leetcode 0206
✅ 292. Nim 游戏
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/nim-game
你和你的朋友,两个人一起玩 Nim 游戏:桌子上有一堆石头,每次你们轮流拿掉 1 - 3 块石头。 拿掉最后一块石头的人就是获胜者。你作为先手。
你们是聪明人,每一步都是最优解。 编写一个函数,来判断你是否可以在给定石头数量的情况下赢得游戏。
- 示例:
输入: 4
输出: false
解释: 如果堆中有 4 块石头,那么你永远不会赢得比赛;
因为无论你拿走 1 块、2 块 还是 3 块石头,最后一块石头总是会被你的朋友拿走。

bool canWinNim(int n){
return n % 4 != 0;
}
执行用时 :
0 ms
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
100.00%
的用户
内存消耗 :
6.6 MB
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
92.20%
的用户
✅ 933. 最近的请求次数
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-recent-calls
我的解释:
//首先有个列表
List<int> l = new List<int>() {} ;
// 每次我们enqueue 这个列表一些 数字,依次是1, 100, 3001, 3002
input: 1
output: l = {1}
input: 100
output: l = {1,100}
input: 3001
output: l = {1,100,3001}
input: 3002
output: l = {1,100,3001,3002}
然后是人工解答:
当 input = 1
l = {1}
按照之前我们理解的意思,我们需要找到 l 中所有大于等于 0( 原为1 - 3000,但是时间没有负数,所以返回0,上面讨论过) 并且小于等于1的数的总个数。我们遍历 l发现有1个数,所以返回 1.<<<<<
当 input = 100
l = {1,100} (1为上一步所加进的)
这次我们要找到l中大于等于0 (100-3000 = -2900 => 0)且小于等于100的值,这里有2个,所以返回2 。<<<<<
当 input = 3001
l = {1,100,3001}
这次我们要找到l中大于等于1(3001- 3000 = 1)且小于等于3001的个数,这里为3,所以返回3。<<<<<<
当 input = 3002
l = {1,100,3001,3002}
找到 大于等于2小于等于3002的个数为3(100,3001,3002),所以返回3。<<<<
- 别人的c 解答:(理解了,需要自己多重复一遍)
#define RET_OK 0
#define RET_ERR 1
#define QUEUE_MAX 3001
typedef struct {
int buf[QUEUE_MAX];
int size;
int cnt;
int head;
int tail;
} RecentCounter;
int rcIsEmpty(RecentCounter *rc)
{
if (rc->cnt == 0) {
return RET_OK;
} else {
return RET_ERR;
}
}
//item 定位head
int rcPeekHead(RecentCounter *rc, int *item)
{
if (rc->cnt == 0) {
return RET_ERR;
}
*item = rc->buf[rc->head];
return RET_OK;
}
//item 定位head ,head 指针增加,cnt 减少,
int rcPollHead(RecentCounter *rc, int *item)
{
if (rc->cnt == 0) {
return RET_ERR;
}
*item = rc->buf[rc->head];
rc->head = (rc->head + 1) % rc->size;
rc->cnt--;
return RET_OK;
}
int rcInTail(RecentCounter *rc, int item)
{
if (rc->cnt == QUEUE_MAX) {
return RET_ERR;
}
rc->buf[rc->tail] = item;
rc->tail = (rc->tail + 1) % rc->size;
rc->cnt++;
return RET_OK;
}
RecentCounter* recentCounterCreate() {
RecentCounter* rc = (RecentCounter*) calloc (1, sizeof(RecentCounter));
if (rc == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
rc->size = QUEUE_MAX;
rc->cnt = 0;
rc->head = 0;
rc->tail = 0;
return rc;
}
// int t: 任何处于 [t - 3000, t] 时间范围之内的 ping 都将会被计算在内,
int recentCounterPing(RecentCounter* obj, int t) {
int ret;
int item = INT_MIN;
int cnt = 0;
while(rcIsEmpty(obj) != RET_OK) {
if (rcPeekHead(obj, &item) != RET_OK) {
break;
}
if ((item + 3000 )< t) {// 残留 tt tdo 疑问 0206 ;done ; when: item 定位到 的 head 加上 3000 仍旧小于t, 那么 需要做: 队列抛弃头;这个答案的作者,非常知道如何使用队列这个有力的武器。
rcPollHead(obj, &item);
} else {
break;
}
}
rcInTail(obj, t);//ok, 这是因为,我们要把3002 也要算进去,所以又 enqueue t 了。
cnt = obj->cnt;
return cnt;
}
void recentCounterFree(RecentCounter* obj) {
if (obj != NULL) {
free(obj);
}
}
作者:jafon
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-recent-calls/solution/c-dui-lie-by-jafon/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
- 我的抄写(下次请用py 是否更快??0206 todo req)
#define YES 1
#define NO 0
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 3001
typedef struct {
int buf[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
int size;
int cnt;
int head;
int tail;
} RecentCounter;
int rcIsEmpty(RecentCounter *rc) {
if (rc->cnt == 0) {
return YES;
} else {
return NO;
}
}
//soldier locate the head's content
int rcPeekHead(RecentCounter *rc, int *soldier){
if (rc->cnt == 0) {
return NO;
}
*soldier = rc->buf[rc->head];
return YES;
}
//soldier locate the head's content and move forward head
// and decrease cnt
int rcPollHead(RecentCounter *rc, int *soldier){
if (rc->cnt == 0) {
return NO;
}
*soldier = rc->buf[rc->head];
rc->head = (rc->head + 1) % rc->size;
rc->cnt--;
return YES;
}
//jst want to enqueue the soldier in the *rc
int rcInTail(RecentCounter *rc, int soldier){
if(rc->cnt == MAX_QUEUE_SIZE){
return NO;
}
rc->buf[rc->tail] = soldier;
rc->tail = (rc->tail + 1) % rc->size;
rc->cnt++;
return YES;
}
//his timu func
RecentCounter* recentCounterCreate() {
RecentCounter* rc = (RecentCounter *) calloc (1, sizeof(RecentCounter));
if(rc == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
rc->size = MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
rc->cnt = 0;
rc->head = 0;
rc->tail = 0;
return rc;
}
//his timu func
int recentCounterPing(RecentCounter* obj, int t) {
int soldier = -999;
int cnt = 0;
while(rcIsEmpty(obj) == NO) {
if(rcPeekHead(obj, &soldier) != YES) {
break;
}
if((soldier + 3000) < t) {
//tt say: soldier == 200, t == 7000;so 3200 < 7000, we need move
//tt the soldier forward to in between 4000(t-3000) and t(7000)
rcPollHead(obj, &soldier);
} else {
break;
}
}
//enqueue the 't'
rcInTail(obj, t);
cnt = obj->cnt;
return cnt;
}
//his timu func
void recentCounterFree(RecentCounter* obj) {
if(obj != NULL){
free(obj);
}
}
/**
* Your RecentCounter struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* RecentCounter* obj = recentCounterCreate();
* int param_1 = recentCounterPing(obj, t);
* recentCounterFree(obj);
*/
/*执行用时 :
264 ms
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
26.67%
的用户
内存消耗 :
38.2 MB
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
78.33%
的用户*/
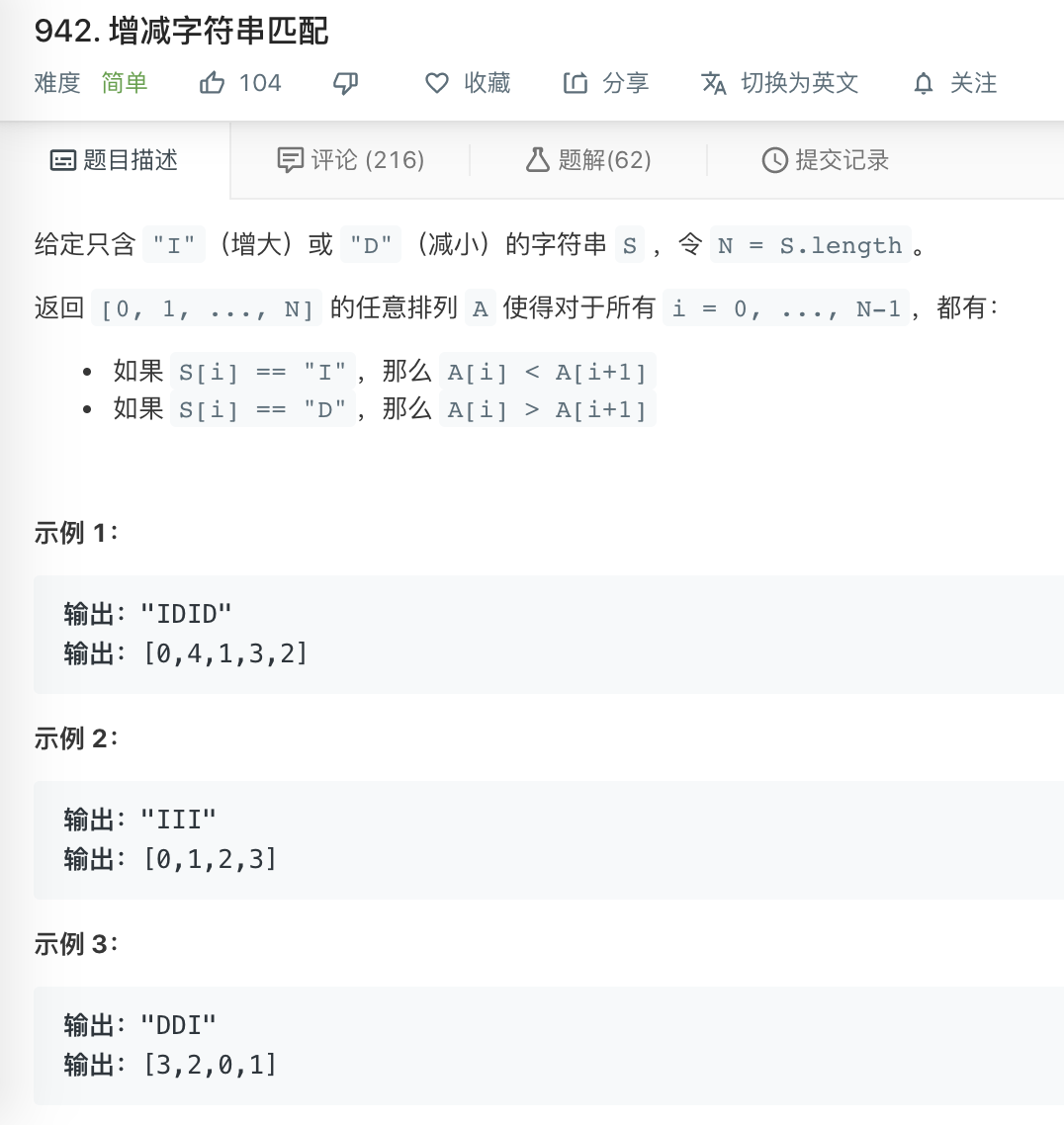
✅ 942. 增减字符串匹配
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/di-string-match
仍旧有需要思考的地方
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* diStringMatch(char * S, int* returnSize){
int left = 0;
int right = strlen(S);
int len = strlen(S);
int *A = malloc(sizeof(int) * (strlen(S) + 1)); // 谨记malloc 语法
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for(j = 0; j < len; j++){
if(S[j] == 'I') {
A[i++] = left++;
} else {
A[i++] = right--;
}
}
A[i++] = right;//思考这里:为什么单独如此一句呢?
*returnSize = i;
return A;
}
执行用时 :
88 ms
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
9.36%
的用户
内存消耗 :
12.9 MB
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
44.53%
的用户
py尝试
class Solution:
def diStringMatch(self, S: str) -> List[int]:
left = 0
right = len(S)
ans = []
for i in S:
if i == 'I':
ans.append(left)
left += 1
else:
ans.append(right)
right -= 1
ans.append(right)
return ans
'''
执行用时 :
68 ms
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
79.74%
的用户
内存消耗 :
14.2 MB
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
52.81%
的用户
'''
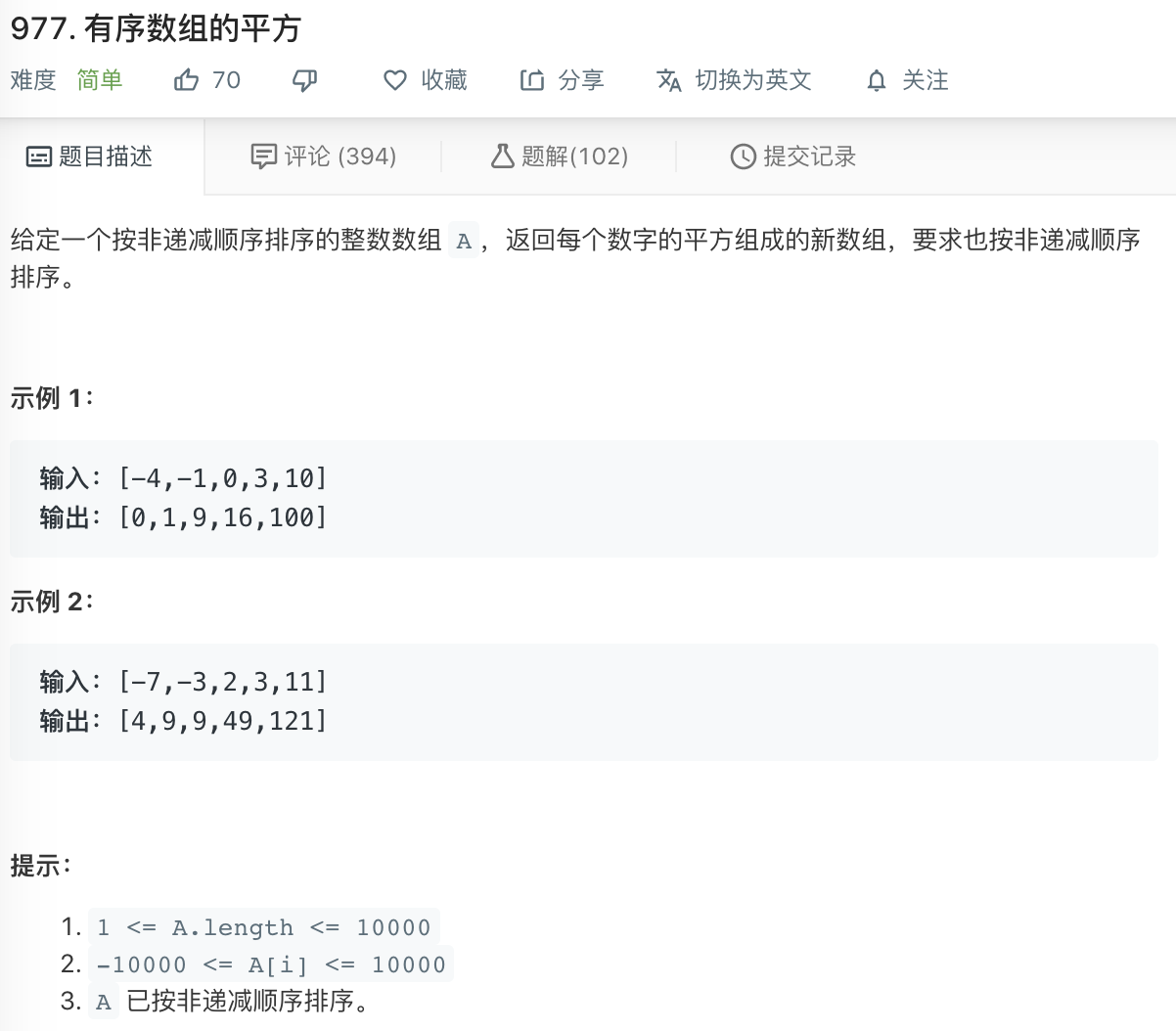
✅ 977. 有序数组的平方
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array
class Solution:
def sortedSquares(self, A: List[int]) -> List[int]:
return sorted([i**2 for i in A])
'''
# for sort: you have:
list.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False)
# for sorted: you have:
sorted()方法,返回一个新的list; ################# 学习点!!!!
# summary:
如果你不需要保留原来的list, 使用list.sort()方法来排序,此时list本身将被修改。通常此方法不如sorted()方便
'''
执行用时 :
312 ms
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
35.49%
的用户
内存消耗 :
15 MB
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
59.04%
的用户
- 他人语:

- c 解答 ,两个指针(soldier) i 和 j 在原来的数组上跑
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* sortedSquares(int* A, int ASize, int* returnSize){
int i = 0, j = ASize - 1;
int k = ASize - 1;
int *ans = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * ASize);
while(i <= j) {
if (abs(A[i]) > abs(A[j])) {
ans[k] = A[i] * A[i];
k--;
i++;
} else {
ans[k] = A[j] * A[j];
k--;
j--;
}
}
*returnSize = ASize;
return ans;
}
执行用时 :
132 ms
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
82.21%
的用户
内存消耗 :
21.5 MB
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
41.91%
的用户


