如何在sv中使用DPI函数
巧妙的使用DPI函数能够给你的验证环境搭建提供很多便利,相当于sv中直接调用c函数,简直不要太爽,节省很多时间。
1.DPI -- sv调用c系统库函数
下面以一个验证环境的class中使用DPI的math库中的函数为例:首先定义一个package,在package中将使用到的DPI函数导入进来,math_pkg可以自定义名字
package math_pkg; //import dpi import "DPI" function real cos (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real sin (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real log (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real log10 (input real in_data); endpackage
在class类中来使用这个math_pkg,下面是以生成一个正弦sin数据为例:
1.要将package导入到类中,可以使用域作用符和通配符把所有的package的函数导入
2.按变量类型正常使用即可
class exam_transaction ; import math_pkg::*; rand bit [31:0] freq; rand bit [ 7:0] ampl; rand bit [15:0] ploda[]; function void post_randomize();//call back randomize this.ploda.delete(); this.ploda = new[freq]; sine_wave; endfunction task sine_wave; const real pi=3.1416; real sin_out; int cnt,i; cnt = 0; i = 0; repeat(freq) begin sin_out = ampl*sin(2*pi*cnt/freq); this.ploda[i] = $itor(sin_out);//real data to bit data if(cnt == freq - 1'd1) begin cnt = 'd0; end else begin cnt = cnt + 1'd1; end end endtask endclass
2.DPI -- sv调用自定义c函数
前面调入的是系统c的math库函数,那如果是自定义的一个c的函数要怎么办呢?其实是类似的,
如果有一个c的函数文件test_c.c
#include<stdio.h> void c_print(char* str){ printf("c_print in running ,input srting is %s\n",str); }
那么只需要在vcs进行编译时c文件也添加到文件列表中即可,这样vcs在编译文件时,会自动使用默认的gcc进行对c文件编译,可通过对vcs设定指定不同的编译器。
在sv中使用时, 也是先使用import将c函数导入进来import "DPI" function void c_print(string str);这里有一点需要注意,就是我们再c中定义的是char*类型但是在sv中就是srting类型了。DPI-C传递的每个变量都有两个相应匹配的定义,一边面向SystemVerilog,一边面向C/C++。这里需要确保每个数据类型必须匹配兼容。其一一对应关系如下图所示
package math_pkg; //import dpi import "DPI" function real cos (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real sin (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real log (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real log10 (input real in_data); import "DPI" function void c_print(string str); endpackage class exam_transaction ; import math_pkg::*; rand bit [31:0] freq; rand bit [ 7:0] ampl; rand bit [15:0] ploda[]; function void post_randomize();//call back randomize this.ploda.delete(); this.ploda = new[freq]; sine_wave; c_print("example_trans input at post_randomize");//use DPI test_c function endfunction task sine_wave; const real pi=3.1416; real sin_out; int cnt,i; cnt = 0; i = 0; repeat(freq) begin sin_out = ampl*sin(2*pi*cnt/freq); this.ploda[i] = $itor(sin_out);//real data to bit data if(cnt == freq - 1'd1) begin cnt = 'd0; end else begin cnt = cnt + 1'd1; end end endtask endclass
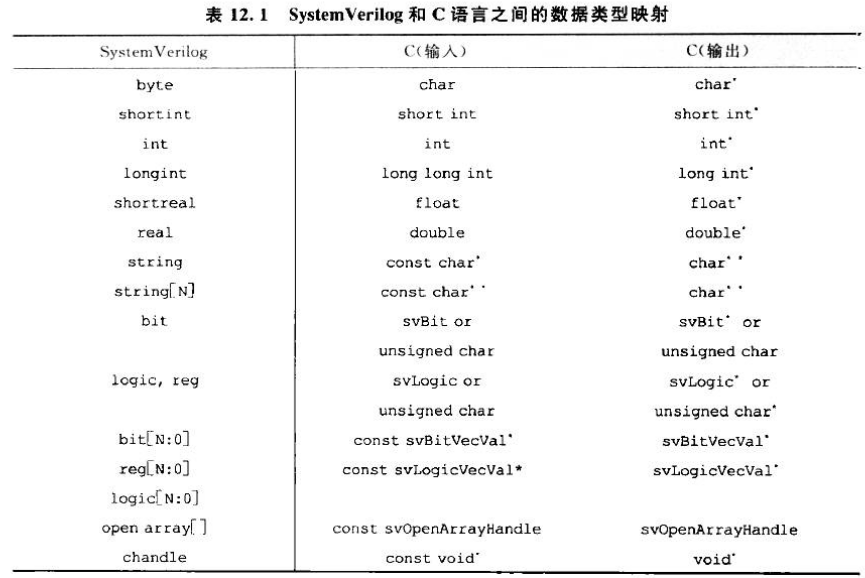
3.DPI -- sv和c互传数据
继续往下,我们已经可以从sv传递一个字符串到c中了,那如果是需要从sv中传递一个数据到c中,经过c的处理再把结果从c中返回给sv要怎么实现呢?下面以一个两输入加法器为例:
c函数中输入变量类型为了和sv中的bit匹配需要为const svBitVecVal 输出变量为svBitVecVal *
#include<svdpi.h> void c_add(const svBitVecVal in1,const svBitVecVal in2,svBitVecVal * outdata){ static unsigned char tmp =0; tmp = in1+in2; *outdata = tmp; }
package math_pkg; //import dpi import "DPI" function real cos (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real sin (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real log (input real in_data); import "DPI" function real log10 (input real in_data); import "DPI" function void c_print(string str); import "DPI" function void c_add(input bit[6:0] in1,input bit[6:0] in2,output bit[7:0] out); endpackage class exam_transaction ; import math_pkg::*; rand bit [31:0] freq; rand bit [ 7:0] ampl; rand bit [15:0] ploda[]; bit [7:0] out_data; function void post_randomize();//call back randomize this.ploda.delete(); this.ploda = new[freq]; sine_wave; c_print("example_trans input at post_randomize");//use DPI test_c print function c_add(12,55,out_data);//use DPI test_c add function $display("add data is %d\n",out_data); endfunction task sine_wave; const real pi=3.1416; real sin_out; int cnt,i; cnt = 0; i = 0; repeat(freq) begin sin_out = ampl*sin(2*pi*cnt/freq); this.ploda[i] = $itor(sin_out);//real data to bit data if(cnt == freq - 1'd1) begin cnt = 'd0; end else begin cnt = cnt + 1'd1; end end endtask endclass
如果是传递数组可参考:http://testbench.in/DP_08_ARRAYS.html






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构