《Introduction to Tornado》笔记05-Mongodb的安装使用及使用Tornado操作Mongodb
下载与安装
WIndows版的下载与安装详见这篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/muguli2008/article/details/80591256
Mac版安装参考这里:xxx
Python操作Mongodb的模块pymongo及相关练习
xxx:
xxx :https://www.cnblogs.com/aademeng/articles/9779271.html
xxx:https://www.cnblogs.com/melonjiang/p/6536876.html
Mongodb中的数据
由于_id字段不同,其他的键值对是可以重复的:
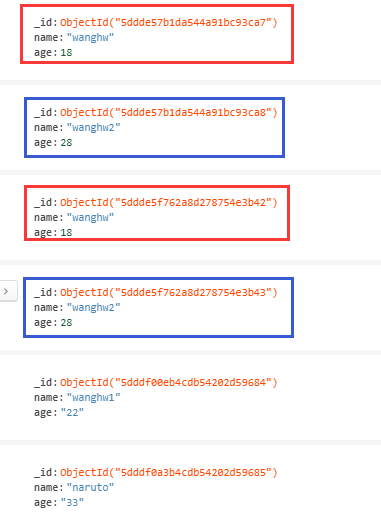
Mongodb文档和json
查找数据得到的结果如下:
# 查找数据 res = collection.find_one({"name":"wanghw"}) print(res,type(res)) # {'_id': ObjectId('5ddde57b1da544a91bc93ca7'), 'name': 'wanghw', 'age': 18} <class 'dict'>
注意结果虽然是一个字典,但是,字典中有一个ObjectID对象,json模块并不知道如何序列化它!
(1)其中最简单的方法(也是我们在本章中采用的方法)是在我们序列化之前从字典里简单地删除_id 键
del res["_id"]
(2)一个更复杂的方法是使用 PyMongo 的 json_util 库,它同样可以帮你序列化其他MongoDB 特定数据类型到 JSON。我们可以在 http://api.mongodb.org/python/current/api/bson/json_util.html 了解更多关于这个库的信息。
tornado与mongodb的结合
从Mongodb中读数据的tornado服务
先从mongodb中用pymongo模块写入一些数据:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import pymongo # client = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017") client = pymongo.MongoClient(host="localhost",port=27017) # 指定数据库 db = client.test print("db:",db) # 指定集合 collection = db.mdata print("collection",collection) # 需要插入的数据 student1 = {"name":"wanghw","age":18} student2 = {"name":"wanghw2","age":28} # 插入多条数据 ret = collection.insert_many([student1,student2]) print("ret:",ret)
根据上面的设置,基于tornado的web服务从数据库中读取数据:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.httpserver import tornado.ioloop import tornado.options import tornado.web import pymongo from tornado.options import define, options define("port", default=8001, help="run on the given port", type=int) class WordHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self, word): # 指定集合 coll = self.application.db.mdata # print(word) # 从mongodb中查找 word_doc = coll.find_one({"name": word}) if word_doc: # 删除_id这个key del word_doc["_id"] self.write(word_doc) else: self.set_status(404) self.write({"error": "word not found"}) class Application(tornado.web.Application): def __init__(self): handlers = [(r"/(\w+)", WordHandler)] # 连接mongodb conn = pymongo.MongoClient("localhost", 27017) # 指定数据库 self.db = conn["test"] tornado.web.Application.__init__(self, handlers,debug=True) if __name__ == "__main__": tornado.options.parse_command_line() http_server = tornado.httpserver.HTTPServer(Application()) http_server.listen(options.port) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
过程说明
(1)开始,我们在程序的最上面导入了 import pymongo 库。然后我们在我们的 TornadoApplication 对象的__init__方法中实例化了一个 pymongo 连接对象。
我们在 Application 对象中创建了一个 db 属性,指向 MongoDB 的 example 数据库。下面是相关的代码:
conn = pymongo.Connection("localhost", 27017) self.db = conn["test"]
def get(self, word): coll = self.application.db.words word_doc = coll.find_one({"word": word}) if word_doc: del word_doc["_id"] self.write(word_doc) else: self.set_status(404) self.write({"error": "word not found"})
(3)在我们将集合对象指定给变量 coll 后,我们使用用户在 HTTP 路径中请求的单词调用find_one 方法。
如果我们发现这个单词,则从字典中删除_id 键(以便 Python 的 json库可以将其序列化),然后将其传递给 RequestHandler 的 write 方法。write 方法将会自动序列化字典为 JSON 格式。
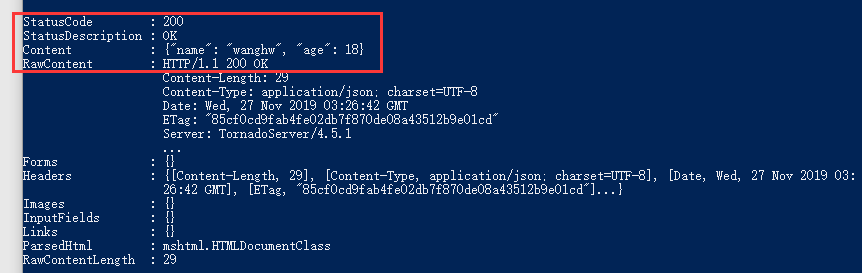
在浏览器中输入:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/wanghw
得到结果:
{"name": "wanghw", "age": 18}
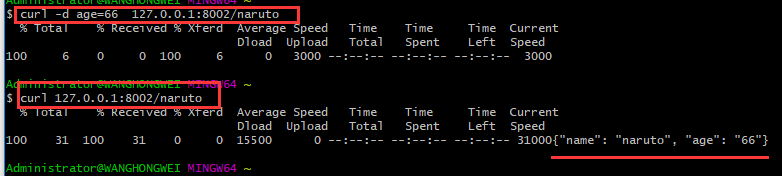
当然也可以使用curl命令进行测试:
curl 127.0.0.1:8000/wanghw
结果如下:
从mongodb中写入数据的tornado服务
还用上面mongodb的数据库与集合,tornado程序如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.httpserver import tornado.ioloop import tornado.options import tornado.web import pymongo from tornado.options import define, options define("port", default=8002, help="run on the given port", type=int) class Application(tornado.web.Application): def __init__(self): handlers = [(r"/(\w+)", WordHandler)] # 连接mongodb conn = pymongo.MongoClient("localhost", 27017) # 指定数据库 self.db = conn["test"] tornado.web.Application.__init__(self, handlers, debug=True) class WordHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self, word): # 指定集合 coll = self.application.db.mdata # print(word) # 从mongodb中查找 word_doc = coll.find_one({"name": word}) if word_doc: # 删除_id这个key del word_doc["_id"] self.write(word_doc) else: self.set_status(404) self.write({"error": "word not found"}) def post(self, word): # 获取post请求传递的age参数 age = self.get_argument("age") # 找到对应的集合 coll = self.application.db.mdata word_doc = coll.find_one({"name": word}) if word_doc: word_doc['age'] = age coll.save(word_doc) else: word_doc = {'name': word, 'age': age} coll.insert(word_doc) del word_doc["_id"] self.write(word_doc) if __name__ == "__main__": tornado.options.parse_command_line() http_server = tornado.httpserver.HTTPServer(Application()) http_server.listen(options.port) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
过程说明
(1)我们首先做的事情是使用 get_argument 方法取得 POST请求中传递的 definition 参数。
(2)然后,就像在 get 方法一样,我们尝试使用 find_one 方法从数据库中加载给定单词的文档。
(3)如果发现这个单词的文档,我们将 age 条目的值设置为从 POST参数中取得的值,然后调用集合对象的 save 方法将改变写到数据库中。
(4)如果没有发现文档,则创建一个新文档,并使用 insert 方法将其保存到数据库中。
(5)无论上述哪种情况,在数据库操作执行之后,我们在响应中写文档(注意首先要删掉_id 属性)。
测试
让我们来测试一下:
我们先用get请求输入一个不存在的name,会返回错误信息:

然后我们使用post请求,将这个姓名添加进去:
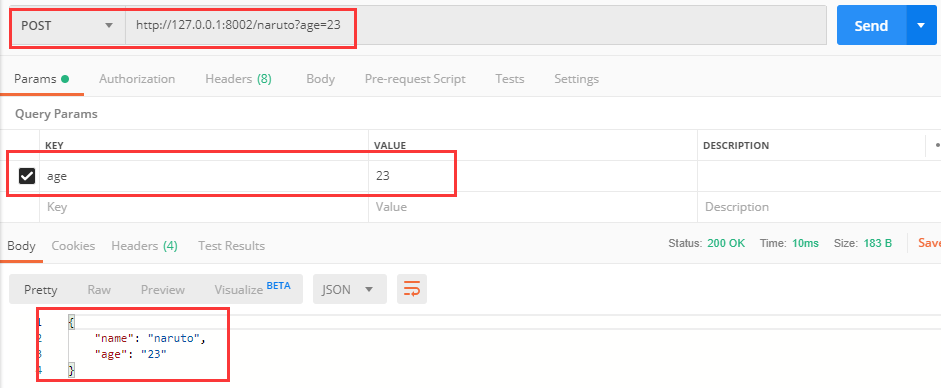
再来查一下发现有这个字典了:
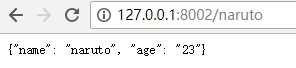
最后我们为这个“已存在的条目”进行更新:
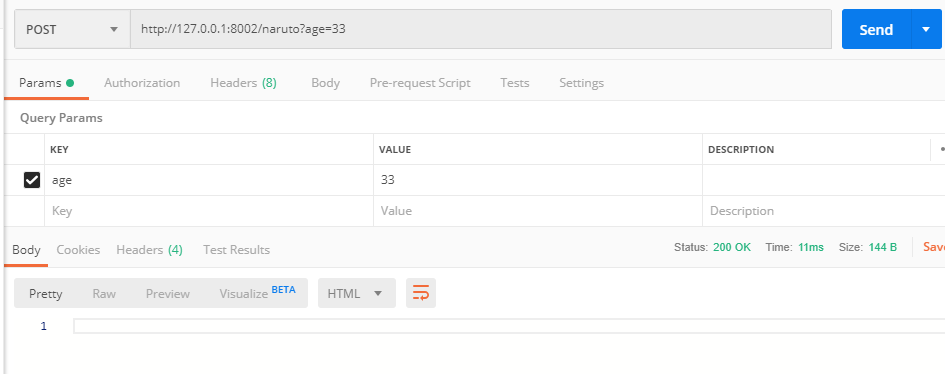
查看更新的结果:
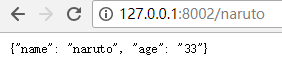
当然可以使用curl命令来测试: