一、前言
使用注解代替之前在spring配置文件中配置目标类、切面类和aop配置。
二、注意
- 需要注意的是,需要在spring配置文件中引入如下,如果不添加,切面类中的@Aspect注解将不起作用
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
-
使用的时候通知单独使用
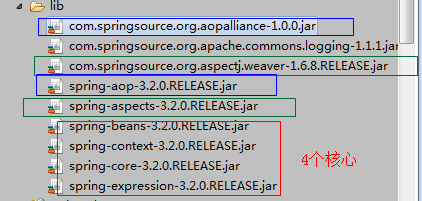
- 导入的jar包
- 当有多个切面,需要考虑其优先级时切面类使用@Order(数字:越小优先级越高) 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/dreamfree/p/4102619.html
三、注解的使用
切面类:
@Aspect 声明切面,修饰切面类,从而获得 通知。
通知:
@Before 前置
@AfterReturning 后置
@Around 环绕
@AfterThrowing 抛出异常
@After 最终
切入点:
@PointCut ,修饰方法 private void xxx(){} 之后通过“方法名”获得切入点引用
四、代码实现
beans.xml
<!-- 扫描注解 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.xx"/> <!-- aspectj自动代理 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
切面类:通知单独使用
package com.xx.myaspect;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 切面类
* @author phoebe
* @Component:类级注解
* @Aspect:切面注解
*/
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class MyAscpect {
/*
* 切点,方法名即是切点的id
* 后面的切点直接引用方法名称即可
* 方法体不需要再配置其他
*/
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.xx.dao.UserDaoImpl.*(..))")
public void pointCut(){}
/*
* 前置通知
* JoinPoint:带有方法名称
*/
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("方法名称是:"+methodName);
}
/*
* 环绕通知需要携带ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数
* 环绕通知类似于动态代理的全过程:ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数可以决定是否执行目标方法。
* 而且环绕通知必须有返回值,返回值即为目标方法的返回值
*
*/
@Around(value="pointCut()")
public Object arround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object obj = null;
String methodName = pjp.getSignature().getName();
try {
//前置通知@Before
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(pjp.getArgs()));
//执行目标方法
obj = pjp.proceed();
//后置通知@After
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends with " + Arrays.asList(pjp.getArgs()));
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常通知@AfterThrowing
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " occurs expection : " + e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//返回通知@AfterReturning
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends");
return obj;
}
}
dao接口类:
package com.xx.dao;
public interface UserDao {
public void run1();
public void run2();
public void run3();
}
dao实现类
package com.xx.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("userDaoImpl")
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public void run1() {
int x = 1/0;
System.out.println("run1");
}
@Override
public void run2() {
System.out.println("run2");
}
@Override
public void run3() {
System.out.println("run3");
}
}
测试类:
package com.xx;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.xx.dao.UserDao;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String xmlPath = "classpath:beans.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserDao userDao = (UserDao) context.getBean("userDaoImpl");
userDao.run1();
userDao.run2();
userDao.run3();
}
}
Best Regards


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号