leetcode: 0204 完成的
大纲:0204 完成的
✅ 657. 机器人能否返回原点
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/robot-return-to-origin/
✅ 1299. 将每个元素替换为右侧最大元素
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/replace-elements-with-greatest-element-on-right-side/
✅ 1051 高度检查器
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/height-checker
✅ 728 自除数
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/self-dividing-numbers
✅ 104 二叉树的最大深度
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
notes
✅1051 高度检查器
首先我们其实并不关心排序后得到的结果,我们想知道的只是在该位置上,与最小的值是否一致
题目中已经明确了值的范围 1 <= heights[i] <= 100
这是一个在固定范围内的输入,比如输入: [1,1,4,2,1,3]
输入中有 3 个 1,1 个 2,1 个 3 和 1 个 4,3 个 1 肯定会在前面,依次类推
所以,我们需要的仅仅只是计数而已
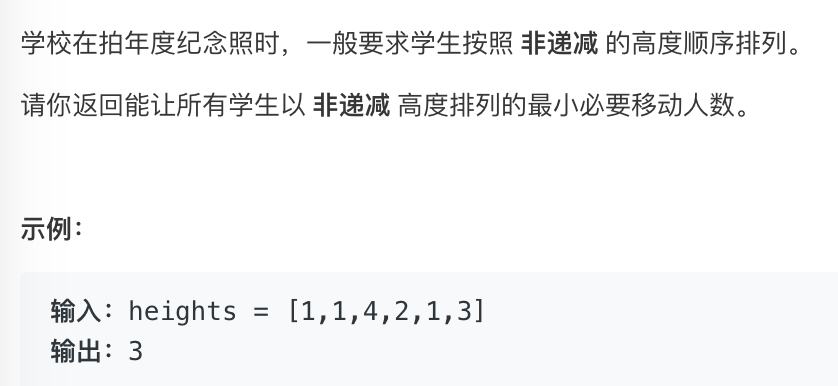
- 错误的一次解答:
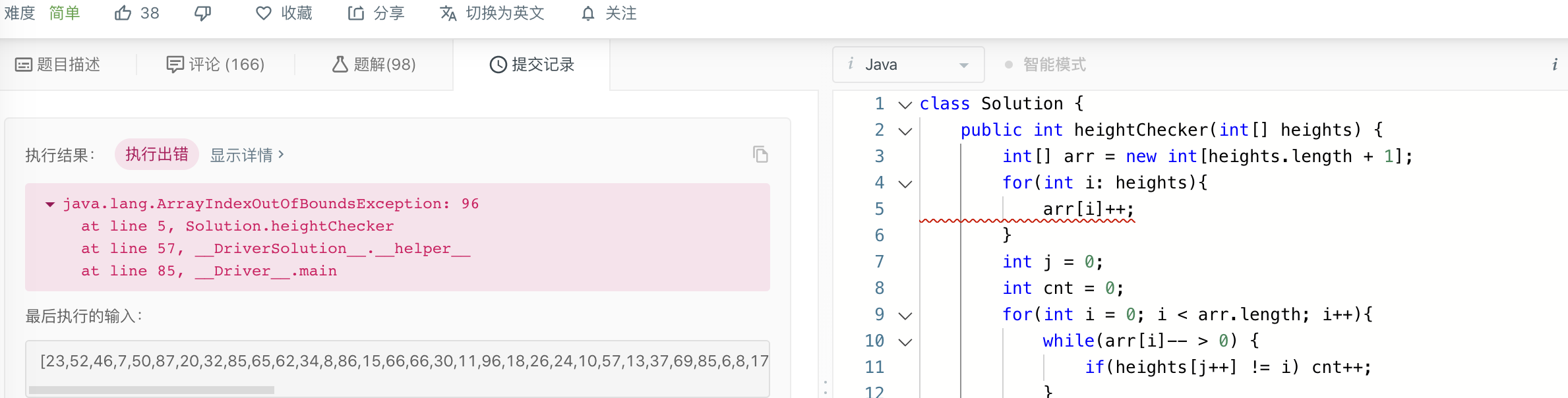
- fix:
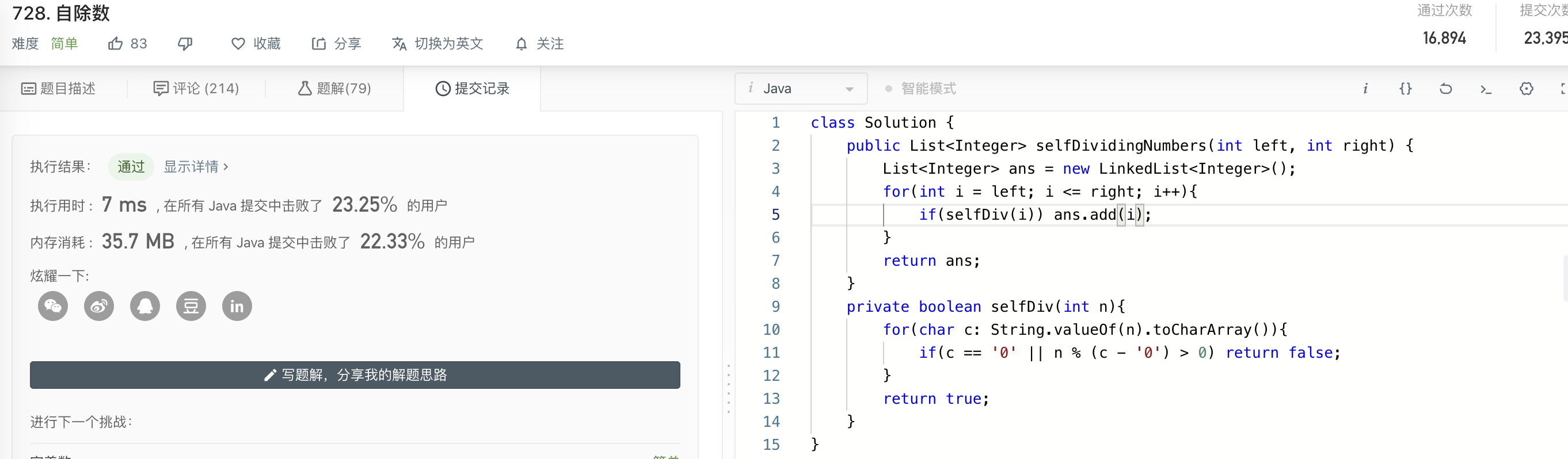
✅ 728 自除数
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/self-dividing-numbers
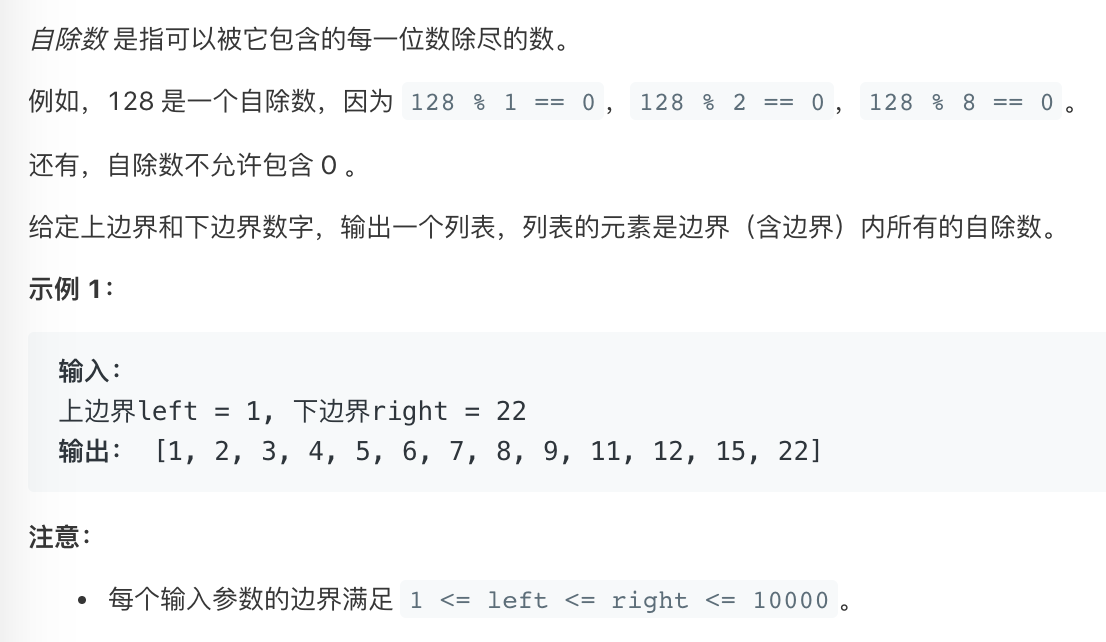
brute
class Solution {
public List<Integer> selfDividingNumbers(int left, int right) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList();
for (int n = left; n <= right; ++n) {
if (selfDividing(n)) ans.add(n);
}
return ans;
}
public boolean selfDividing(int n) {
for (char c: String.valueOf(n).toCharArray()) {
if (c == '0' || (n % (c - '0') > 0))
return false;
}
return true;
}
/*
Alternate implementation of selfDividing:
public boolean selfDividing(int n) {
int x = n;
while (x > 0) {
int d = x % 10;
x /= 10;
if (d == 0 || (n % d) > 0) return false;
}
return true;
*/
}
c解答:
//tt 主要是 temp%10 这个技巧,此可以 提取出 数中的每个位的数,
//tt eg: 128 依次提出: 8, 2, 1
//tt 总结就是 temp%10 这个技巧, 替代了 上述java 中的 `String.valueOf(n).toCharArray()`
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* selfDividingNumbers(int left, int right, int* returnSize){
int cnt=0;
int*num=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(right-left+1));
for(int i=left;i<=right;i++)
{
int temp=i;
int flag=0;
while(temp!=0)
{
if(temp%10==0||(i%(temp%10))!=0)
{
flag=1;
break;
}
temp/=10;
}
if(flag!=1)
num[cnt++]=i;
}
*returnSize=cnt;
return num;
}
java switch 语句
switch(expression){
case value :
//语句
break; //可选
case value :
//语句
break; //可选
//你可以有任意数量的case语句
default : //可选
//语句
}
java api: array 直接有 length 属性 ,不必:length()
✅104 二叉树 的最大高度,py java 对比

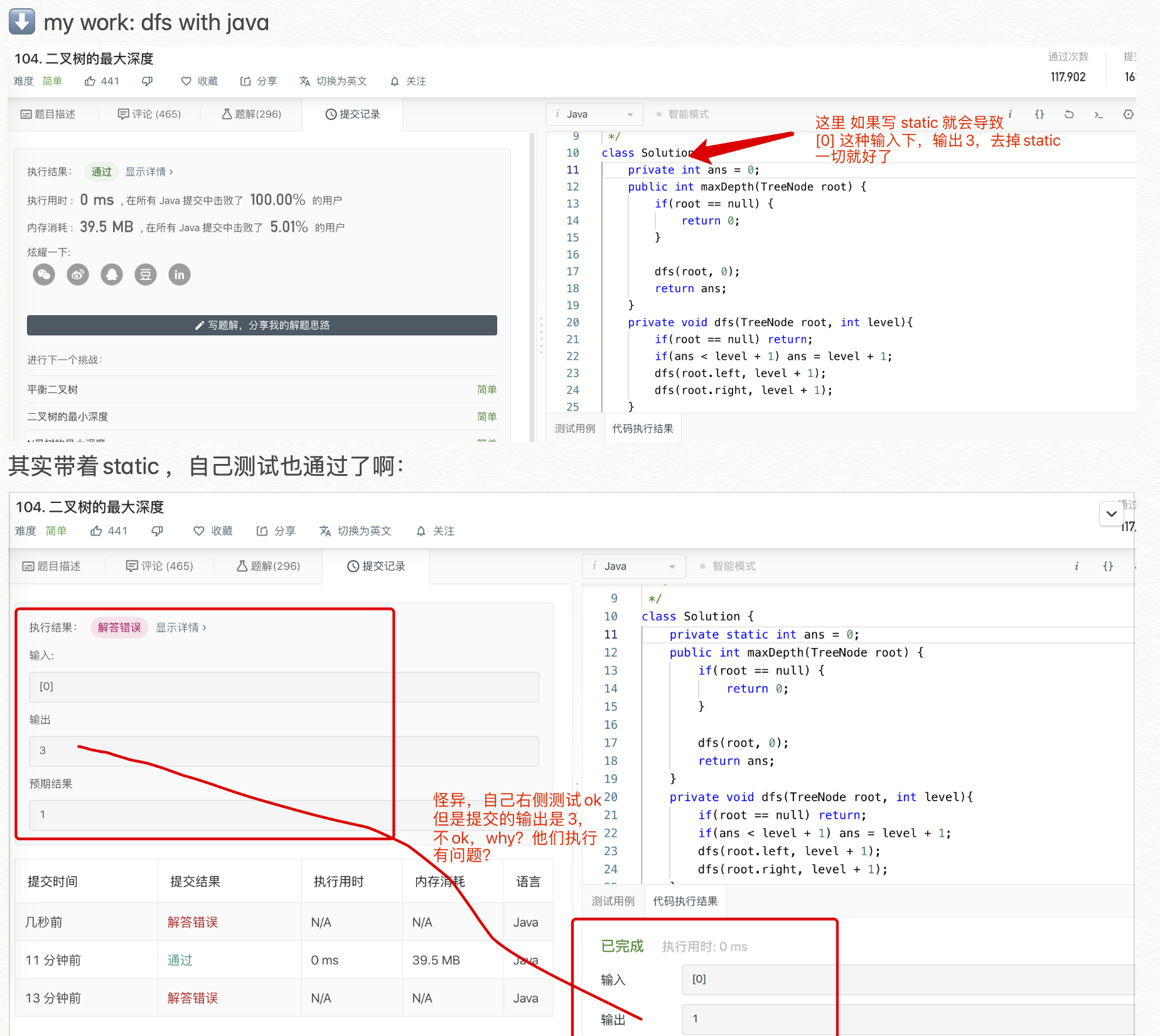
- code:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
// BFS way, use Queue
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
depth += 1;
int fixedQueueSize = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < fixedQueueSize; i++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
JAVA数组的toString()方法不能直接输出数组内容
你需要: Arrays.toString(array)
java Queue 的 offer, poll
LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。
//add()和remove()方法在失败的时候会抛出异常(不推荐)
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
//添加元素
queue.offer("a");
queue.poll()); //返回第一个元素,并在队列中删除
- 纯递归似乎很好:
✅657机器人回到原点
class Solution {
public boolean judgeCircle(String moves) {
char [] allMovesSplited = moves.toCharArray();
int len = allMovesSplited.length;
int i = 0;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
while(i < len) {
switch(allMovesSplited[i]) {
case 'U':
y++;
break;
case 'D':
y--;
break;
case 'L':
x--;
break;
case 'R':
x++;
break;
default:
break;
}
i++;
}
return x==0 && y==0;
}
}
//or
class Solution {
public boolean judgeCircle(String moves) {
int col = 0, row = 0;
for(char ch : moves.toCharArray()){
if(ch == 'U') row++;
else if(ch == 'D') row--;
else if(ch == 'L') col--;
else col++;
}
return col == 0 && row == 0;
}
}
✅1299 将每个元素替换为右侧最大元素(倒序来的思路很好)
class Solution {
public int[] replaceElements(int[] arr) {
//brute way
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++){
int maxInLatter = arr[i + 1];
for(int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if(arr[j] > maxInLatter){
//update the newest max
maxInLatter = arr[j];
}
}
arr[i] = maxInLatter;
}
//update the lastest one to -1;
arr[arr.length - 1]= -1;
return arr;
}
}
//better
class Solution {
public int[] replaceElements(int[] arr) {
int max = -1;
for(int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = max;
if(tmp > max){
max = tmp;
}
}
return arr;
}
}


