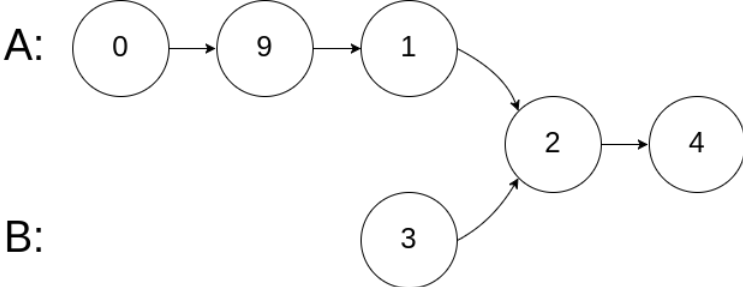
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
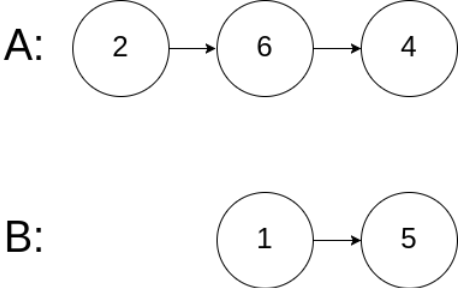
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回
null. - 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode p = headA, q = headB;
int loop = 2;
while (loop > 0){
if (p == q) return q;
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
if (p == null) {
p = headB;
loop--;
}
if (q == null) q = headA;
}
return null;
}
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode p = headA, q = headB;
while (p != q){ //都是null,就第二圈都到头了,省了计算loop的时间
p = p == null ? headB : p.next;
q = q == null ? headA : q.next;
}
return p;
}
}
206. 反转链表
简单
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶:
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
while (head != null){
ListNode p = head;
head = head.next;
p.next = res.next;
res.next = p;
}
return res.next;
}
}
21. 合并两个有序链表
简单
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = res;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null){
if (l1.val < l2.val){
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
while (l1 != null){
cur.next = l1;
cur = cur.next;
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null){
cur.next = l2;
cur = cur.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
return res.next;
}
}
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
简单
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
示例 1:
输入: 1->1->2
输出: 1->2
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->2->3->3
输出: 1->2->3
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null){
if (cur.val == cur.next.val){
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
中等
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
说明:
给定的 n 保证是有效的。
进阶:
你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode first = head, second = head;
while (n-- > 0) first = first.next;
if (first == null) return head.next;
while (first.next != null){
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
return head;
}
}
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
中等
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例:
给定 1->2->3->4, 你应该返回 2->1->4->3.
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode ans = new ListNode(0);
ListNode pre = ans;
pre.next = head;
ListNode l, r;
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.next != null){
l = pre.next;
r = l.next;
l.next = r.next;
pre.next = r;
r.next = l;
pre = l;
}
return ans.next;
}
}
445. 两数相加 II
中等
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
进阶:
如果输入链表不能修改该如何处理?换句话说,你不能对列表中的节点进行翻转。
示例:
输入:(7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
StringBuilder a = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
ListNode cur1 = l1, cur2 = l2;
while(cur1 != null){
a.append(cur1.val);
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur2 != null){
b.append(cur2.val);
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
StringBuilder sum = new StringBuilder();
int la = a.length();
int lb = b.length();
int len = la > lb ? la : lb;
int carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){
carry += la-i-1 < 0 ? 0 : a.charAt(la-i-1)-'0';
carry += lb-i-1 < 0 ? 0 : b.charAt(lb-i-1)-'0';
sum.append(carry%10);
carry /= 10;
}
if (carry > 0) sum.append(carry);
sum.reverse();
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = res;
for (char c : sum.toString().toCharArray()){
ListNode node = new ListNode(c-'0');
cur.next = node;
cur = cur.next;
}
return res.next;
}
}
234. 回文链表
简单
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
进阶:
你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (head != null){
list.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int len = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len/2; i++){
if (list.get(i).intValue() != list.get(len-i-1).intValue()) {
//list里是对象,不是基本数据类型,不能直接用==判断
//也可以写成:!Objects.equals(list.get(i), list.get(len-i-1))
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
725. 分隔链表
中等
给定一个头结点为 root 的链表, 编写一个函数以将链表分隔为 k 个连续的部分。
每部分的长度应该尽可能的相等: 任意两部分的长度差距不能超过 1,也就是说可能有些部分为 null。
这k个部分应该按照在链表中出现的顺序进行输出,并且排在前面的部分的长度应该大于或等于后面的长度。
返回一个符合上述规则的链表的列表。
举例: 1->2->3->4, k = 5 // 5 结果 [ [1], [2], [3], [4], null ]
示例 1:
输入:
root = [1, 2, 3], k = 5
输出: [[1],[2],[3],[],[]]
解释:
输入输出各部分都应该是链表,而不是数组。
例如, 输入的结点 root 的 val= 1, root.next.val = 2, \root.next.next.val = 3, 且 root.next.next.next = null。
第一个输出 output[0] 是 output[0].val = 1, output[0].next = null。
最后一个元素 output[4] 为 null, 它代表了最后一个部分为空链表。
示例 2:
输入:
root = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], k = 3
输出: [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 10]]
解释:
输入被分成了几个连续的部分,并且每部分的长度相差不超过1.前面部分的长度大于等于后面部分的长度。
提示:
root的长度范围:[0, 1000].- 输入的每个节点的大小范围:
[0, 999]. k的取值范围:[1, 50].
class Solution {
public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode root, int k) {
ListNode cur = root;
int N = 0; //统计数量
while (cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
N++;
}
int width = N / k;
int rem = N % k; //前面链表长度多一个的数量
ListNode[] ans = new ListNode[k];
cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0), write = head;
for (int j = 0; j < width + (i < rem ? 1 : 0); ++j) {
write.next = new ListNode(cur.val);
write = write.next;
if (cur != null) cur = cur.next;
}
ans[i] = head.next;
}
return ans;
}
}
328. 奇偶链表
中等
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
输出: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
说明:
- 应当保持奇数节点和偶数节点的相对顺序。
- 链表的第一个节点视为奇数节点,第二个节点视为偶数节点,以此类推。
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
ListNode odd = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = odd;
ListNode even = new ListNode(0);
ListNode q = even;
while (head != null){
p.next = head;
head = head.next;
p = p.next;
p.next = null;
if (head == null) break;
q.next = head;
head = head.next;
q = q.next;
q.next = null;
}
p.next = even.next;
return odd.next;
}
}
频率排序
92,426,2,25,143,23,148,379



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号