Data Structure and Algorithm - Day 04
-
20. Valid Parentheses
Given a string
scontaining just the characters'(',')','{','}','['and']', determine if the input string is valid.An input string is valid if:
- Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
- Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
Example 1:
Input: s = "()" Output: trueExample 2:
Input: s = "()[]{}" Output: trueExample 3:
Input: s = "(]" Output: falseExample 4:
Input: s = "([)]" Output: falseExample 5:
Input: s = "{[]}" Output: trueConstraints:
1 <= s.length <= 104sconsists of parentheses only'()[]{}'.
// violence recursion class Solution { Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); { map.put('(', -3); map.put('[', -2); map.put('{', -1); map.put('}', 1); map.put(']', 2); map.put(')', 3); } public boolean isValid(String s) { int len = s.length(); if (len == 0) return true; if (len == 1) return false; for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { int left = map.get(s.charAt(i)); int right = map.get(s.charAt(i+1)); if (left < 0 && left == -right) { return isValid(s.substring(0, i) + s.substring(i+2, len)); } } return false; } }// stack class Solution { public boolean isValid(String s) { Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>(); Map<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put('}', '{'); map.put(']', '['); map.put(')', '('); for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { if (map.containsKey(c)) { if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != map.get(c)) { return false; } stack.pop(); } else { stack.push(c); } } return stack.isEmpty(); } } -
155. Min Stack
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
- push(x) -- Push element x onto stack.
- pop() -- Removes the element on top of the stack.
- top() -- Get the top element.
- getMin() -- Retrieve the minimum element in the stack.
Example 1:
Input ["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"] [[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]] Output [null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2] Explanation MinStack minStack = new MinStack(); minStack.push(-2); minStack.push(0); minStack.push(-3); minStack.getMin(); // return -3 minStack.pop(); minStack.top(); // return 0 minStack.getMin(); // return -2Constraints:
- Methods
pop,topandgetMinoperations will always be called on non-empty stacks.
class MinStack { Stack<Integer> stack1; Stack<Integer> stack2; /** initialize your data structure here. */ public MinStack() { stack1 = new Stack<>(); stack2 = new Stack<>(); } public void push(int x) { stack1.push(x); int min = stack2.isEmpty() || x < stack2.peek() ? x : stack2.peek(); stack2.push(min); } public void pop() { stack1.pop(); stack2.pop(); } public int top() { return stack1.peek(); } public int getMin() { return stack2.peek(); } } -
84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Given an array of integers
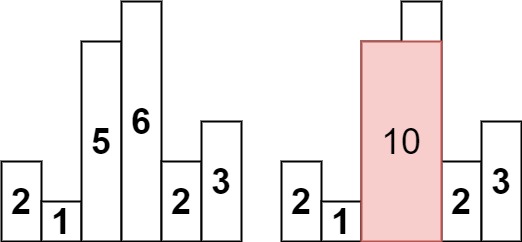
heightsrepresenting the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.Example 1:
![img]()
Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] Output: 10 Explanation: The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1. The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.Example 2:
![img]()
Input: heights = [2,4] Output: 4Constraints:
1 <= heights.length <= 1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
// violence O(n^2) overtime class Solution { public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) { int len = heights.length; int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { int minHeight = heights[i]; for (int j = i; j < len; j++) { minHeight = Math.min(minHeight, heights[j]); res = Math.max((j-i+1)*minHeight, res); } } return res; } }// stack O(n) class Solution { public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(-1); int res = heights[0], len = heights.length; // left bound is certain for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { while (stack.peek() != -1 && heights[stack.peek()] >= heights[i]) { int area = (i - 1 - stack.peek()) * heights[stack.pop()]; res = Math.max(res, area); } stack.push(i); } // right bound is certain while (stack.peek() != -1) { res = Math.max(res, (len - 1 - stack.peek()) * heights[stack.pop()]); } return res; } } -
641. Design Circular Deque
Design your implementation of the circular double-ended queue (deque).
Your implementation should support following operations:
MyCircularDeque(k): Constructor, set the size of the deque to be k.insertFront(): Adds an item at the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful.insertLast(): Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful.deleteFront(): Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful.deleteLast(): Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful.getFront(): Gets the front item from the Deque. If the deque is empty, return -1.getRear(): Gets the last item from Deque. If the deque is empty, return -1.isEmpty(): Checks whether Deque is empty or not.isFull(): Checks whether Deque is full or not.
Example:
MyCircularDeque circularDeque = new MycircularDeque(3); // set the size to be 3 circularDeque.insertLast(1); // return true circularDeque.insertLast(2); // return true circularDeque.insertFront(3); // return true circularDeque.insertFront(4); // return false, the queue is full circularDeque.getRear(); // return 2 circularDeque.isFull(); // return true circularDeque.deleteLast(); // return true circularDeque.insertFront(4); // return true circularDeque.getFront(); // return 4Note:
- All values will be in the range of [0, 1000].
- The number of operations will be in the range of [1, 1000].
- Please do not use the built-in Deque library.
class MyCircularDeque { int cap; Deque<Integer> deque; /** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the deque to be k. */ public MyCircularDeque(int k) { cap = k; deque = new LinkedList<>(); } /** Adds an item at the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean insertFront(int value) { if (cap == 0) return false; deque.addFirst(value); cap--; return true; } /** Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean insertLast(int value) { if (cap == 0) return false; deque.addLast(value); cap--; return true; } /** Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean deleteFront() { if (deque.isEmpty()) return false; deque.removeFirst(); cap++; return true; } /** Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean deleteLast() { if (deque.isEmpty()) return false; deque.removeLast(); cap++; return true; } /** Get the front item from the deque. */ public int getFront() { if (deque.isEmpty()) return -1; return deque.peekFirst(); } /** Get the last item from the deque. */ public int getRear() { if (deque.isEmpty()) return -1; return deque.peekLast(); } /** Checks whether the circular deque is empty or not. */ public boolean isEmpty() { return deque.isEmpty(); } /** Checks whether the circular deque is full or not. */ public boolean isFull() { return cap == 0; } } -
42. Trapping Rain Water
Given
nnon-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.Example 1:
![img]()
Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] Output: 6 Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.Example 2:
Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5] Output: 9Constraints:
n == height.length0 <= n <= 3 * 1040 <= height[i] <= 105
class Solution { public int trap(int[] height) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) { while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]) { int index = stack.pop(); if (stack.isEmpty()) break; int h = height[index]; res += (i - stack.peek() - 1) * (Math.min(height[i], height[stack.peek()]) - h); } stack.push(i); } return res; } }class Solution { public int trap(int[] height) { if (height.length == 0) return 0; int l = height[0], r = height[height.length - 1]; // max of l & r int i = 0, j = height.length - 1; int res = 0; while (i < j) { if (l < r) { // right higher, deside by left_max res += l - height[i]; i++; l = Math.max(l, height[i]); } else { res += r - height[j]; j--; r = Math.max(r, height[j]); } } return res; } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号